42 methane molecular orbital diagram
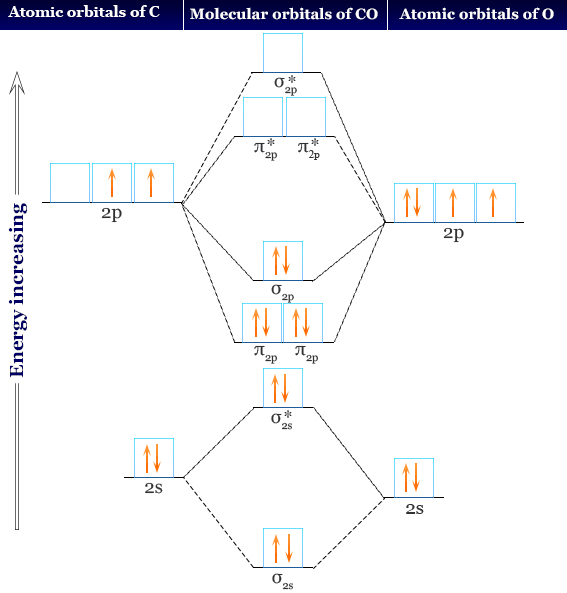
EOF Molecular orbital theory - Wikipedia Molecular orbital (MO) theory uses a linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) to represent molecular orbitals resulting from bonds between atoms. These are often divided into three types, bonding, antibonding, and non-bonding.A bonding orbital concentrates electron density in the region between a given pair of atoms, so that its electron density will tend to attract each of the …
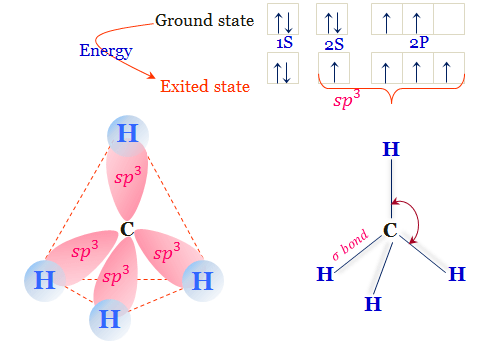
Covalent Bonds & Shapes of Molecules - University of Texas ... • Figure 1.13 Orbital overlap pictures of methane, ammonia, and water. VB: Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals 32 • The mathematical combination of one 2s atomic orbital wave function and two 2p atomic orbital wave functions forms three equivalent sp2 hybrid orbitals. sp2 Hybridization, with electron population for carbon to form double bonds ...

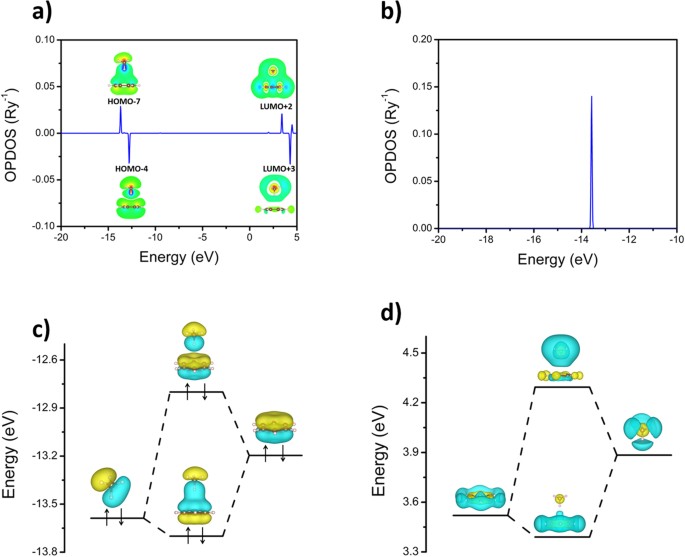
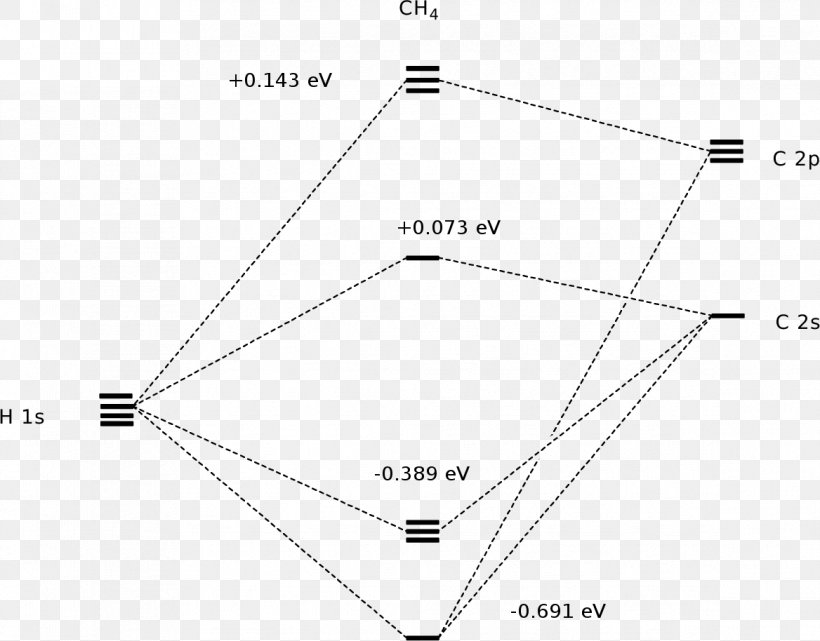
Methane molecular orbital diagram
How Many Total Atoms Are In A Molecule Of Methane? 👌 (2022 ... 1 mol methane (CH4) contains 6.02*1023 molecules 1 molecule CH4 contains 5 atoms (1X C + 4 x H) Total atoms in 1 mol methane = 5*6.02*10^23 = 3*10^24 atoms in total. Answered by Adalberto Russel on Tue, Jul 6, 2021 1:39 AM Catalytic molten metals for the direct conversion of ... 17/11/2017 · Metals that are active catalysts for methane (Ni, Pt, Pd), when dissolved in inactive low–melting temperature metals (In, Ga, Sn, Pb), produce stable molten metal alloy catalysts for pyrolysis of methane into hydrogen and carbon. All solid catalysts previously used for this reaction have been deactivated by carbon deposition. In the molten alloy system, the insoluble … How you can Determine whether a Molecule Is Planar ... This gives a total of 4n+2 π electrons. You can see how this works with the molecular orbital diagram for the aromatic compound, benzene, below. Benzene has 6 π electrons. Its first 2 π electrons fill the lowest energy orbital, and it has 4 π electrons remaining. These 4 fill in the orbitals of the succeeding energy level.
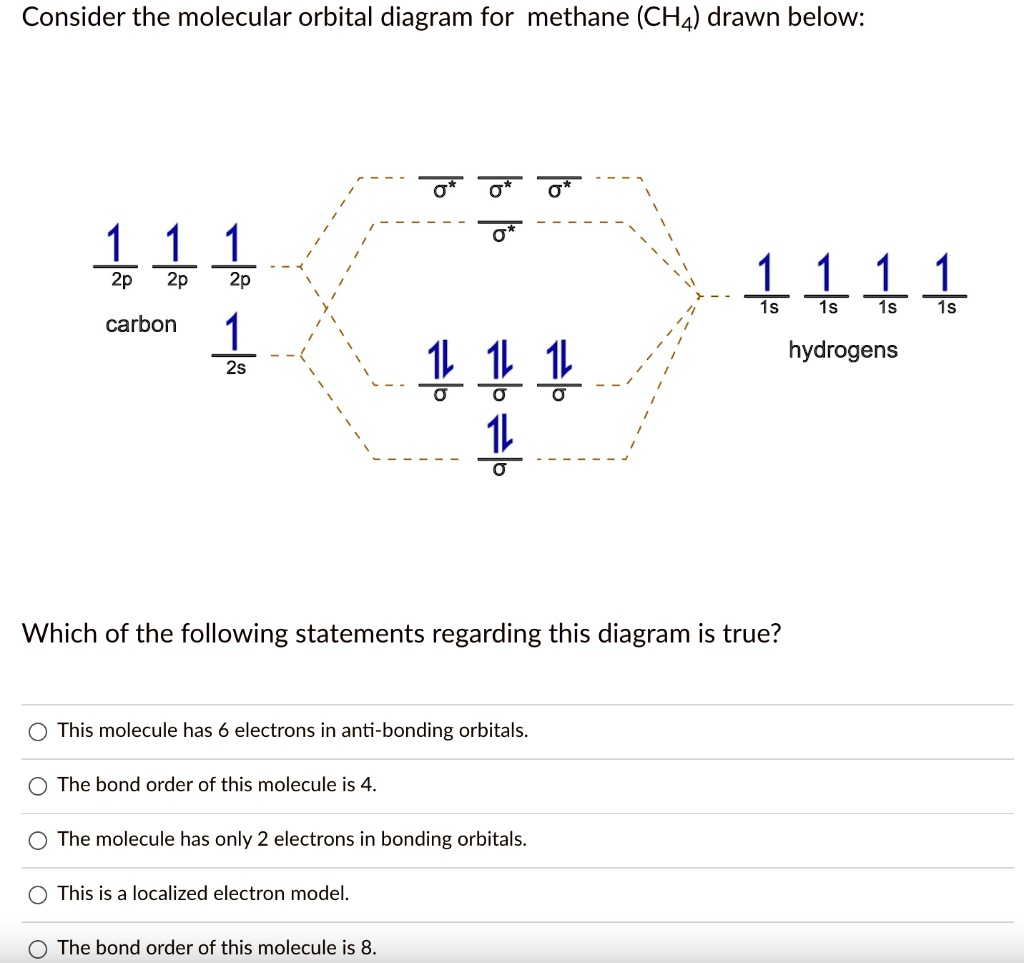
Methane molecular orbital diagram. Orbital Shape And Hybridization Of Molecules the next part. The molecular shape of H3O+ is a trigonal pyramid and electronic geometry is tetrahedral. From the above chart, we can see that In chemistry, orbital hybridisation (or hybridization) is the concept of mixing atomic orbitals to form new hybrid orbitals (with different energies, shapes, etc., than the component atomic orbitals) What Is The Molecular Geometry Of Ch4 (Methane), What Is ... So, this is how four sigma bonds are formed in a methane molecule with no pi bond where the sigma bond further contributes to the hybridization of the carbon atom. Molecular Orbital diagram of CH4 The molecular orbital diagram helps with determining how mixing and overlapping have taken place in a molecule to conclude upon the hybridization type. Electron Configuration Questions and Answers - Study.com Use the molecular orbital theory to determine the ground-state electron configuration of F_2 and F_2^{+}. View Answer. An element with 37 protons … Phase Diagram for the Methane-Ethane System and Its ... Peak shifts of the ethane band centered around 2880 cm −1 and methane band centered around 2904 cm −1 in a 0.4 methane-0.6 ethane mixture.
Interactive 3D Chemistry Animations — ChemTube3D Periodic Table. ChemTube3D contains interactive 3D chemistry animations and structures, with supporting information, for students studying some of the most important topics in advanced school chemistry and university chemistry courses. Use the menus to explore them. 39 square planar orbital diagram - Wiring Diagrams Manual Molecular Orbitals of Square-Planar Tetrahydrides | VIPEr Apr 18, 2014 · This in-class activity walks students through the preparation of a molecular-orbital diagram for methane in a square-planar environment. Molecular Structure & Bonding - Michigan State University Here, the correlation diagram correctly accounts for the paramagnetic character of this simple diatomic compound. Likewise, the orbital correlation diagram for methane provides another example of the difference in electron density predicted by molecular orbital calculations from that of the localized bond model. Click on the compound names for ... Difference Between Bonding And Antibonding Orbitals ... This is a combination of orbital and two p orbitals. Sp 3 example of is methane. This is a of s orbital and three p orbitals. If you add exponents of orbitals, you the amount of sigma bonds with that bond. Sp 2 hybridize orbital has p that is not hybridized so can form pi bond. This means sp orbitals allow for the formation of a double bond.
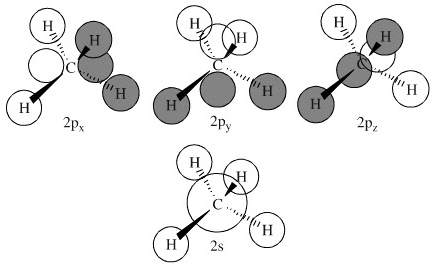
(Get Answer) - 4. Molecular orbital theory. Borane (BH3 ... Derive a molecular orbital diagram shown below for borane by performing the same steps as above in problem #3: (1) Determine a G describing the three H 1s atomic orbitals, (2) factor this G into a linear combination of Girr, and (3) complete the molecular orbital diagram exactly as described above for methane. 4. Molecular orbital theory. Molecular Weight Of Methane Gas? 👌 (2022) - QA | «Oil And ... How to create a molecular orbital diagram for methane? Methane (CH4) has tetrahedral geometry and Td point group symmetry Derive a molecular orbital diagram for methane by performing the following steps: a. Methane formula weight calculator? Molar mass of CH4 = 16.04246 g/mol. Convert grams Methane to moles or moles Methane to grams. Methane Formula: Structure, Uses, Properties - Embibe Structure of Methane Now let us delve deep into the structure and other molecular details of Methane. Formula The molecular formula of methane is \ ( {\rm {C}} { {\rm {H}}_4}\). It is a group-\ (14\) hydride and the simplest alkane. It is a one-carbon compound in which single bonds attach the carbon to four hydrogen atoms. Molar Mass 1.7: sp³ Hybrid Orbitals and the Structure of Ethane ... This orbital overlap is often described using the notation: sp3 (C)- sp3 (C). Each of the remaining sp3 hybrid orbitals overlaps with the s orbital of a hydrogen atom to form carbon-hydrogen σ bonds. The σ carbon-carbon bond has a bond length of 154 pm, and a bond strength of 377 kJ/mol.
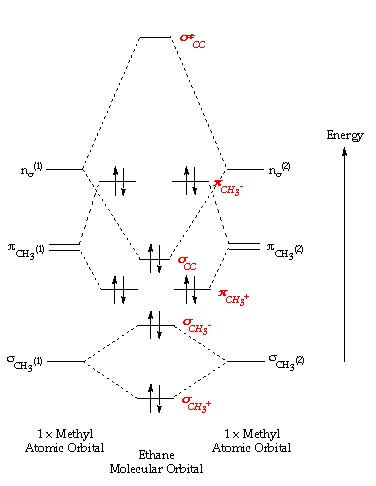
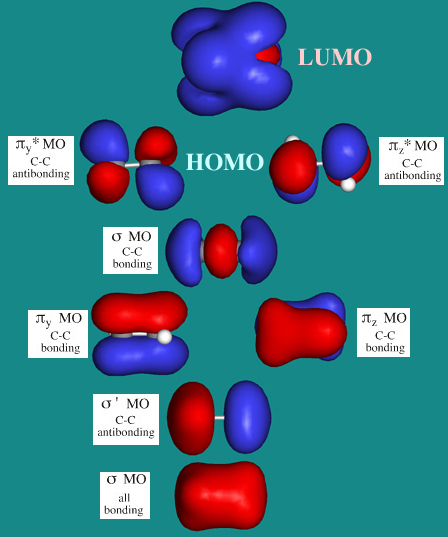
C2H4 Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, Hybridization ... Apr 11, 2022 · C2H4 Molecular Orbital (MO) Diagram. The molecular orbital theory is a concept of quantum mechanics where atomic linearly combines to form molecular orbitals and we describe the wave nature of atomic particles. Here, bond strength depends on the overlapping degree which in turn depends on the spatial proximity of the combining atoms.
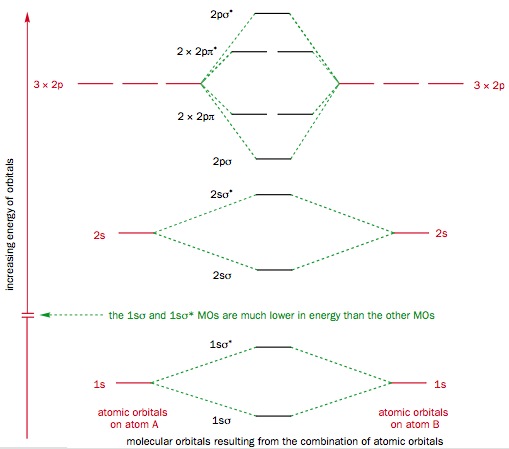
AP Chemistry- Practice Bonding Questions for Exam - Quia The following molecular orbital diagram may be used for the following problems. For oxygen and fluorine, the σ 2p orbital should be lower in energy than the π 2p. However, the diagram will still yield correct bond order and magnetic behavior for these molecules.
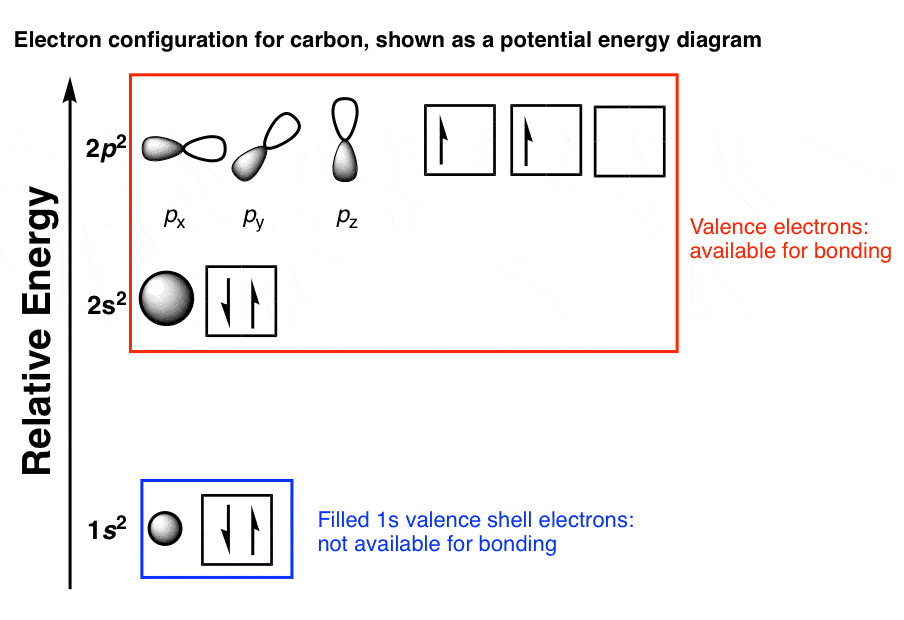
Molecular Orbital Theory Molecular Orbital Theory: Electrons are located in the molecule, ... Valence bond theory predicts four identical C-H bonds in methane.30 pages
Molecular orbital diagram - Wikipedia A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine …
CH4 Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, and Hybridization 15/04/2022 · Molecular Orbital diagram of CH4. The molecular orbital diagram helps with determining how mixing and overlapping have taken place in a molecule to conclude upon the hybridization type. As per the figure, the four sp3 hybrid orbitals of the carbon mixes and overlaps with four 1s atomic orbitals of the hydrogen. Each carbon and hydrogen bond (C-H) forms due …
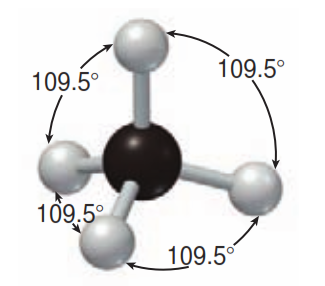
Methane: Molecular Geometry - Hybridization - Molecular ... Lewis structure: A Lewis structure or Lewis representation (also known as electron raster diagram, Lewis raster formula, Lewis point structure, or point electron structure) is a two-dimensional diagram used in chemistry to show the bonding between atoms of a molecule and the lone electron pairs that may be present in this molecule.
Methane - Wikipedia Methane is a tetrahedral molecule with four equivalent C-H bonds. Its electronic structure is described by four bonding molecular orbitals (MOs) resulting from the overlap of the valence orbitals on C and H.
ORBITALS and MOLECULAR REPRESENTATION In picture 1 we show the molecular orbital structure of F2. In picture 2 we show the overlapping p orbitals, which form the bond between the two fl uorine atoms, in red and green gradients. The dashed lines show the remaining p orbitals which do not take part in the bonding. σ z y x σ* x y z Construct the molecular orbital diagram for ...
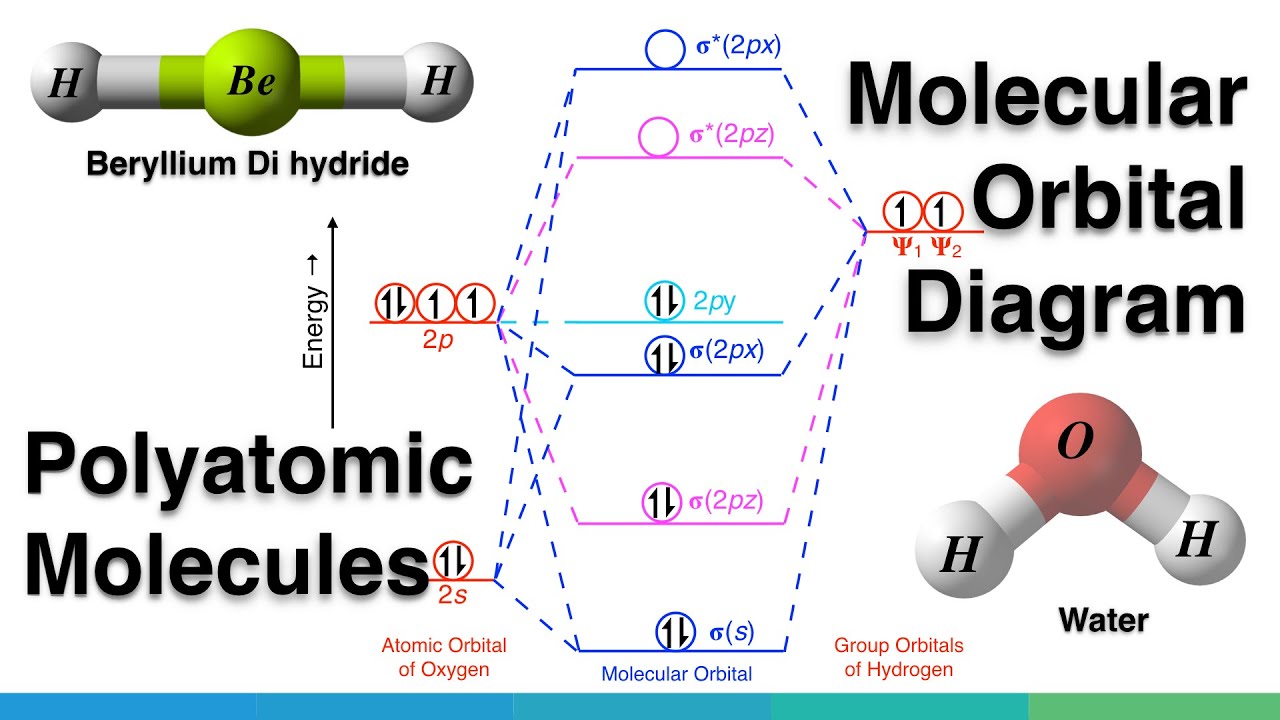
Polyatomic Molecular Orbital Theory - La Salle University MO diagram of homonuclear diatomic molecules ... 4) MO theory and molecular geometry (Walsh diagrams) ... Molecular Orbital Theory – LGOs for methane.29 pages
Alkanes- Definition, Structure, Properties, Reactions, Uses Methane, ethane, propane, and butane are all present in the gas state. C 5-C 17 alkanes are colorless liquids, whereas higher alkanes are wax-like solids. Alkanes are nonpolar compounds. They are soluble in nonpolar solvents like benzene, carbon tetrachloride, etc. The boiling point of alkanes rises with increasing molecular weight.
Methane Activation by (MoO3)5O− Cluster Anions: The ... The reactivity of (MoO 3) 5 O − can be traced back to the appropriate orientation of the lowest unoccupied molecular orbitals (LUMO) that is essentially the 2p orbital of the O b.− atom. This study not only makes up the blank of thermal methane activation by the O b .− radical on negatively charged clusters but also yields new insights ...
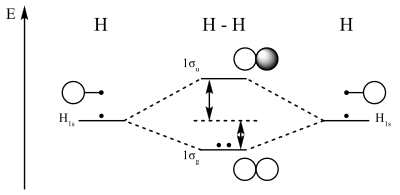
atomic structure - Explanation of the missing 1-s orbital ... 99.9999...99 % of the four atomic orbitals 1 s of H are forming molecular orbitals with the 2 s and 2 p of the carbon atom. The rest, .000..01 % is forming a dim molecular orbital with the 1 s of the carbon. As a result, this molecular orbital is not different from the 1 s of the carbon atom. - Maurice Mar 30 at 18:45
How you can Determine whether a Molecule Is Planar ... This gives a total of 4n+2 π electrons. You can see how this works with the molecular orbital diagram for the aromatic compound, benzene, below. Benzene has 6 π electrons. Its first 2 π electrons fill the lowest energy orbital, and it has 4 π electrons remaining. These 4 fill in the orbitals of the succeeding energy level.
Catalytic molten metals for the direct conversion of ... 17/11/2017 · Metals that are active catalysts for methane (Ni, Pt, Pd), when dissolved in inactive low–melting temperature metals (In, Ga, Sn, Pb), produce stable molten metal alloy catalysts for pyrolysis of methane into hydrogen and carbon. All solid catalysts previously used for this reaction have been deactivated by carbon deposition. In the molten alloy system, the insoluble …
How Many Total Atoms Are In A Molecule Of Methane? 👌 (2022 ... 1 mol methane (CH4) contains 6.02*1023 molecules 1 molecule CH4 contains 5 atoms (1X C + 4 x H) Total atoms in 1 mol methane = 5*6.02*10^23 = 3*10^24 atoms in total. Answered by Adalberto Russel on Tue, Jul 6, 2021 1:39 AM














0 Response to "42 methane molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment