42 ray diagram for convex mirrors
Convex mirror: The convex mirror is the curved mirror where the reflective surface bulges out towards the position of the light source. Image Formation by Concave and Convex Mirrors: Convex Mirror Ray Diagram: When an object is placed at infinity a virtual image will be formed at the focus... A curved mirror is a mirror with a curved reflecting surface. The surface may be either convex (bulging outward) or concave (recessed inward).
Convex Mirrors - Diverging Rays are reflected and diverge, giving the illusion that the rays originated inside the mirror. Diverging mirrors always produce virtual images that are smaller then the object. Ray Diagrams for Convex Mirrors Incident Ray Reflected Ray Parallel to principal axis Reflects out...
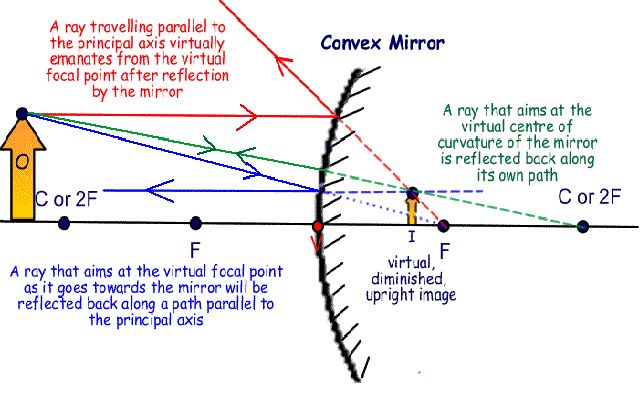
Ray diagram for convex mirrors
We know that not only a plane mirror produces an image of an object in front of it - a convex spherical mirror does, too! You can also explore how the image is constructed, by turning on and off the principal rays. These are the three special rays that are used for the construction of the image. For a Convex Mirror, The focus and center of curvature is on the right side of the mirror. So, there will only be 2 cases. They are. Object is Placed at Infinity. Object is Placed between Principal axis and Infinity. Case 1 - Object is Placed at infinity. This Demonstration lets you visualize the ray diagrams for concave and convex spherical mirrors. By manipulating the object and mirror locations, you can create real or virtual images. The ray parallel to the principal axis and the ray that hits the center of the mirror are drawn.
Ray diagram for convex mirrors. The convex mirror image is always a virtual image, standing like an object, and looks smaller than the real thing. It is used in car rearview mirrors and surveillance mirrors because If the object is outside the focus of the mirror: It is a real image, which is enlarged or reduced by the distance from the mirror. A ray diagram for the case in which the object is located in front of the focal point is shown in the diagram at the right. The ray 1 or th... All ray diagrams for convex mirrors look essentially like the image below, with the placement of the image somewhere between the mirror and the focal point. The ray tracing for convex mirrors follow this general sketch. Two rays leave the tip of the object, one approaches the mirror parallel and... Ray Diagrams for Concave Mirrors. • image is formed where the outgoing rays cross • two principal rays are sufficient to find image Concave mirrors: Shaving and makeup mirrors Solar cookers Satellite dishes (for EM waves). Convex mirrors: Passenger side rear-view mirrors Anti-shoplifting...
Understanding ray diagrams will become easier if you learn more about terms used in ray diagram and image formed by concave and convex mirror. 5. Any incident ray which is not parallel to the principal axis is also reflected diagonally. Types of Spherical Mirror: Concave and Convex Mirror. These ray diagrams depend on the position of the object. General rules for image formation using ray diagrams: Any ray of light that passes through the mirror, is always In case, of a convex mirror, there are only two possible positions where the object can be positioned and an image can be formed. As the ray diagram shows, the image for a convex mirror is virtual, and upright compared to the object. A convex mirror will reflect a set of parallel rays in all directions; conversely, it will also take light from all directions and reflect it in one direction, which is exactly how it's used in stores and cars. Convex lens forms real image because of positive focal length and concave lens forms virtual image because of negative focal length. In mirrors, images are formed through reflection but lenses form images through refraction. This is explained with the help of ray diagrams as follows
A convex mirror forms a virtual image.The cartesian sign convention is used here. Using a ray parallel to the principal axis and one incident upon the center of the mirror, the position of the image can be constructed by back-projecting the rays which reflect from the mirror. The virtual image that is formed will appear smaller and closer to the mirror than the object. Convex concave ray diagrams. chauber. Mirror ppt. DallasSmith15. Concave mirrors. Abbinaya Helbig. 2. The path of three rays that are known is used construct the diagram. These are:
Rays traveling parallel to the principal axis are reflected and appear to be coming from the principal... Convex mirror used in vehicles: Convex mirrors are commonly used as rear-view mirrors in case of automobiles and vehicles because it can diverge Image Formation By Concave Mirror And Their Ray Diagrams. Two possibilities of the position of the object are possible in the case of a convex mirror... Image formation by spherical mirrors is an interesting topic of the Light chapter. Here along with the ray diagram, you will get the related details like Object position, image position, and nature of the image.
A ray diagram for a convex mirror shows that the image will be located at a position behind the convex mirror. Furthermore, the image will be upright, reduced in size (smaller than the object), and virtual. This is the type of information that we wish to obtain from a ray diagram.
Concave And Convex Mirror: Generally there are 2 types of spherical mirrors - Convex and Concave mirror. In this article, we will discuss what are Concave Mirror and Convex Mirror, how they are formed, Concave and Convex Mirror differences, definitions, examples, ray diagrams, uses, and...
1 Convex Mirrors Center of curvature and focal point both located behind mirror The image for a convex mirror is always virtual and upright also the kind of mirror used on the passenger side of many cars Ray Diagram for Convex Mirror Sign convention remains same REMEMBER focal point...
The Physics Classroom » Curriculum Corner » Reflection and Mirrors » Ray Diagrams for Convex Mirrors The document shown below can be downloaded and printed. Teachers are granted permission to use them freely with their students and to use it as part of their curriculum.
Ray Diagram for Convex Mirror. Terms Used in Convex Mirror Imaging. Incident ray - The ray of light that is incident on the surface. As a security device in supermarkets, grocery stores, and convenient stores since the convex mirror gives a broad view of the area around corners.
"Any incident ray traveling towards a convex mirror such that its extension passes through the focal point will reflect and travel parallel to the principal axis". The purpose of drawing ray diagrams is to find the location, size, direction, and type of image formed by a convex mirror.
Convex spherical mirrors are made from a section of an outer silvered ball. The image formed in a convex mirror is always erect, virtual and diminished in size. Constructing a ray diagram for a convex mirror. A ray travelling parallel to the principal axis virtually emanates from the virtual focal point after...
This physics video tutorial provides the ray diagrams for a concave and convex mirror. It also contains a few examples and practice problems along with the...
Thus the ray diagram of the shaving mirror is same as that of convex lend. For an object kept in front of a convex mirror , ray parallel to principle axis will appear to diverge from the focus while the ray passing through the center of curvature will retrace it's path, the point of intersection will be the point...
Use ray diagrams and the mirror equation to calculate the properties of an image in a spherical mirror. The image in a plane mirror has the same size We can define two general types of spherical mirrors. If the reflecting surface is the outer side of the sphere, the mirror is called a convex mirror.
Let's explore the ray tracing technique to figure out the properties of images when things are kept in front of a concave or a convex mirror.
Ray Diagrams - Concave Mirrors. The Anatomy of a Curved Mirror. Reflection of Light and Image Formation. The diagram below shows two light rays emanating from the top of the object and incident towards the mirror. Describe how the reflected rays for these light rays can be drawn without...
describe ray diagrams for plane, concave, and convex mirrors • describe the characteristics of images including size, orientation, and whether they are real or virtual. In this chapter, you will • draw ray diagrams for plane, concave, and. convex mirrors • interpret ray diagrams to predict the.
Below are the ray diagram rules for convex mirrors, which allow you to predict where the light rays from an object will travel and then focus in the eye of an observer. Rule 1. Take a line from an object parallel to the principal axis and where it touches the convex mirror take another line to the principal focal point. Rule 2.
This Demonstration lets you visualize the ray diagrams for concave and convex spherical mirrors. By manipulating the object and mirror locations, you can create real or virtual images. The ray parallel to the principal axis and the ray that hits the center of the mirror are drawn.
For a Convex Mirror, The focus and center of curvature is on the right side of the mirror. So, there will only be 2 cases. They are. Object is Placed at Infinity. Object is Placed between Principal axis and Infinity. Case 1 - Object is Placed at infinity.
We know that not only a plane mirror produces an image of an object in front of it - a convex spherical mirror does, too! You can also explore how the image is constructed, by turning on and off the principal rays. These are the three special rays that are used for the construction of the image.

0 Response to "42 ray diagram for convex mirrors"
Post a Comment