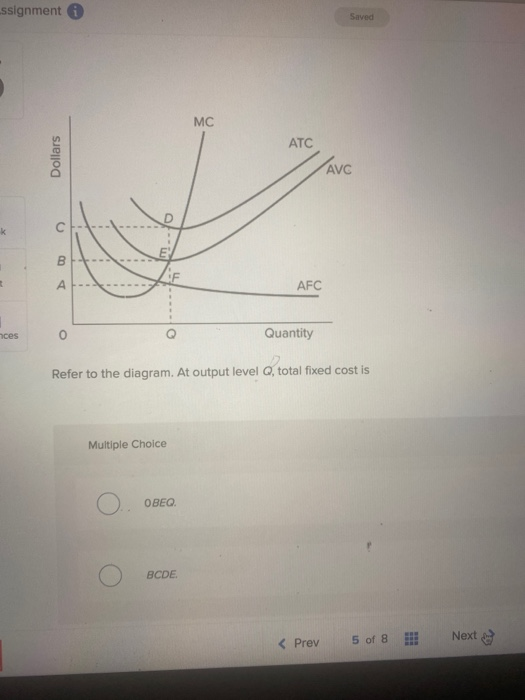
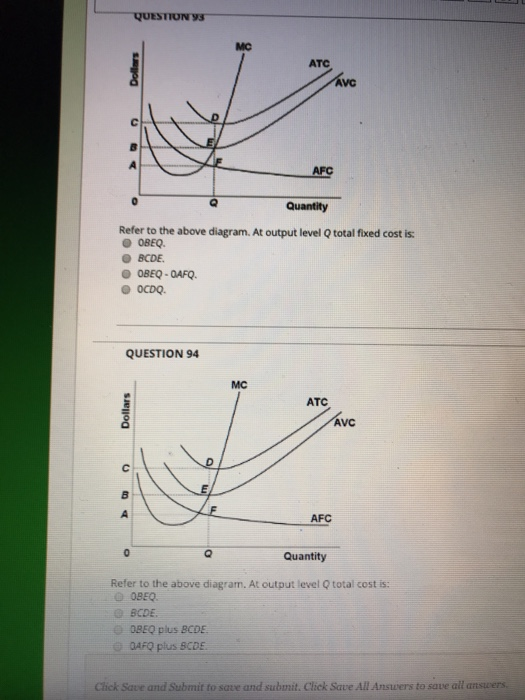
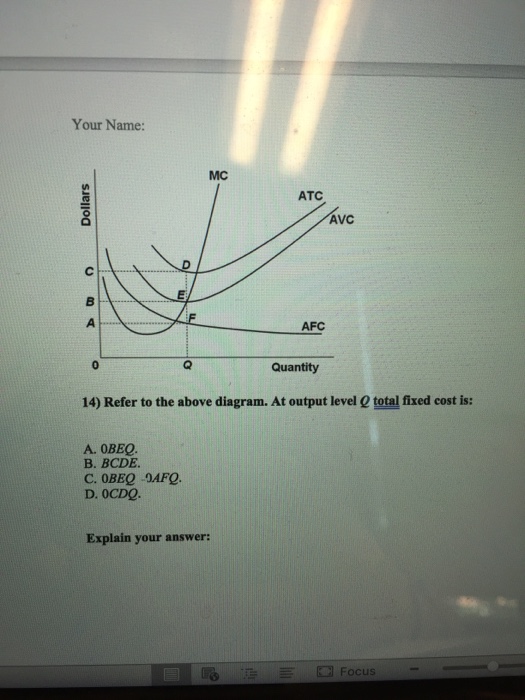
44 refer to the diagram. at output level q, total fixed cost is
econ exam #2 Flashcards - Quizlet Refer to the above diagram showing the average total cost curve for a purely competitive firm. At the long-run equilibrium level of output, this firm's total revenue: 400 Econ202 Exam 2 Solutions - Get Homework Done Question 2. Answer the next question (s) on the basis of the following output data for a firm. Assume that the amounts of all non-labor resources are fixed. Refer to the above data. Diminishing marginal returns become evident with the addition of the: a. sixth worker. b. fourth worker.
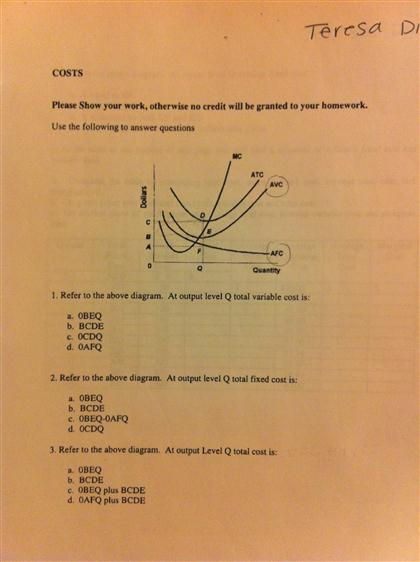
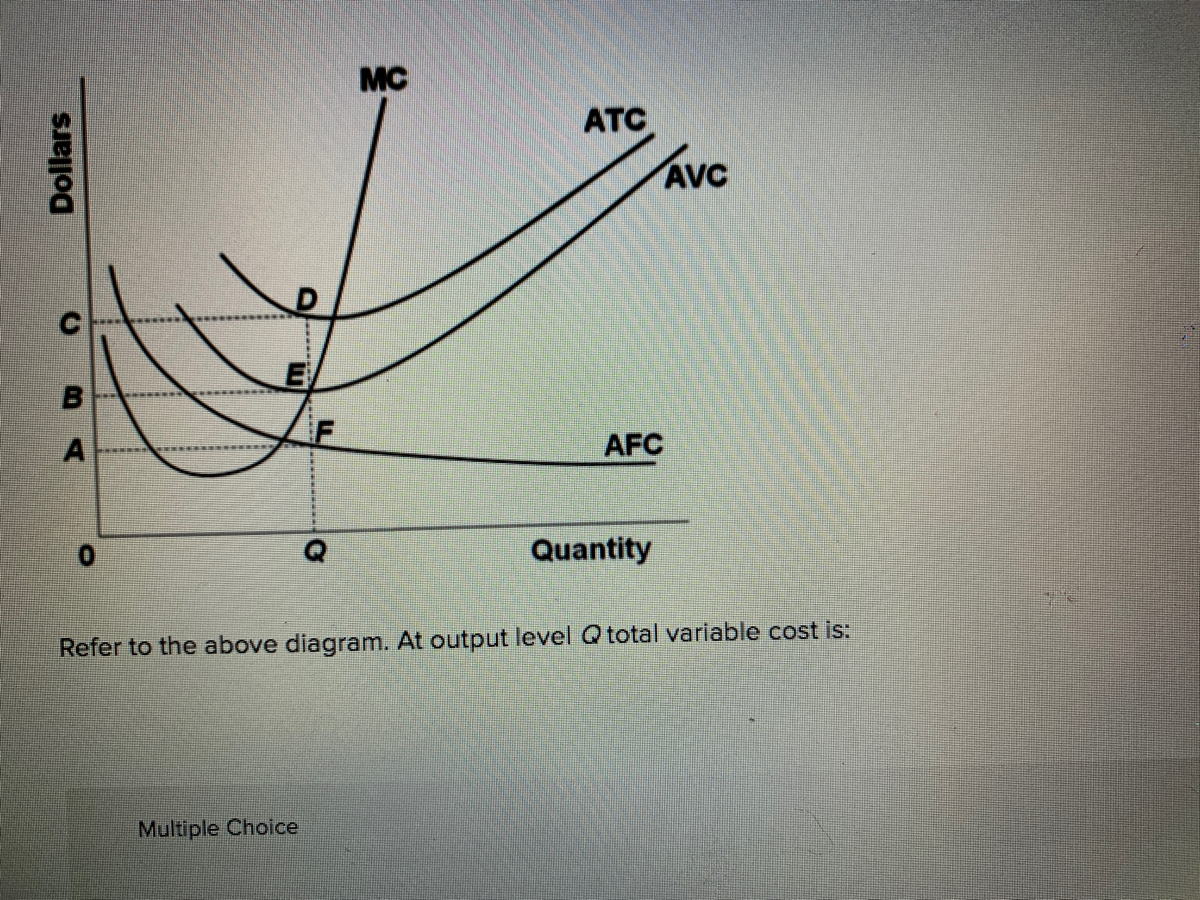
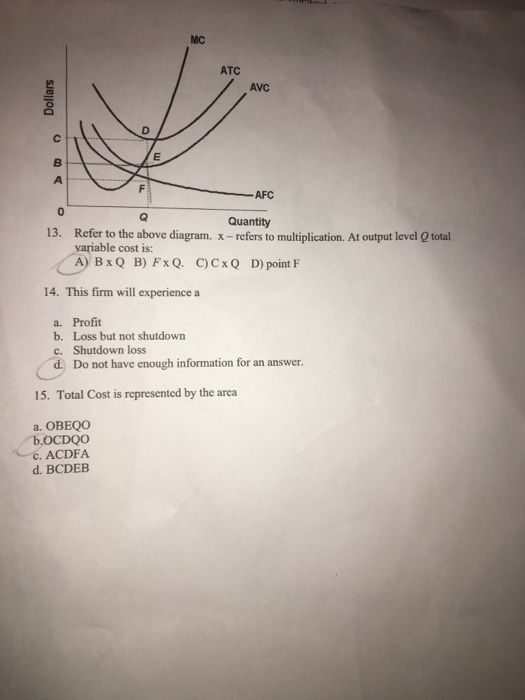
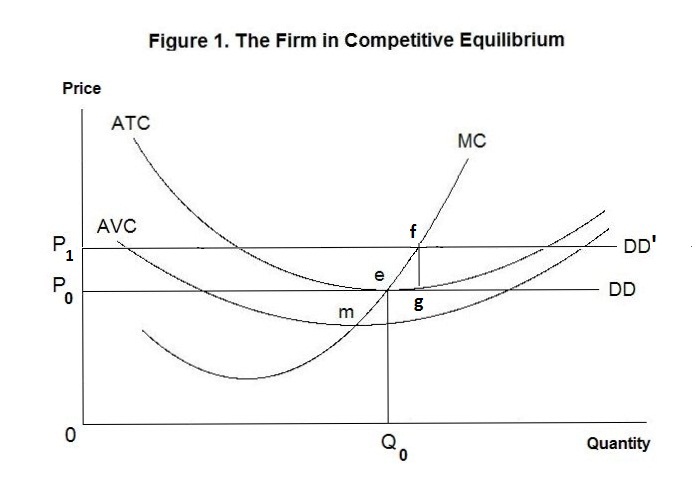
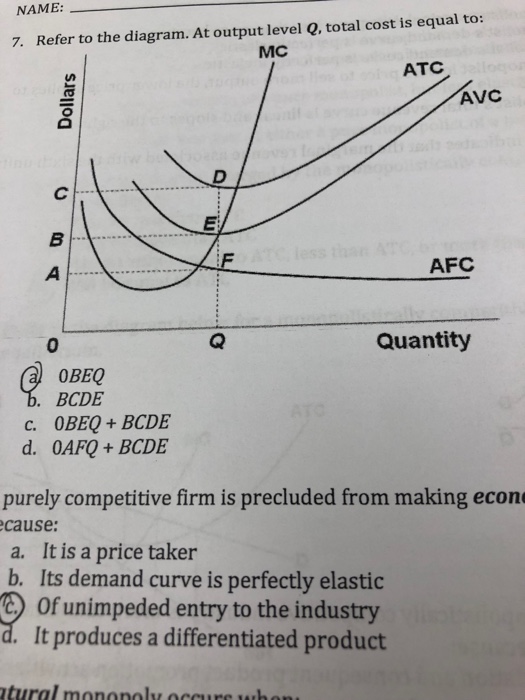
Refer to the above diagram At output level Q total cost is ... Refer to the above diagram at output level q total TVC = Q x AVC = OBEQ. A is correct fixed cost: A) is equal to EF. B) is equal to QE. C) is measured by both QF and ED. D) cannot be determined from the information given. This is the correct answer, C, since the height of the AFC or the height between ATC and AVC at Q is a measure of AFC 23.
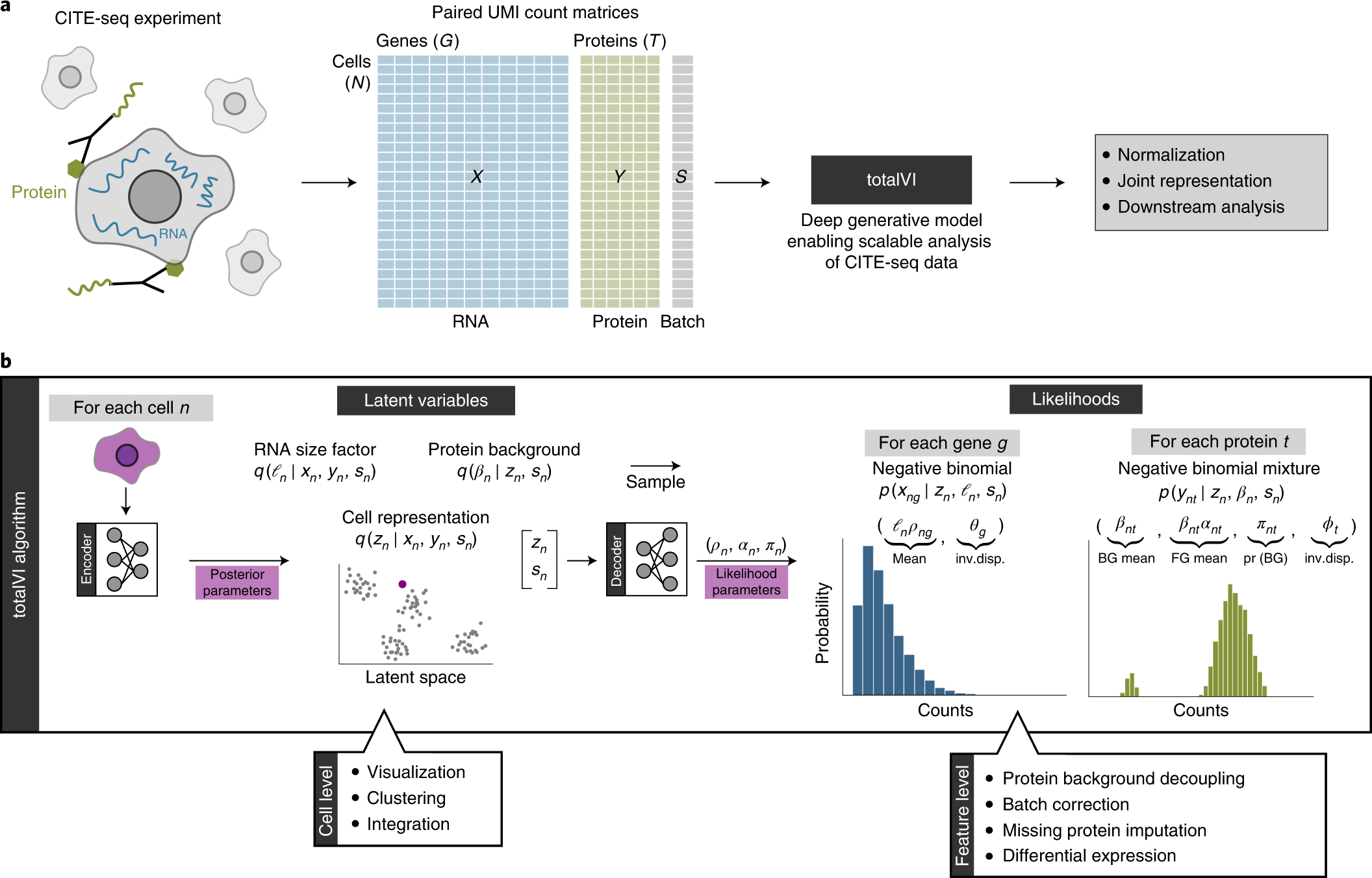
Refer to the diagram. at output level q, total fixed cost is
Type: T... - Martinsville Indiana Computer Repair - Facebook 176. Refer to the above diagram. For output level Q, per unit costs of C are: A) unobtainable and imply the inefficient use of resources. B) unobtainable, given resource prices and the current state of technology. C) obtainable, but imply the inefficient use of resources. D) obtainable and imply that resources are being combined efficiently ... Various Theories of Cost (With Diagram) - Economics Discussion Average fixed cost is the total fixed cost divided by the number of units of output produced. Thus: Since, total fixed cost is a constant quantity, average fixed cost will steadily fall as output increases, thus, the average fixed cost curve slopes downward throughout the length. It can be shown with the help of a figure 5. Classification of Fixed Costs (With Diagram) As we have seen above that the total cost is made up of both the fixed cost and the variable cost. They are represented in the diagram given below—here OX and OY are the two axes; along OX is represented the quantity produced and along OY the cost. FC, a single horizontal line, represents the fixed cost and the area above it the variable cost ...
Refer to the diagram. at output level q, total fixed cost is. Refer to the above diagram. At output level Q, the total ... Get the detailed answer: Refer to the above diagram. At output level Q, the total fixed cost is: a. 0BEQ b. BCDE c. 0BEQ - 0AFQ d. 0CDQ Ch. 22 Costs of Production Foreign Language ... - Cram.com A) Average total cost is the difference between average variable cost and average fixed cost. B) Marginal cost measures the cost per unit of output associated with any level of production. C) When marginal product rises, marginal cost must also rise. DOCX Cape Economics St. Anthony'S College - Home Construct a table to show the Total Fixed Cost, Total Variable Cost, Total Cost, Average Variable Cost, Average Total Cost and Marginal Cost for garments produced if the manufacturer's Total Fixed Cost is $30.00 and his variable costs consist of wages of $20 per worker per day.[12 marks] 42 refer to figure 11-5. identify the curves in the diagram. 1. If average total cost is $50 and average fixed cost is $15 when output is 20 units, then the firm's total variable cost at that level of output is. Figure 11-7 Figure 11-7 shows the cost structure for a firm. Refer to Figure 11-7. When the output level is 100 units average fixed cost is A. $10. B. $8. C. $5. D.
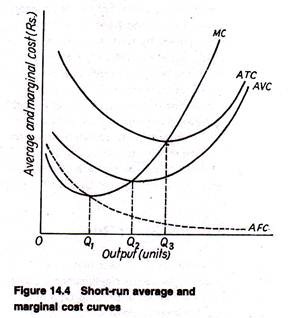
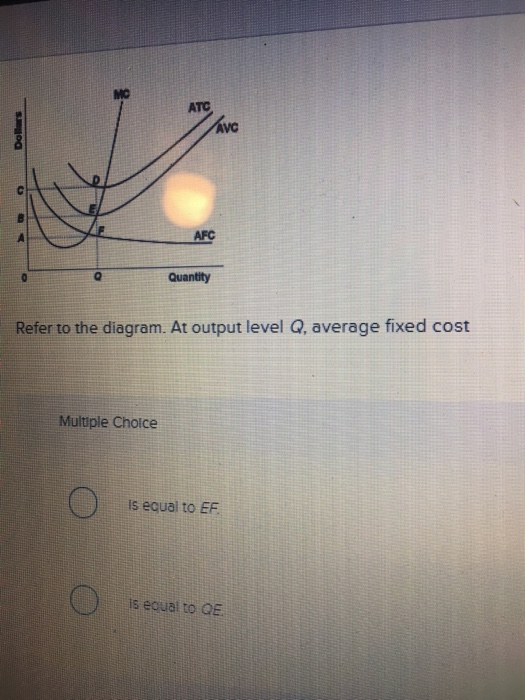
Solved > 6) In a short-run production process ... - ScholarOn 9) Refer to Figure 7.1. At output level Q 1 . A) marginal cost is falling. B) average total cost is falling. C) average variable cost is less than average fixed cost. D) marginal cost is less than average total cost. E) all of the above . 10) Refer to Figure 7.1. At output level Q 2 . A) average fixed cost is increasing. Microeconomics (ECON-2302) Flashcards | Quizlet Refer to the above diagram. At output level Q average fixed cost: ~ is equal to EF. ~ is equal to QE. ~ is measured by both QF and ED. ~ cannot be determined from the information given. 40 refer to the diagram. by producing at output level q ... By producing output level Q: Refer to the above diagram At output level Q total cost is ... C is the correct answer. . 22. Refer to the above diagram. At output level Q average 24. Refer to the above diagram. The vertical distance between ATC and AVC reflects: A) the law of diminishing returns. B) the average fixed cost at each level of output. Short Run Average Costs: Marginal Cost, AFC, AVC, Formulas ... 3. Average Total Cost (ATC) The average total cost is the sum of the average variable cost and the average fixed costs. That is, ATC = AFC + AVC. In other words, it is the total cost divided by the number of units produced. The diagram below shows the AFC, AVC, ATC, and Marginal Costs (MC) curves: It is important to note that the behaviour of ...
Microeconomics: Trivia Questions On Production And Cost ... Scenario 2: The production function for earthquake detectors (Q) is given as follows:Q = 4K 1/2 L 1/2 , where K is the amount of capital employed and L is the amount of labor employed.The price of capital, P K, is $18 and the price of labor, P L, is $2Refer to Scenario 2.Suppose that in order to produce Q=48 detectors 16 units of labor and 9 units of capital were being used. PDF Practice Business and Cost - Mount Saint Mary College A. all possible levels of output. B. 10 to 30 units of output. C. 30 to 60 units of output. D. all outputs greater than 40. 22. Refer to the above diagram. For output level Q, per unit costs of Bare: A. unattainable and imply the inefficient use of resources. B. unattainable, given resource prices and the current state of technology. Question : Figure 11-7 Figure 11-7 shows the cost ... Figure 11-7 Figure 11-7 shows the cost structure for a firm. 31) Refer to Figure 11-7. When the output level is 100 units, average fixed cost is A) $10. B) $8. C) $5. D) This cannot be determined from the diagram. 32) Refer to Figure 11-7. When output level is 100, what is the total cost of production? A) $20 Refer To The Diagram. At Output Level Q Total Cost Is ... Refer to the Diagram. at Output Level Q total Cost is: profit maximization to obtain the profit maximizing output quantity we start by recognizing that profit is equal to total revenue tr minus total cost tc given a table of logic gate in electronics a logic gate is an idealized or physical device implementing a boolean function that is it performs a logical operation on one or more
Do You Have Enough Knowledge On Microeconomics ... - ProProfs Scenario 2: The production function for earthquake detectors (Q) is given as follows: Q = 4K 1/2 L 1/2, where K is the amount of capital employed and L is the amount of labor employed.The price of capital, P K, is $18 and the price of labor, P L, is $2 Refer to Scenario 2.Suppose that in order to produce Q=48 detectors 16 units of labor and 9 units of capital were being used.
revcosts change in average total cost which results from producing one more unit of output. 10. Assume that in the short run a firm is producing 100 units of output, has average total costs of $200, and average variable costs of $150.
At output level Q, total fixed cost is equal to ____. a ... Answer to: At output level Q, total fixed cost is equal to ____. a. 0BEQ. b. BCDE. c. 0BEQ - 0AFQ. d. 0CDQ. By signing up, you'll get thousands of...
Question 56 Refer to the diagram At output level Q total ... Question 56 Refer to the diagram At output level Q total fixed cost is 0BEQ BCDE from ECON 150 at Brigham Young University, Idaho
Cost-Output Relationship - MBA Knowledge Base Total cost is the actual money spent to produce a particular quantity of output. Total Cost is the summation of Fixed Costs and Variable Costs. TC=TFC+TVC Up to a certain level of production Total Fixed Cost i.e., the cost of plant, building, equipment etc, remains fixed.
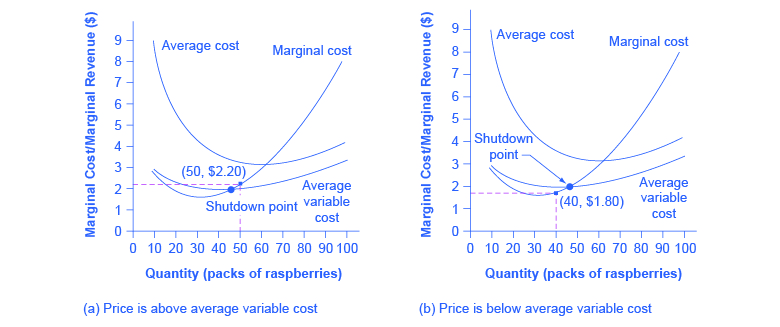
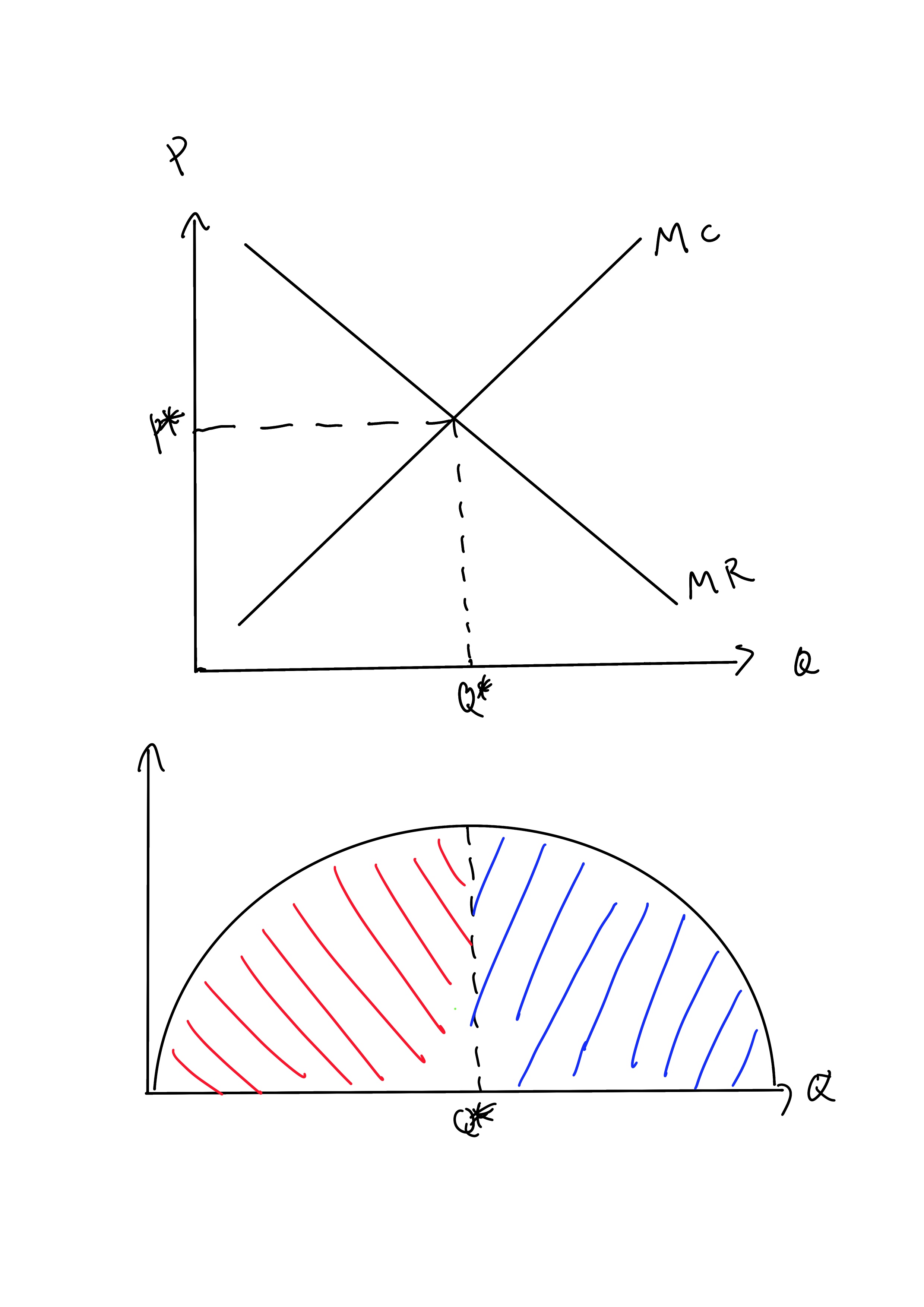
Answered: Refer to the diagram to the right which… | bartleby ASK AN EXPERT. Business Economics Q&A Library Refer to the diagram to the right which shows the demand and cost curves facing a monopolist. Suppose the monopolist represented in the diagram to the right produces positive output. What is the profit maximizing/loss- minimizing output level? O A. 880 units O B. 630 units Oc. 850 units O D. 800 units.
Solved Refer to the above diagram. At output level Q total ... Business; Economics; Economics questions and answers; Refer to the above diagram. At output level Q total fixed cost is: A. 0BEQ. B. BCDE. C. 0BEQ, -0AFQ.
(Get Answer) - Did I do this correctly? ATC AVC Dollars D ... MC ATC Dollars AVC 0 UO - AFC D Quantity Refer to the above diagram. The vertical distance between ATC and AVC reflects: o marginal cost at each level of output. o the average fixed cost at each level of output. o the presence of economies of scale....
ECON 202 Blanchard Exam 2 - Subjecto.com Refer to the data. At 6 units of output, total fixed cost is ____ and total cost is ____. a. $25; $50 b. $50; $300 c. $100; $200 d. $150; $300. d. $150; $300. When a firm is maximizing profit, it will necessarily be: a. maximizing profit per unit of output b. maximizing the difference between total revenue and total cost. c. minimizing total cost
DOC Microeconomics, 7e (Pindyck/Rubinfeld) - NURI YILDIRIM'S ... The average total cost of a given level of output is the slope of the line from the origin to the total cost curve at that level of output. ... Refer to Figure 7.1. The diagram above contains _____ cost curves. A) short run . B) intermediate run ... At output level Q2 . A) average fixed cost is increasing. B) average variable cost equals ...
Chapter 6: Price Elasticity of Demand Refer to the above diagram. At output level Q average fixed cost: 1. is equal to EF. 2. is equal to QE. 3. is measured by both QF and ED. 4. cannot be determined from the information given. ... Refer to the above data. The average total cost of producing 3 units of output is: 1. $14. 2. $12. 3. $13.50. 4. $16. 11.
Classification of Fixed Costs (With Diagram) As we have seen above that the total cost is made up of both the fixed cost and the variable cost. They are represented in the diagram given below—here OX and OY are the two axes; along OX is represented the quantity produced and along OY the cost. FC, a single horizontal line, represents the fixed cost and the area above it the variable cost ...
Various Theories of Cost (With Diagram) - Economics Discussion Average fixed cost is the total fixed cost divided by the number of units of output produced. Thus: Since, total fixed cost is a constant quantity, average fixed cost will steadily fall as output increases, thus, the average fixed cost curve slopes downward throughout the length. It can be shown with the help of a figure 5.
Type: T... - Martinsville Indiana Computer Repair - Facebook 176. Refer to the above diagram. For output level Q, per unit costs of C are: A) unobtainable and imply the inefficient use of resources. B) unobtainable, given resource prices and the current state of technology. C) obtainable, but imply the inefficient use of resources. D) obtainable and imply that resources are being combined efficiently ...



/diseconomies_of_scale_final-db85c494049d42aca10deb37e214a013.png)




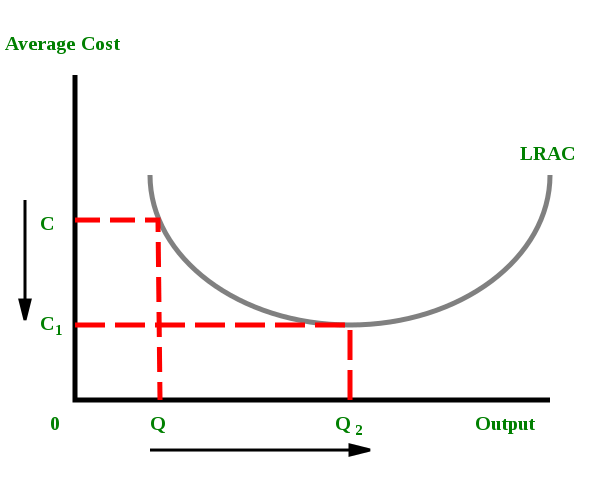
/MinimumEfficientScaleMES2-c9372fffba0a4a1ab4ab0175600afdb6.png)










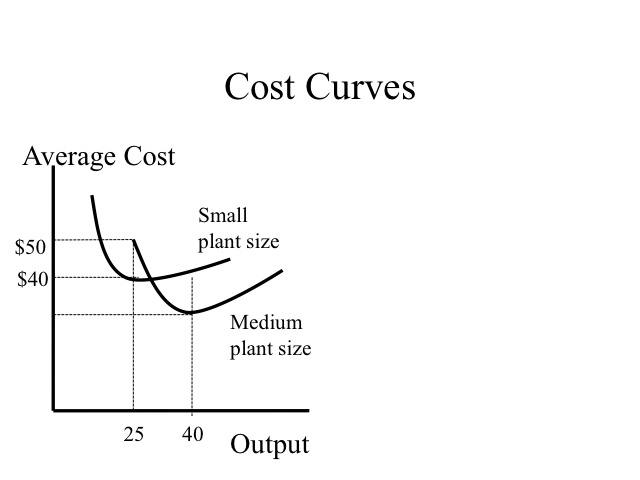


0 Response to "44 refer to the diagram. at output level q, total fixed cost is"
Post a Comment