40 tundra food web diagram
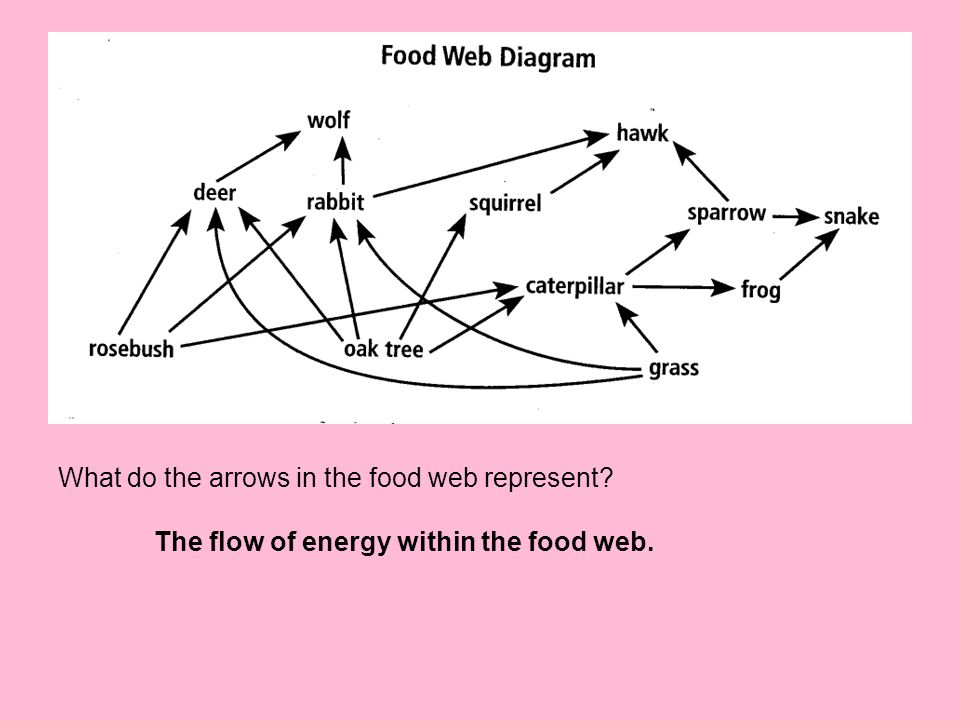
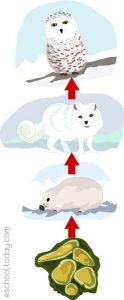
At the top of the food web, the Polar Bear reigns.The only predator for the Polar bear is Man (not shown on this ecosystem chart).Polar bears eat the Arctic seal and the Atlantic salmon and has no predator thus for making it the top of its food web.Below is a list of who eats who:. The Arctic seal is eaten by the polar bear and eats the Atlantic salmon A food web is a network of many food chains and more complex. See the food web illustration below—you can pick out a basic food chain from the web, Green plants — Grasshopper — Frog — Bird — Hawk. An example of a simple food web. In the diagram above, the arrows show the direction of energy flow. It points to the animal doing the ...
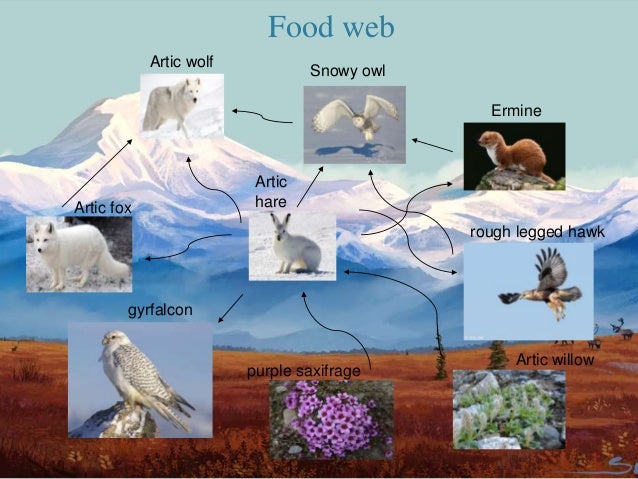
The food chain in the Arctic Tundra consists of predators such as owls, foxes, wolves, and polar bears at the top of the chain. Predators hunt herbivores, plant eating animals, such as caribou, lemmings, and hares. Mosquitoes, flies, moths, grasshoppers, arctic bumblebees, and other insects are at the bottom of the arctic food chain. ...

Tundra food web diagram
Habitat Description. The Arctic Tundra A treeless area between the icecap and the tree line of arctic regions, having a permanently frozen subsoil and supporting low-growing vegetation such as lichens, mosses, and stunted shrubs. is a very unique habitat with its own defining food web. I will be focusing on the Arctic tundra found in northern Alaska since that is where the Toolik Research ... In other words, a tundra is sort of like a cold desert, but, a tundra does have more vegetation (plants) than a desert because of the extra rain. Tundras are areas at the top of the world in the arctic circle. Some tundras are Alaska, Northern parts of Canada, the Arctic (North Pole), parts of Russia, Greenland and other parts of Northern Europe. I discovered Tundra during the pandemic when I couldn't go to market, which usually costs me at least $3000 per year. Now, I save that by using Tundra like my own market whenever I want. On Tundra, I find new products that get my customers excited and keep them coming back. "Eliminates the cost of simply buying and selling wholesale products ...
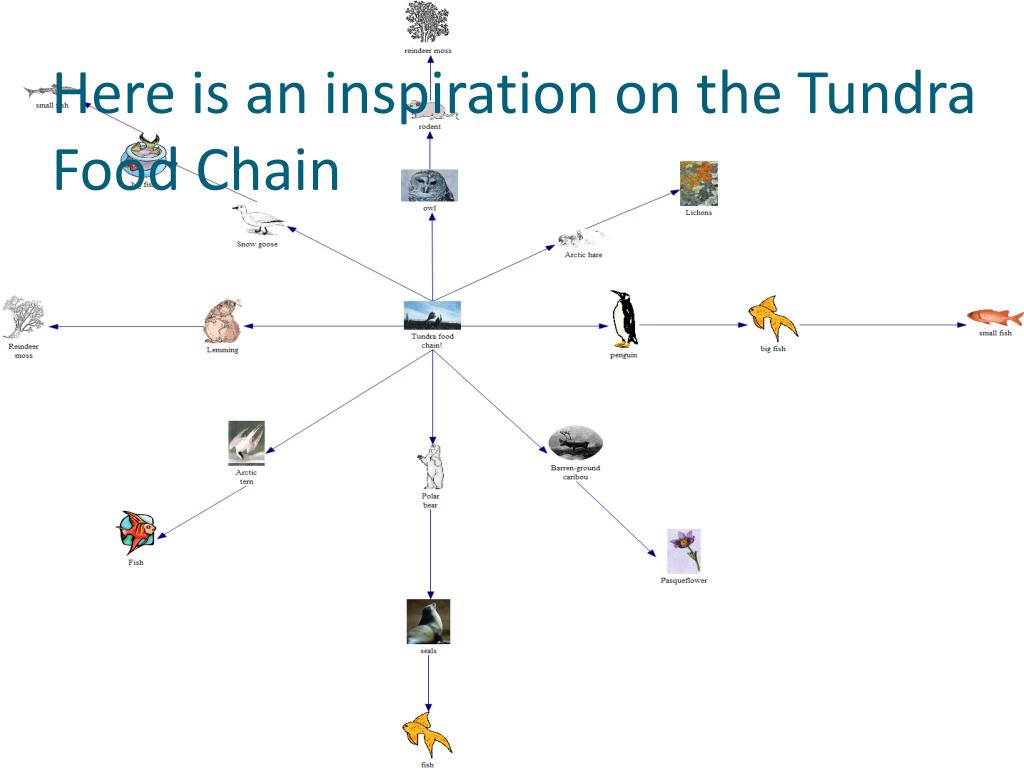
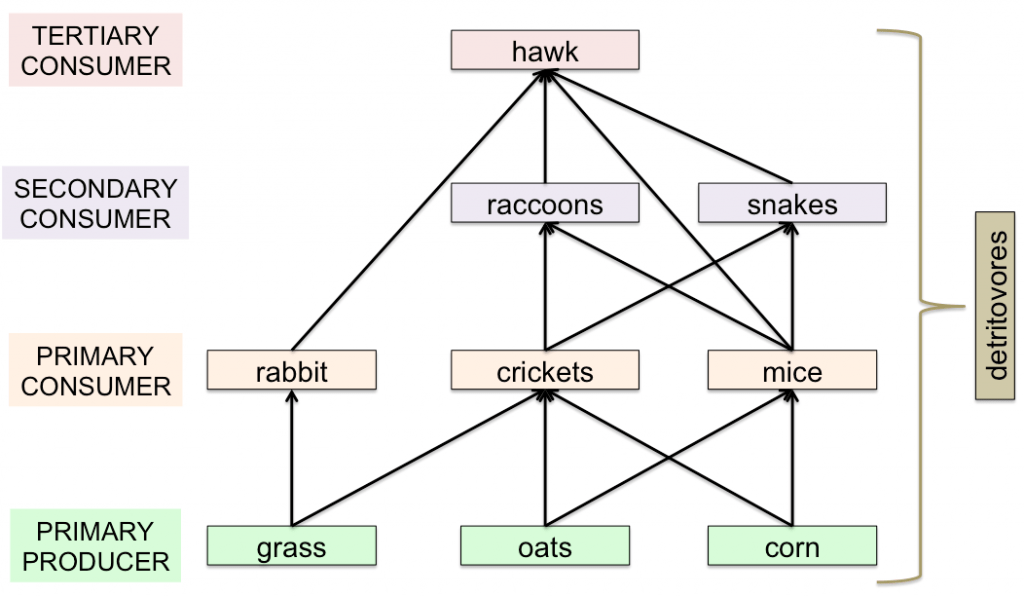
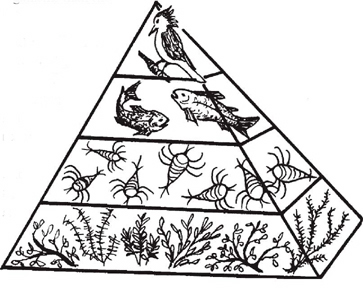
Tundra food web diagram. A food web provides a fuller and more realistic picture of how energy moves through a biome, because it indicates multiple connections, overlaps and relationships. In the Arctic tundra, many types producers, including flowering plants, low shrubs, sedges, grasses, mosses and algae, use the sun's energy during the process of photosynthesis. Ben Janke. This is a food chain of BIOTIC factors. They are animals or plants that have been alive or are alive. Dead rodents or bacteria are both biotic factors. Food webs are 100% consisted of biotic factors. FOOD WEB. 3 years 7 months ago. 5. Load the Interactive Food Web (pg. 6) and compare it to your class's list of species. Add any missing species and discuss how arrows in a food web follow the flow of energy rather than representing who eats whom. 6. Divide the class into small groups (3-4 students). Ask each group to choose a focus species A food chain is a network of links in a food web. Here, the producers are consumed by the predators-primary and secondary consumers and then the detritivores and finally by decomposers. When many such individual food chains occur in an ecosystem, it is known as Food Web. A food chain shows a direct transfer of energy between organisms.
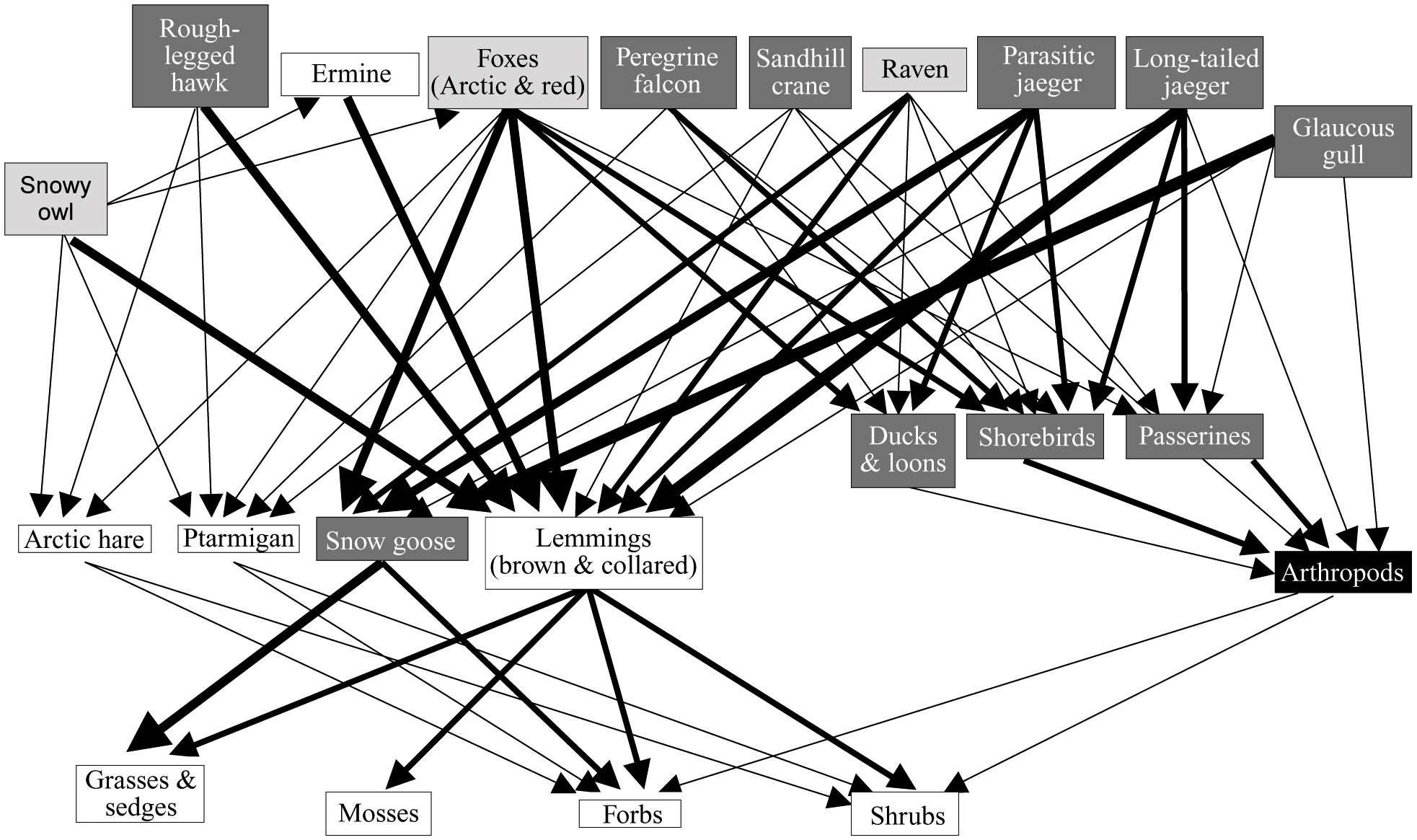
Food produced here. Despite unforgiving conditions, like permafrost and high altitudes, food is still produced able to be produced in the tundra. Fungi, lichens, flowers and shrubs all provide the necessary nutrients for herbivores to survive in this climate. Fish is a staple for people living in and around the tundra, salmon is the most eaten ... The fragile food chains of tundra support some of the most amazing species on the planet, including the likes of gray wolves, polar bears, snowy owls, and Arctic foxes. For tundra plants and animals, survival is not just about battling the harsh environment of this biome, but is equally about being a part of its complex food web. Arctic - Polar Region Food Web Activity. To understand the Arctic Food Web, first read about the Arctic Biome using this link. Then read about the different trophic levels of a typical Food Chain (below). The trophic level is the position that an organism (plant or animal) occupies in a food chain - what it eats, and what eats it. A food chain diagram is a visual representation of the flow of food energy through an ecosystem. Typical food chains start with a producer and are composed of at least three types of organisms. For example, when zooplankton eat ... • Slide #18: Use the provided tundra food web to review what a food web is.
Tundra is the coldest of all biomes. Tundra ultimately means treeless plain. Noted for frost-molded landscapes, extremely low temperatures, little precipitation, poor nutrients, and short growing seasons. Average winter temp. is -30 degrees fahrenheit. Average summer temp. is 37-54 degrees fahrenheit. Arctic Wolf. Now, look at the diagram below for an illustration of a food chain in the Tundra. Tundra Food Chain. Omnivore Snowy owls have smaller golden eyes claws covered with feathers. They are found mainly in the arctic open and treeless spaces. They usually perch on the ground and wait for yummy food (arctic fox, lemmings, and other birds and fish). Food chains & food webs. Energy flow & primary productivity. Practice: Food chains and food webs. This is the currently selected item. Next lesson. Biogeochemical cycles. Energy flow & primary productivity. Biology is brought to you with support from the Amgen Foundation. Biology is brought to you with support from the. Food web and chain some factors that effect population growth is the harsh environment of the tundra, theres not enough food for large populations, and the amount of predators. The arctic seal is eaten by the polar bear and eats the atlantic salmon . ARCTIC TUNDRA ecosystem food web diagram Tundra Biome . This is a food web.
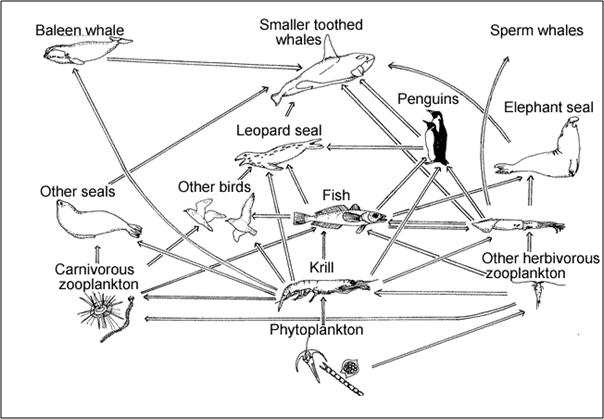
A generalized tundra food web. Exact relationships and species depend on geographic location. The interconnected nature of a food web means that as numbers of one species increase (or decrease), other populations change in response. An often-discussed tundra example is the lemming population.
Tundra Food Web Food web and Explanation. This food web shows the cycle at which food is transferred between organisms. First, the sun helps grow the plants (through photosynthesis) to provide food for the herbivores to graze. Then the carnivores hunt and eat the herbivores to regain its their energy.
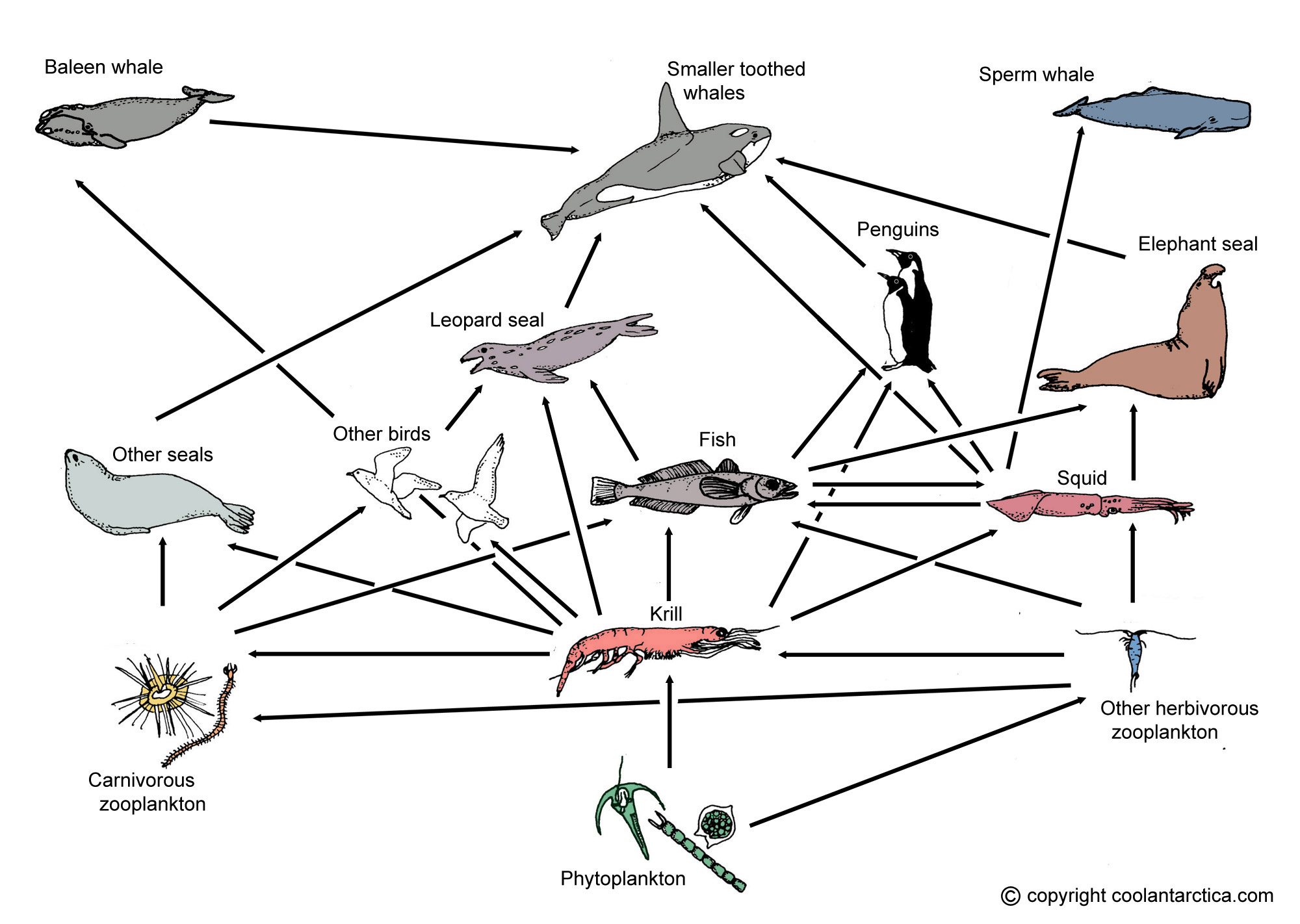
ARCTIC food web. Producers are highlighted in green, Primary Consumers in yellow, and Secondary Consumers in red. This is an example of an arctic tundra food web. The organisms on the very bottom are the producers who convert sunlight into usable energy through photosynthesis. Producers in the arctic are mostly small shrubs and lichen, like ...
ARCTIC TUNDRA ecosystem food web diagram | Tundra Biome: biome, tundra. Helen McKnockiter. 146 followers. Arctic Tundra Animals. Arctic Hare. Arctic Wolf. Ecosystems Projects. Biology Projects. Science For Kids. Science And Nature. Animal Habitats. Biomes. More information.... More like this ...
Tundra Biome Food Web. Every ecosystem consists of plants, herbivores, and carnivores. Food chains identify who eats whom to demonstrate the flow of energy in a oneway, linear relationship. For ...
Amazon Rainforest Food Web. This is an Amazon Rainforest Food Web. See if you can identify all the parts of the food web that make this a functioning, healthy ecosystem. Look for: The Producers - the trees, shrubs, bromeliads and other plants. The Primary Consumers - the macaws, monkeys, agouti, tapir, butterflies, sloths, toucans.
food webs lesson plan - a complete science lesson using the 5e method of instruction - kesler science At the end of this comprehensive food webs lesson plan, students will be able to diagram the flow of energy through living systems, including food chains and food webs.
Food Chains A food chain is a series of steps in which organisms transfer energy by eating and being eaten. Consumers are organisms that cannot harness energy directly from the physical environment. Consumers • Herbivores eat only plants. • Carnivores eat only animals. • Omnivores eat plants and animals. • Insectivores eat only insects.
Apr 2, 2015 - Explore Cindy Martinez's board "Biology Project" on Pinterest. See more ideas about biology projects, arctic tundra, tundra.
Tundra Food Web ( Block Diagram) Use Creately's easy online diagram editor to edit this diagram, collaborate with others and export results to multiple image formats. We were unable to load the diagram. You can edit this template and create your own diagram. Creately diagrams can be exported and added to Word, PPT (powerpoint), Excel, Visio ...
I discovered Tundra during the pandemic when I couldn't go to market, which usually costs me at least $3000 per year. Now, I save that by using Tundra like my own market whenever I want. On Tundra, I find new products that get my customers excited and keep them coming back. "Eliminates the cost of simply buying and selling wholesale products ...
In other words, a tundra is sort of like a cold desert, but, a tundra does have more vegetation (plants) than a desert because of the extra rain. Tundras are areas at the top of the world in the arctic circle. Some tundras are Alaska, Northern parts of Canada, the Arctic (North Pole), parts of Russia, Greenland and other parts of Northern Europe.
Habitat Description. The Arctic Tundra A treeless area between the icecap and the tree line of arctic regions, having a permanently frozen subsoil and supporting low-growing vegetation such as lichens, mosses, and stunted shrubs. is a very unique habitat with its own defining food web. I will be focusing on the Arctic tundra found in northern Alaska since that is where the Toolik Research ...

Heat Transfer Food Chain Food Web Ecosystem Air Masses Convection Currents Weather Weather Instruments Weather Weather Instruments Energy Potential And Kinetic Energy Potential And Kinetic Energy Weather Instruments Electric Current And S


















0 Response to "40 tundra food web diagram"
Post a Comment