44 hepatic portal circulation diagram
Other articles where hepatic portal system is discussed: circulatory system: The blood vessels: They are called the hepatic (liver) and renal (kidneys) portal systems. The hepatic system is important because it collects blood from the intestine and passes it to the liver, the centre for many chemical reactions concerned with the absorption of food into the body and the control of substances… We are pleased to provide you with the picture named Hepatic portal system anatomical diagram.We hope this picture Hepatic portal system anatomical diagram can help you study and research. for more anatomy content please follow us and visit our website: www.anatomynote.com. Anatomynote.com found Hepatic portal system anatomical diagram from plenty of anatomical pictures on the internet.
normal circulatory conditions of the portal circulation deficient and inconclusive. Theportal circulation presents aproblem bothfromthe anatomicalandphysiological standpoints, andthe conceptions of its intrahepatic anatomymustof necessity influence ourinterpretationofthevaso-motorreactionsinthissystem. Itis obviousthattheremust
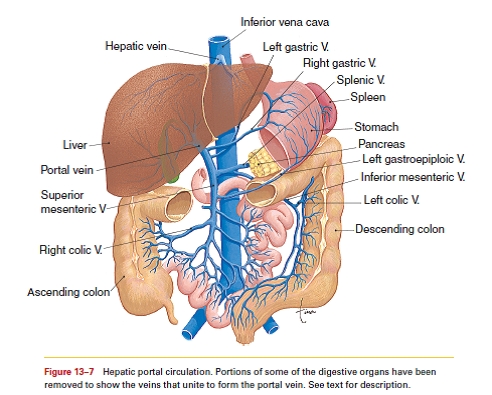
Hepatic portal circulation diagram
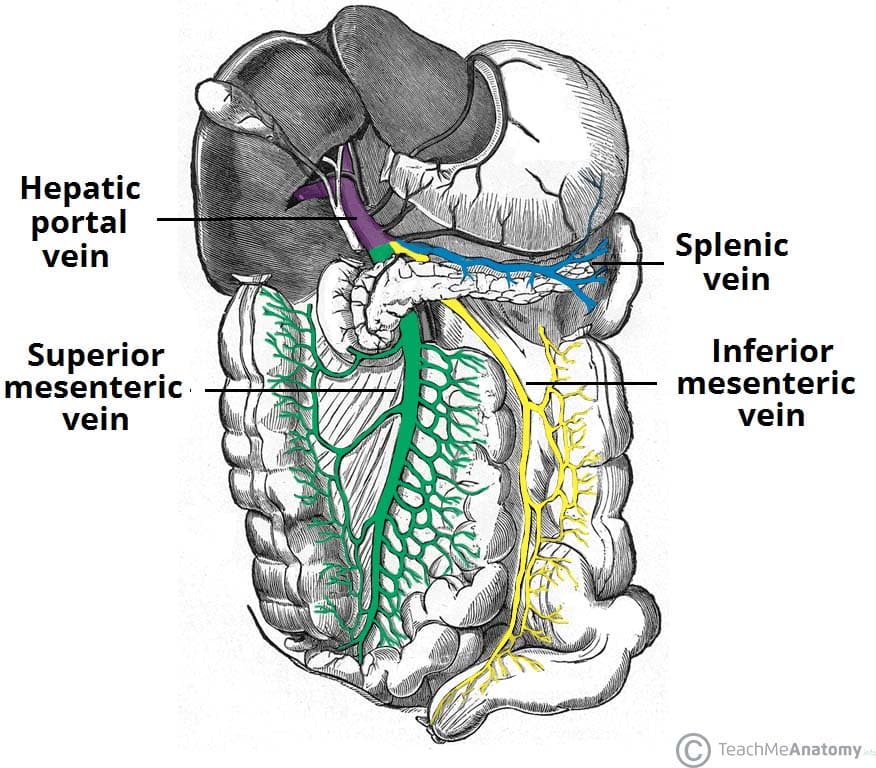
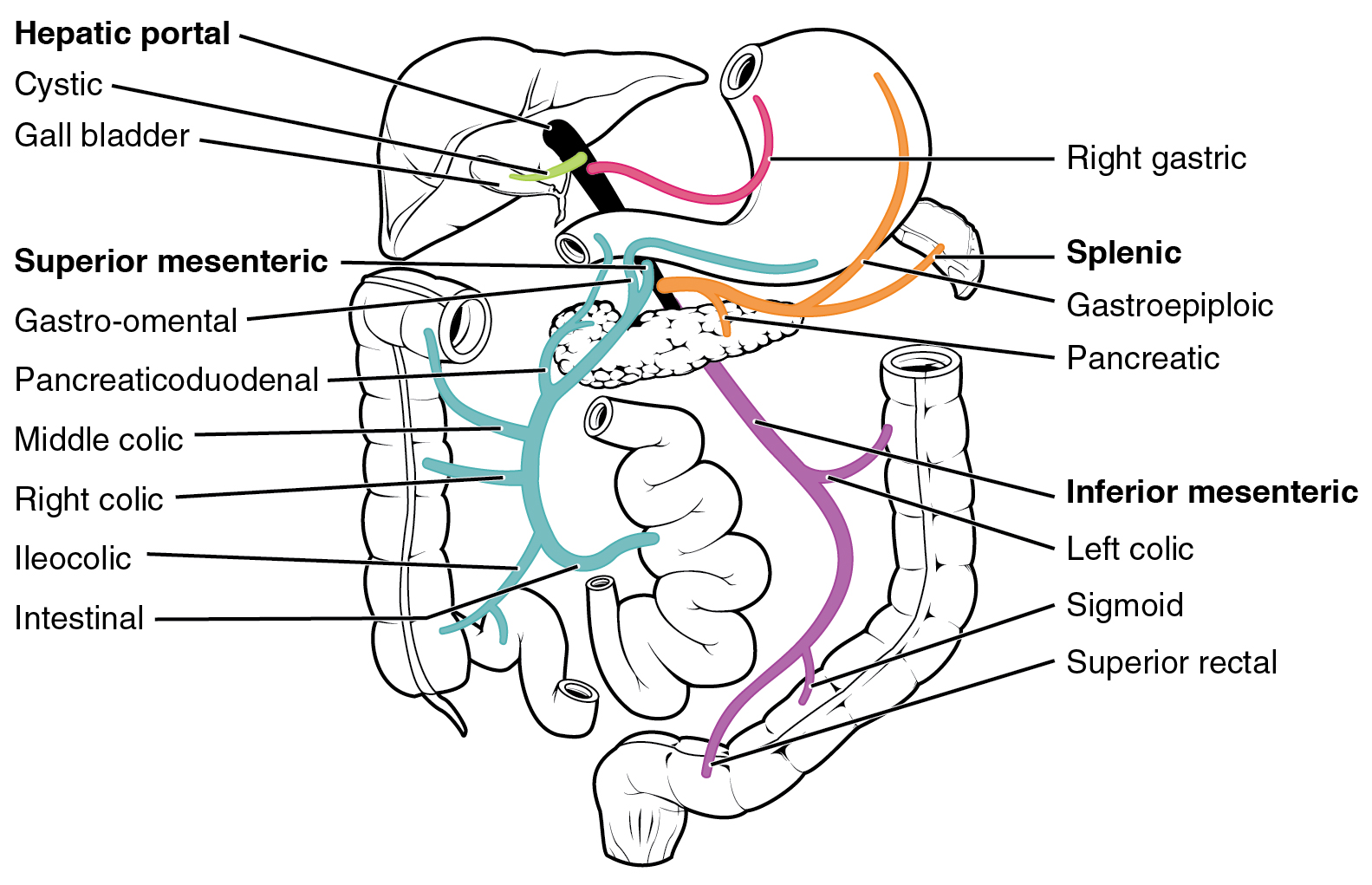
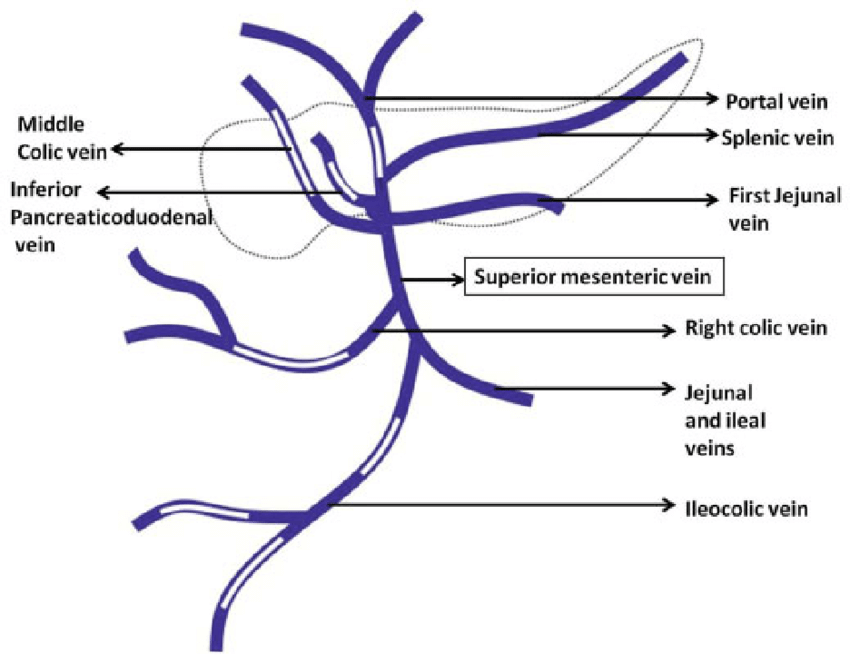
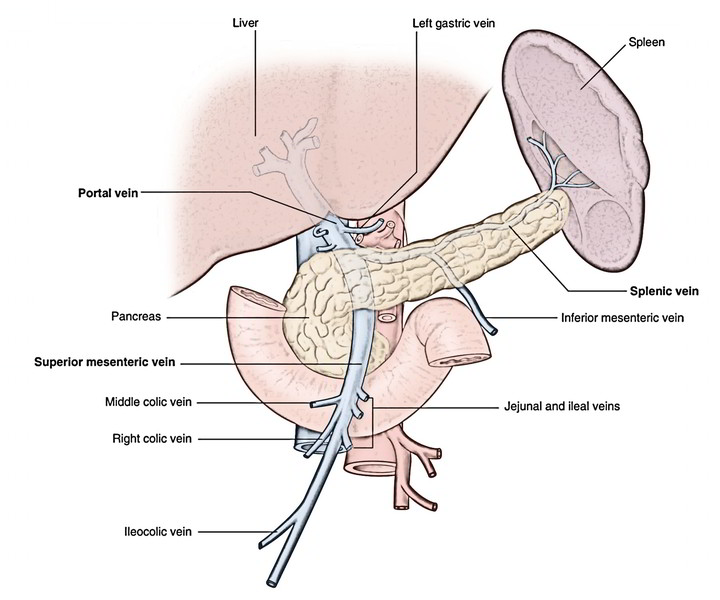
The hepatic portal circulation definition is that flows of blood from the beginning of the hepatic portal system to the end of it. furthermore, It emerges from capillaries of the spleen and organs of the digestive system and ends in. hepatic sinusoids- special vascular structures in the liver that function such as capillaries. The liver has a dual blood supply, receiving most of its blood flow (75%) as deoxygenated blood from the portal vein, and the rest from the hepatic artery. The portal vein is a low-pressure system of valveless vessels which does not autoregulate according to hepatic oxygen demand, but rather according to supply (eg. with meals, the portal vein dilates and increases its flow). The main vessel of the hepatic portal system is the hepatic portal vein (Figures 3.31 and 3.32), a large vein that lies in the gastrohepatoduodenal ligament alongside the hepatic artery and anterior part of the bile duct.The hepatic portal vein is formed by the confluence of three main vessels, the gastric, pancreaticomesenteric, and lienomesenteric veins.
Hepatic portal circulation diagram. Hepatic portal circulation: A diagram that shows the hepatic portal vein and its territory. Liver Function. The liver is thought to be responsible for up to 500 ... Basilic vein . Brachial vein . Median cubital vein . Dorsal venous arch . Small saphenous vein . Digital veins . Great saphenous vein . Ulnar vein The Portal Circulation. The liver is unusual in that it has a double blood supply; the right and left hepatic arteries carry oxygenated blood to the liver, and the portal vein carries venous blood from the GI tract to the liver. The portal venous blood contains all of the products of digestion absorbed from the GI tract, so all useful and non ... In human anatomy, the hepatic portal system is the system of veins comprising the hepatic portal vein and its tributaries. It is also called the portal venous system (although it is not the only example of a portal venous system) and splanchnic veins, which is not synonymous with hepatic portal system and is imprecise (as it means visceral veins and not necessarily the veins of the abdominal ...
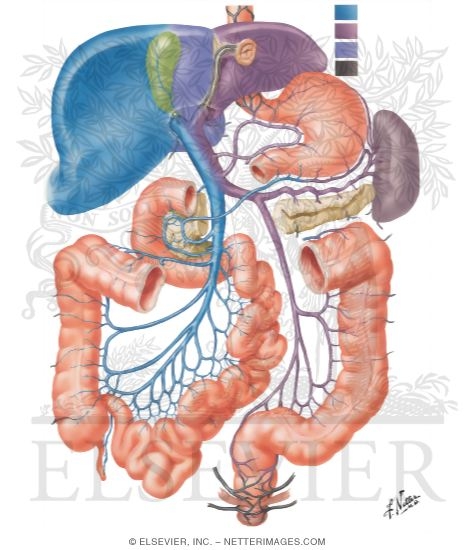
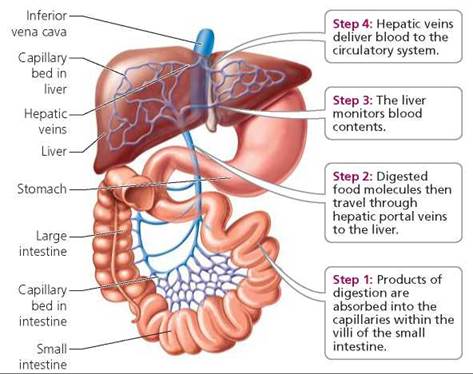
The hepatic portal vein is one of the most important vein that receives blood from the body and transports it into the liver for filtration and processing. This vein is part of the hepatic portal system that receives all of the blood draining from the abdominal digestive tract, as well as from the pancreas, gallbladder, and spleen. 'Hepatic' means of or relating to the liver, therefore the ... Portal Circulation. The portal venous system drains the intestines, pancreas, and spleen with numerous collateral anastomoses to other venous beds of the abdomen. There is a mixing of portal and systemic blood circulation within the sinusoids, and all the blood eventually drains from the liver via the hepatic veins to the inferior vena cava. Oxygenated blood flows in from the hepatic artery. Nutrient-rich blood flows in from the hepatic portal vein. The liver holds about one pint (13%) of the body's blood supply at any given moment. The liver consists of 2 main lobes. Both are made up of 8 segments that consist of 1,000 lobules (small lobes). Of the total hepatic blood flow (100-130 ml/min per 100 g of liver, 30 ml/min per kilogram of body weight), one fifth to one third is supplied by the hepatic artery. About two thirds of the hepatic blood supply is portal venous blood. The gross vascular supply of the liver is conceptually described in Figures 2.1 and 2.2.
Hepatic Portal Circulation study guide by christian_garlick8 includes 10 questions covering vocabulary, terms and more. Quizlet flashcards, activities and games help you improve your grades. The hepatic portal system is designed to require the digested elements to pass through the liver before entering the general circulation. The digestive organs are then drained by the hepatic portal vein. This vein is created by the conjuncture of the superior mesenteric vein and the splenic vein. HEPATIC PORTAL SYSTEM DIAGRAM Hepatic Portal System and Its Functions. The hepatic portal system is a complex system of hepatic portal veins and their capillaries. It is also known as the portal venous system. The hepatic portal system is a crucial part of the circulatory system. However, there are other systems of veins in the body that are referred to as the portal venous ... Key Terms. hepatic arteries: A blood vessel that supplies oxygenated blood to the liver.; hepatic portal vein: A vessel located in the abdominal cavity that is formed by the union of the superior mesenteric and splenic veins that channel blood from the gastrointestinal tract and spleen to the capillary beds in the liver.; cofactors: A substance, especially a coenzyme or a metal, that must be ...
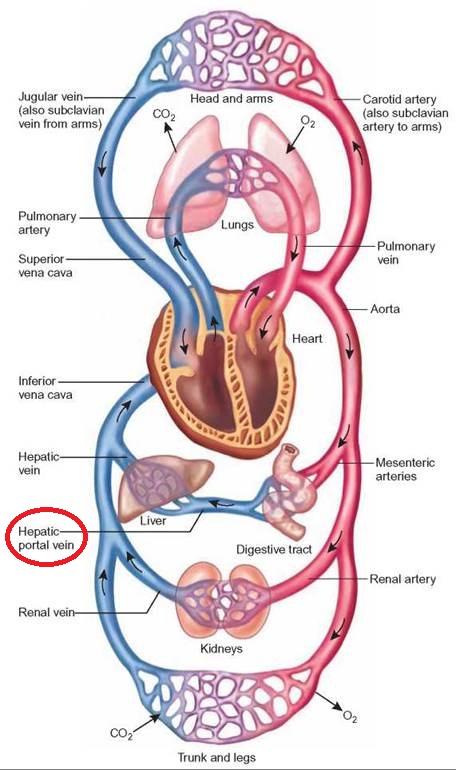
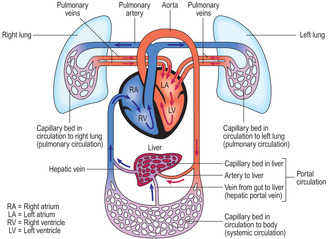
Circulatory Pathways. The blood vessels of the body are functionally divided into two distinctive circuits: pulmonary circuit and systemic circuit. The pump for the pulmonary circuit, which circulates blood through the lungs, is the right ventricle.The left ventricle is the pump for the systemic circuit, which provides the blood supply for the tissue cells of the body.
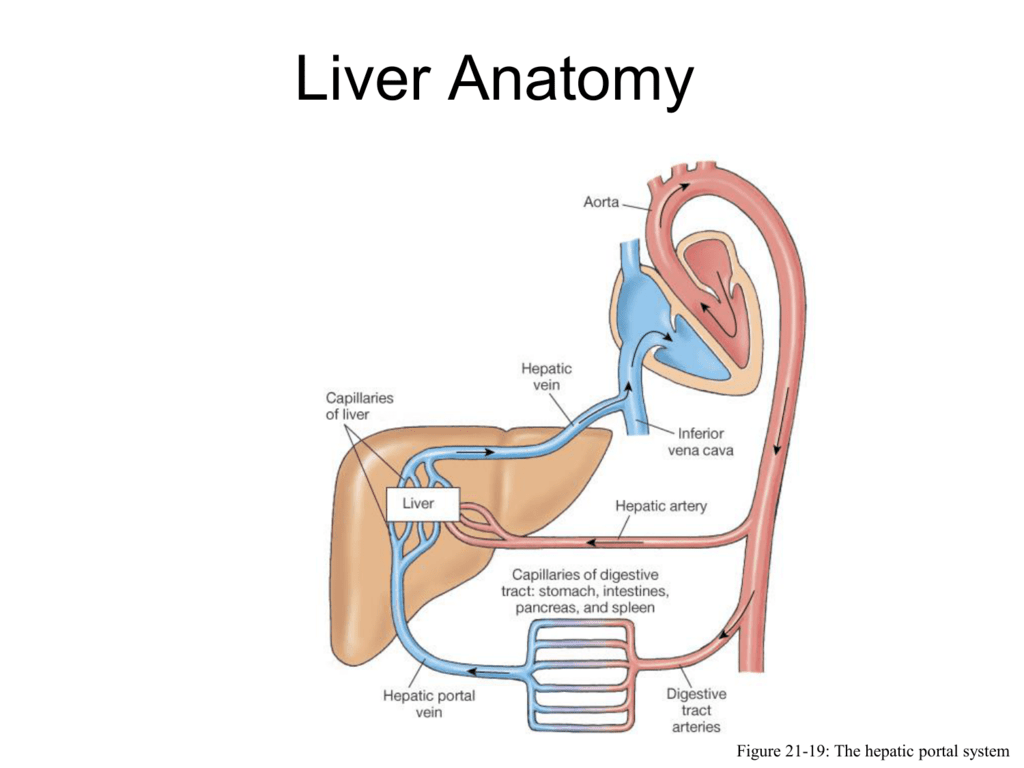
Normal hepatic circulation is a high flow - low resistance system. Branches of the portal vein deliver 1000-1500 ml/min of blood into the sinusoids of the hepatic lobules. Normal portal venous pressure is 5-10 mm Hg.* The blood passes through the sinusoids and drains into the inferior vena cava. Inferior vena cava pressure ranges from -5 to +5 ...
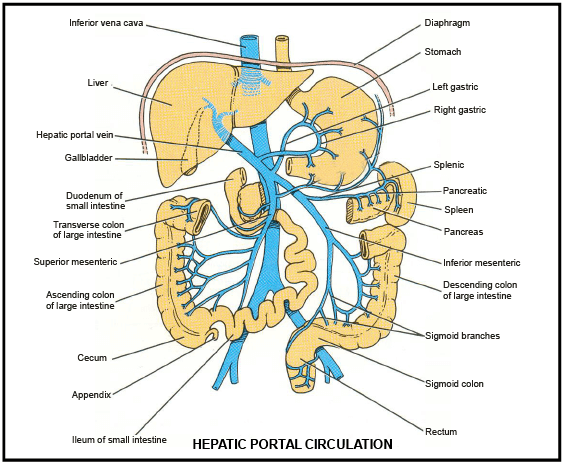
Portal circulation is the flow of blood from one organ to another, without going through the heart. The term is most often used to refer to how blood moves through the network of veins in the gut and digestive organs, such as the spleen and pancreas, and is carried to the liver. This particular system is known as the hepatic portal system ...
Concept Me To learn the concept of how blood flows through various circulatory routes, draw a schematic diagram (of a design of your choice that clearly shows the structures through which blood flows in the following routes: 1. Hepatic portal circulation (include routes all the way to and from the heart in your diagram) 2. Fetal circulation 3.
The hepatic portal system is the system of veins comprising the hepatic portal vein and its tributaries. It is responsible for directing blood from the region of the gastrointestinal tract between the esophagus and rectum and also includes venous drainage from the supplementary organs such as the spleen and pancreas.
Following is a diagram showing the blood circulation of the body. We can see hepatic portal vein here (a part of portal system), this vein begins in a capillary (of intestines) and ends in another capillary (of liver). The hepatic portal circulation travels from the intestine of the digestive tract to the liver.
The liver is unusual in that it has a double blood supply; the right and left hepatic arteries carry oxygenated blood to the liver, and the portal vein carries ...
The hepatic portal system is a series of veins that carry blood from the capillaries of the stomach, intestine, spleen, and pancreas to capillaries in the liver. It is part of the body's ...
After percolating through the liver (the hepatic portal system), the blood drains into the hepatic veins and then into the inferior vena cava. It is now back in systemic circulation and on its way back to the heart and lungs. The blood from the digestive organs is brought to the liver through the hepatic portal vein. The hepatic
The hepatic portal circulation is important in that it captures substances from the digestive system and sends them to the liver to be metabolized. Depending on the substance, such as medication ...
Start studying LABEL VEINS OF HEPATIC PORTAL SYSTEM. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
Download scientific diagram | Hepatic portal lymphatic circulation diagram. from publication: The current immune function of hepatic dendritic cells | While only a small percentage of the liver as ...
Reabsorbed into circulation at the ileum (they the enter recycling pathway: enterohepatic circulation). Travel through the hepatic portal vein back to the liver where they are recycled and re-secreted into newly formed bile. Note: The hepatic portal vein drains nutrient-rich blood from the small intestine to the liver for metabolic processing.
The main vessel of the hepatic portal system is the hepatic portal vein (Figures 3.31 and 3.32), a large vein that lies in the gastrohepatoduodenal ligament alongside the hepatic artery and anterior part of the bile duct.The hepatic portal vein is formed by the confluence of three main vessels, the gastric, pancreaticomesenteric, and lienomesenteric veins.
The liver has a dual blood supply, receiving most of its blood flow (75%) as deoxygenated blood from the portal vein, and the rest from the hepatic artery. The portal vein is a low-pressure system of valveless vessels which does not autoregulate according to hepatic oxygen demand, but rather according to supply (eg. with meals, the portal vein dilates and increases its flow).
The hepatic portal circulation definition is that flows of blood from the beginning of the hepatic portal system to the end of it. furthermore, It emerges from capillaries of the spleen and organs of the digestive system and ends in. hepatic sinusoids- special vascular structures in the liver that function such as capillaries.
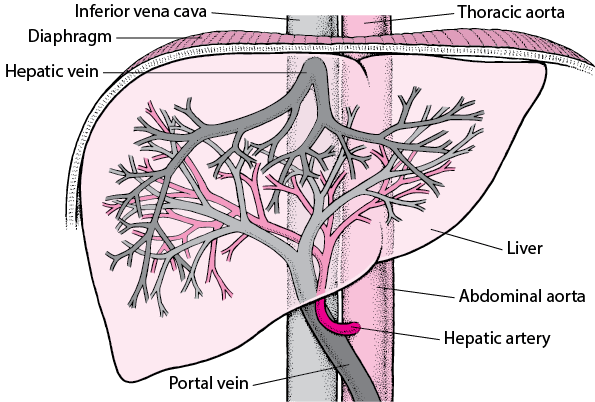
Overview Of Blood Vessel Disorders Of The Liver Liver And Gallbladder Disorders Msd Manual Consumer Version



























0 Response to "44 hepatic portal circulation diagram"
Post a Comment