43 molecular orbital diagram for f2
Molecular Orbital Diagrams simplified. Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The first major step is understanding the difference between two major theories: Valence Bond Theory and Molecular Orbital Theory. Valence bond (VB) theory gave us a qualitative picture of chemical bonding, which was useful for predicting the shapes of molecules, bond strengths, etc. It fails to describe some bonding situations accurately because it ignores the wave nature of the electrons.
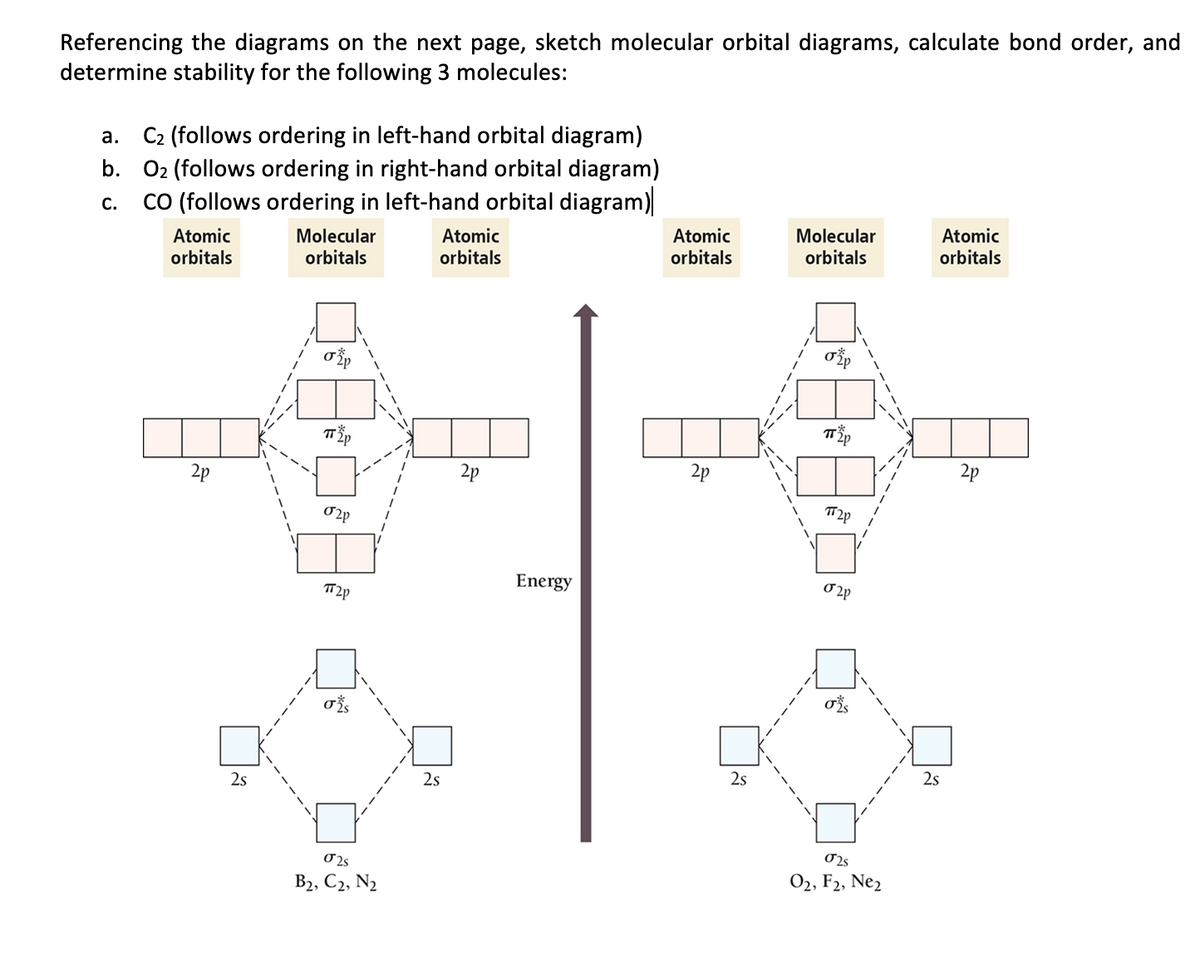
Before we can draw a molecular orbital diagram for B₂, we must find the in-phase and out-of-phase overlap combinations for boron's atomic orbitals. The video below describes how to generate molecular orbital diagrams for B₂ and other diatomic molecules from Row 2 elements of the...
Molecular orbital diagram for f2
The Lewis theory of chemical bonding helps us visualize the arrangement of atoms—how they are attached or bonded—in molecules. The valence electrons in each atom are the ones that participate in the bonding, and hence they are the only ones displayed in the Lewis structures. It is to be noted though that this theory about the electronic structure is quite primitive and most limited. In a typical Lewis structure, each valence electron is represented as a dot, and a covalent bond between two atoms (formed as a result of sharing of two electrons) is represented as a line. Several atoms tend to seek eight electrons in their valence shell through chemical bonding; this is referred to as the octet rule and is reflected in the Lewis structure of a molecule. Hydrogen is an exception, though; it seeks a duplet, not octet, because it has only one electron in its K shell, and thus needs only one more to achieve the maximum capacity of K shell. Noble gases already have completely filled valance... • The following slide illustrates the relative energies of the molecular orbitals compared to the original atomic orbitals. • Because the energy of the two electrons is lower than the energy of the individual atoms, the molecule is stable. Figure 9.26: (a) The molecular orbital energy-level diagram for the... Feb 03, 2022 · The orbital diagram for a diatomic molecule is. To find the bond order, add the 15 electrons in the molecular orbitals (the blue-colored energy levels in the diagram) one at a time until you have used them up. They completely fill all the orbitals except the highest-energy antibonding sigma 2p orbital.
Molecular orbital diagram for f2. The molecular orbital energy diagram predicts that He2 will not be a stable molecule, since it has equal numbers of bonding and antibonding Eight possible homonuclear diatomic molecules might be formed by the atoms of the second period of the periodic table: Li2, Be2, B2, C2, N2, O2, F2, and Ne2. For example, an ns/ns overlap for a homonuclear diatomic molecule gives rise to a partial MO diagram like this: and an np/np overlap for O2 and F2 gives: So, the full MO diagram is: Thus, the valence electron configuration is: (σ2s)2(σ* 2s)2(σ2pz)2(π2px)2(π2py)2(π* 2px)2(π* 2py)2. Answer link. 36 Molecular Orbital Theory Diatomic molecules: MO diagrams for Li2 to F2 2s-2pz mixing Remember that the separation between the ns and np orbitals increases with increasing atomic number. This means that as we go across the 2nd row of the periodic table, the amount of mixing decreases... The molecular orbital diagram representing this order of energy levels is shown in fig. This kind of mixing of orbitals or symmetry interaction is not applicable for O2 and F2 molecule formation because of larger energy gap between 2s and 2p orbitals for these atoms.
molecular orbital diagram for F2. number of elections in the sigma*2p molecular orbital is. their molecular orbital diagrams are more symmetrical than those of homonuclear diatomic molecules. which of the following statements about nitrogen oxide, NO, is FALSE. The orbital diagram for a diatomic molecule is. To find the bond order, add the 15 electrons in the molecular orbitals (the blue-colored energy levels in the diagram) one at a time until you have used them up. They completely fill all the orbitals except the highest-energy antibonding sigma 2p orbital. Click here to get an answer to your question ✍️ 37. Draw molecular orbital diagram for F2 molecule. Also, give its electronic configuration, bond order ... 1. Sketch the qualitative molecular orbital diagram for XeF2. The molecule is linear and symmetric. Assume the valence 5s-orbitals of Xe are sufficiently Determine the primary MOs that determine the bond order. Compare the general features of your MO diagram to the MO diagram for [F-H-F]...
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms. Answer (1 of 6): Here is the solution, > * For O2 molecule, > * For F2 molecule, Thanks for reading. For the ion F2+:a) Draw the molecular orbital diagram.b) Calculate the bond order.c) Would this ion exist?d) Write the electron configuration of the ion.————... - MO diagrams for Inorganic complexes. • It is a waste of both the lecturers and students time if the tutorial to ends up being a lecture covering questions. 5. An introduction to Molecular Orbital Theory.
Molecular orbital diagrams are diagrams of MO energy levels, shown as short horizontal lines in the center. Atomic orbitals (AO) energy levels are shown Symmetry also allows for overlap between the H 1s and F 2pz orbitals, and these two atomic orbitals have a small energy separation; they therefore...
Molecular orbital theory uses group theory to describe the bonding in molecules; it comple-ments and extends the introductory bonding models in Chapter 3 . In such interactions are so weak, we will not include them in other molecular orbital. energy level diagrams. Additional labels describe the orbitals.
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular.
The molecular orbital diagram for an O2 molecule would therefore ignore the 1s electrons on both oxygen atoms and concentrate on the interactions Experiments have shown that O2 and F2 are best described by the model in the figure above, but B2, C2, and N2 are best described by a model that...
Draw the molecular orbital diagram for F2 ground state.
In molecular orbital (MO) approach - overlap orbitals for the whole molecule -bonding is therefore DELOCALISED. We will look first at DIATOMIC MOLECULES and only later move on to POLYATOMIC MOLECULES. Molecular Orbital Energy Level Diagram for a Heteronuclear Diatomic.
I'm trying to build a molecular orbital diagram for BF3 and I'm running into problems with irreducible representations on the F side. 2s for B has an irreducible representation of A1. 2p for B has an irreducible representation of E' and A''2. 2s for F considered non bonding.
Draw molecular orbital diagram for F 2 molecule. Also, gives its electronic configuration, bond order and magnetic property. Hint: The Molecular Orbital Theory (MOT) explains the formation of the molecule in a better way than Valence Bond Theory (VBT). The bond order calculations are feasible using MOT and so is the description of electronic ...
Figure 4.10.1: Molecular Orbital Energy-Level Diagrams for Homonuclear Diatomic Molecules.(a) For F2, with 14 valence electrons (7 To obtain the molecular orbital energy-level diagram for O2, we need to place 12 valence electrons (6 from each O atom) in the energy-level diagram shown in...
Draw the molecular orbital (MO) electron diagram for the F2 molecule. Be sure your diagram contains all of the electrons in the molecule, including any core electrons. Question: Draw the molecular orbital (MO) electron diagram for the F2 molecule. Be sure your diagram contains all of the electrons in the molecule, including any core electrons.
The filled molecular orbital diagram shows the number of electrons in both bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals. Eight possible homonuclear diatomic molecules might be formed by the atoms of the second period of the periodic table: Li2, Be2, B2, C2, N2, O2, F2, and Ne2.
Download scientific diagram | Qualitative molecular orbital diagram of HF −. The 2σ orbital, coming from the F 2 s orbital, is nonbonding. From this diagram, the bond order of HF − is calculated to be 0.5. from publication: Identification of a Simplest Hypervalent Hydrogen Fluoride Anion in Solid Argon...
A bare molecular orbital diagram is presented and you must drag the correct orbitals and labels onto the diagram. The diagram is then completed by filling the energy levels with the correct number of electrons. The following molecules are currently available: Molecules of the First Row
Molecular Orbital Theory: To simplify things, we will consider the interaction of the orbitals containing valence electrons to create molecular orbitals. Have you ever thought about how sigma and pi bonds are formed? What is the difference between diamagnetic and paramagnetic behaviour?
Molecular orbital diagram and bond order of fluorine molecule . Fluorine molecule is formed by the combination of atomic orbitals of two fluorine atoms, each having nine electrons, thus making 18 electrons.; These 18 electrons are filled in various molecular orbitals, in the increasing order of their energies (aufbau principle) and on the basis of Hund's rule and Pauli's exclusion principle as ...
Figure 9-2 Molecular orbital (MO) diagram for the combination of the 1s atomic orbitals on two identical atoms (at the left) to form two MOs. You should now work Exercises 19 and 20. The Fluorine Molecule, F2. Each fluorine atom has 9 electrons, so there are 18 electrons in F2.
The diagram shows how the molecular orbitals in lithium hydride can be related to the atomic orbitals of the parent atoms. Notice that the relative energies of the 2p-derived σ and π bonding molecular orbitals are reversed in O2 and F2. This is attributed to interactions between the 2s orbital each atom...
Orbitals and molecular representation atomic orbitals. While Lewis diagrams and energy level structures can show connectivity and energy relationships of mol-ecules, they do not show the shape of the molecules. In picture 1 we show the molecular orbital structure of F2.
Nov 01, 2021 · When we make the molecular orbital energy level diagram of f2 molecule then, we will get this configuration: 1σs 2, 1σ*s 2, 2σs 2, 2σ* 2, σ2pz 2, π2p x 2, π2p y 2, πp x * 2, π2p y * 2. From this electronic configuration, we can see that there are a total of ten bonding molecular orbitals and eight antibonding molecular orbitals.
When two fluorine atoms bond, the sigma(2p) bonding molecular orbitals are lower in energy than the pi(2p) bonding orbitals.F2(2+) has a bond order of 2, so ...
This video is about MO Diagram #2 - F2
Feb 03, 2022 · The orbital diagram for a diatomic molecule is. To find the bond order, add the 15 electrons in the molecular orbitals (the blue-colored energy levels in the diagram) one at a time until you have used them up. They completely fill all the orbitals except the highest-energy antibonding sigma 2p orbital.
• The following slide illustrates the relative energies of the molecular orbitals compared to the original atomic orbitals. • Because the energy of the two electrons is lower than the energy of the individual atoms, the molecule is stable. Figure 9.26: (a) The molecular orbital energy-level diagram for the...
The Lewis theory of chemical bonding helps us visualize the arrangement of atoms—how they are attached or bonded—in molecules. The valence electrons in each atom are the ones that participate in the bonding, and hence they are the only ones displayed in the Lewis structures. It is to be noted though that this theory about the electronic structure is quite primitive and most limited. In a typical Lewis structure, each valence electron is represented as a dot, and a covalent bond between two atoms (formed as a result of sharing of two electrons) is represented as a line. Several atoms tend to seek eight electrons in their valence shell through chemical bonding; this is referred to as the octet rule and is reflected in the Lewis structure of a molecule. Hydrogen is an exception, though; it seeks a duplet, not octet, because it has only one electron in its K shell, and thus needs only one more to achieve the maximum capacity of K shell. Noble gases already have completely filled valance...

0 Response to "43 molecular orbital diagram for f2"
Post a Comment