44 profit maximization in the cost curve diagram
Profit Maximization In The Cost Curve Diagram On time Delivery. 5. Have routine homework and academic assignments completed at affordable prices. Give us your assignments Profit Maximization In The Cost Curve Diagram and a subject matter expert will get it done quickly and painlessly. Better grades can be yours without stress! Client #2423522. Solved 4. Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram ... Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram Suppose that the market for dress shirts is a competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm operating in this market. Hint: After placing the rectangle on the graph, you can select an endpoint to see the coordinates of that point.
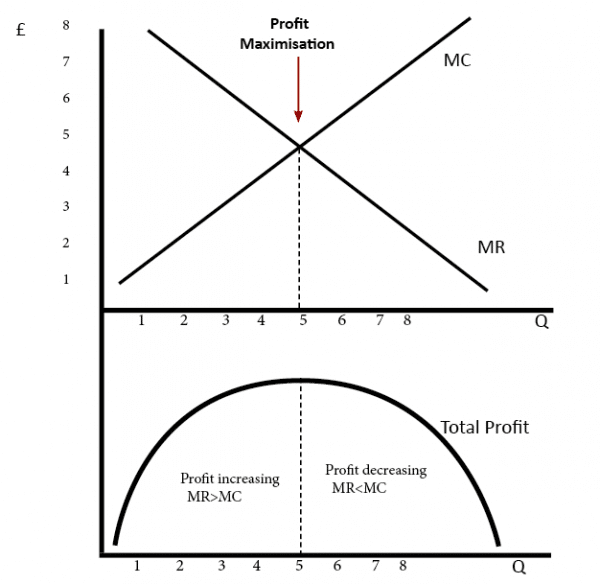
Profit Maximisation - Economics Help Profit = Total Revenue (TR) - Total Costs (TC). Therefore, profit maximisation occurs at the biggest gap between total revenue and total costs. A firm can maximise profits if it produces at an output where marginal revenue (MR) = marginal cost (MC) Diagram of Profit Maximisation To understand this principle look at the above diagram.
Profit maximization in the cost curve diagram
EOF Profit Maximization for a Monopoly | Microeconomics The total cost curve is upward-sloping. Profits will be highest at the quantity of output where total revenue is most above total cost. The profit-maximizing level of output is not the same as the revenue-maximizing level of output, which should make sense, because profits take costs into account and revenues do not. Unit 15 Inflation, unemployment, and monetary policy - CORE Firms raise their prices to protect their profit margins when the cost of imported oil rises. Firms across the economy will behave this way so the price level will rise. This reduces the real wage of employees, so the price-setting curve shifts down (to see how firms set their prices following an oil price rise, see the Einstein at the end of this section). At the initial employment level this ...
Profit maximization in the cost curve diagram. Profit maximization - Wikipedia There would be no effect on the total revenue curve or the shape of the total cost curve. Consequently, the profit maximizing output would remain the same. This point can also be illustrated using the diagram for the marginal revenue-marginal cost perspective. A change in fixed cost would have no effect on the position or shape of these curves. Profit maximization (video) | Khan Academy Profit maximization. AP.MICRO: CBA‑2 (EU) , CBA‑2.D (LO) , CBA‑2.D.1 (EK) Transcript. Learn about the profit maximization rule, and how to implement this rule in a graph of a perfectly competitive firm, in this video. Profit Maximization In The Cost Curve Diagram Aplia Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram Consider a competitive market for shirts. The following graph shows the. labeled graph; makes sure you indicate where the optimal consumption now 3 ($5) or $15 and the price of good Y is now 3($10) or $30), the budget line Giffen goods are a type of goods whose demand curve is an upward sloping line. As shown in Figure 3 profit is the difference between ... As shown in Figure 3 profit is the difference between total revenue and total from MATH 102 at University of Iowa
Profit Maximization In The Cost Curve Diagram Aplia Answers Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram Suppose that the market for black sweaters is a competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm operating in this market. In the short run, at a market price of $15 per sweater, this firm will choose to 97% (30). Question: Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram. Utility Maximization Problem Questions and Answers - Study.com Get help with your Utility maximization problem homework. Access the answers to hundreds of Utility maximization problem questions that are explained in a … 4. profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram Q&A 4. profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram Answer In a competitive market individual price does not influence the market. Hence it is a horizontal line. Price remains equal to marginal revenue and average revenue. In short run to maximise profit firm chooses that unit to produce where price is equal to marginal cost. Profit Maximization In The Cost Curve Diagram Aplia Answers Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram. Suppose that the market for air fresheners is a competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost curves. graph, and every Learning-By-Doing example to make sure the text was as clear as pos- sible. (b) For this linear demand curve, we can find the price .
Profit Maximization Model of a Firm (With Diagram) Profit Maximization Model of a Firm (With Diagram) ... TC curve depicts total economic costs at different levels of output. It will be seen from the upper part of Fig.2.1 at OM level of output, total revenue equals total economic costs and therefore at this level of output the firm is just breaking even. ... In the lower part of Figure 2.1 we ... Isoquant - Wikipedia Isoquant vs. Indifference Curve. While an indifference curve mapping helps to solve the utility-maximizing problem of consumers, the isoquant mapping deals with the cost-minimization and profit and output maximisation problem of producers. Indifference curves further differ to isoquants, in that they cannot offer a precise measurement of utility, only how it is relevant to a … The Production Process (With Diagram) - Economics Discussion Because all inputs have a cost, the long-run concept of returns to scale has significant implications for the behaviour of the long-run cost curve, and these results are shown in panels (a’), (b’), (c’) in Fig. 13.15. We shall deal more completely with the linkage between returns to scale and long-run costs. Here, Fig. 13.15 highlights the nature of the inverse relationship … Assisting students with assignments online - Success Essays Get 24⁄7 customer support help when you place a homework help service order with us. We will guide you on how to place your essay help, proofreading and editing your draft – fixing the grammar, spelling, or formatting of your paper easily and cheaply.
Welfare economics - Wikipedia In the diagram below, the curve MN is a social utility frontier. Point D corresponds with point C from the earlier diagram. Point D is on the social utility frontier because the marginal rate of substitution at point C is equal to the marginal rate of transformation at point A. Point E corresponds with point B in the previous diagram, and lies inside the social utility frontier …
Profit maximization in the cost curve diagram - imaneguly Profit maximization in the cost curve diagram suppose that the market for cashmere sweaters is a competitive market. It is an economic profit just high enough to keep a firm engaged in its current activity. Profit maximization in the cost curve diagram suppose that the market for candles is a competitive market.
Solved 4. Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram ... Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram Suppose that the market for black leather purses is a competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm operating in this market.
Profit Maximization In The Cost Curve Diagram Profit Maximization In The Cost Curve Diagram. online payment process is 100% confidential and secure. Once you place your. Profit Maximization In The Cost Curve Diagram. order, our writer will start working on your paper. However, the cost of your essay can vary depending upon the academic level, the number of required pages, and the deadline.
Top 3 Theories of Firm (With Diagram) - Economics Discussion The total cost curve is always non-linear and has got nothing to do with the market structure. The slope of the revenue curve depends on elasticity of demand and is crucially dependent on the market structure. Since most real life markets are imperfectly competitive we assume non-linear total revenue function, too. Subtracting the TC curve from the TR curve we derive the total net …
Profit Maximization In The Cost Curve Diagram Profit Maximization In The Cost Curve Diagram, Transgender Essay Introduction, Esl Dissertation Hypothesis Editor Service Online, Convert Cv To Resume Service. Profit Maximization In The Cost Curve Diagram. 1. Support. 24h CHAT ONLINE. 82%. Customer #7263. Subscribe to our newsletter
Maximizing Profit and the Average Cost Curve - YouTube Being able to predict your company's profit is a very useful tool. In this video, we introduce the third concept you need to maximize profit — average cost. ...
Monopoly Production and Pricing Decisions and Profit ... Profit Maximization. In traditional economics, the goal of a firm is to maximize their profits. This means they want to maximize the difference between their earnings, i.e. revenue, and their spending, i.e. costs. To find the profit maximizing point, firms look at marginal revenue (MR) – the total additional revenue from selling one additional unit of output – and the marginal cost (MC ...
Profit-Maximising Behaviour of a Firm (With Diagram) Profit-Maximising Behaviour of a Firm (With Diagram) The following points highlight the top two approaches to explain the profit maximising behaviour of a firm. Approach # 1. Equilibrium of a Firm—The Total Revenue and Total Cost Approach: Profit becomes maximum irrespective of the market situation, when the difference between total revenue ...
Profit Maximization In The Cost Curve Diagram of any mistakes. Each Profit Maximization In The Cost Curve Diagramessay is formatted according to the required academic referencing style, such as APA, MLA, Harvard and Chicago. Thus, being written and edited by our professionals, your essay will achieve perfection. Our writing staff is working to meet your needs and
Unit 15 Inflation, unemployment, and monetary policy - CORE Firms raise their prices to protect their profit margins when the cost of imported oil rises. Firms across the economy will behave this way so the price level will rise. This reduces the real wage of employees, so the price-setting curve shifts down (to see how firms set their prices following an oil price rise, see the Einstein at the end of this section). At the initial employment level this ...
Profit Maximization for a Monopoly | Microeconomics The total cost curve is upward-sloping. Profits will be highest at the quantity of output where total revenue is most above total cost. The profit-maximizing level of output is not the same as the revenue-maximizing level of output, which should make sense, because profits take costs into account and revenues do not.
EOF

0 Response to "44 profit maximization in the cost curve diagram"
Post a Comment