41 ray diagram for mirror
Ray Diagrams - Concave Mirrors Class 10 Notes | EduRev Dec 04, 2021 - Ray Diagrams - Concave Mirrors Class 10 Notes | EduRev is made by best teachers of Class 10. This document is highly rated by Class 10 students and has been viewed 265 times. Concave and Convex Mirrors - Ray Diagrams... - GeeksforGeeks Used in shaving mirrors: Converging mirrors are most widely used in shaving because they have reflective and curved surfaces. Image Formation By Concave Mirror And Their Ray Diagrams. When the object is kept at infinity: As the parallel rays coming from the object converge at the principal focus...
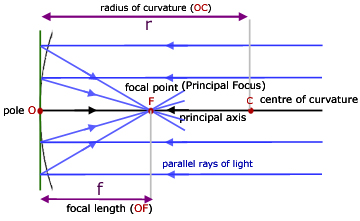
Rules for drawing Ray Diagram in Concave and Convex Mirror ... 23.4.2020 · For a concave mirror , we see that ray passing through focus becomes parallel to principal axis after reflection For a convex mirror, since focus is on the right side, it appears that ray passes through focus, and then it becomes parallel to principal axis Rule 3 - Ray passing through Center of Curvature will follow the same path back after reflection
Ray diagram for mirror
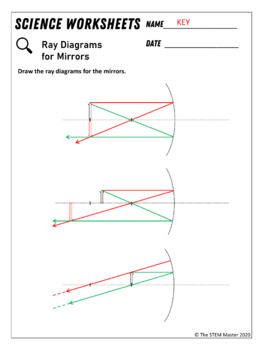
Drawing ray diagrams for plane mirrors - Mini Physics - Learn Physics This is a short tutorial on how to draw ray diagrams for plane mirrors. Click on the images to view a larger version. Initially, we have an object in front of a Lines joining the object to the positions of the reflected rays on the mirror represent the incident rays. Properties of image formed in plane mirror Convex Mirror image formation- Conditions, Ray Diagram, Uses Ray diagrams are necessary for understanding the formation of an image by a convex mirror. For constructing ray diagrams and to learn the image formation, we should consider at least two incident rays coming from the object. RAY DIAGRAMS FOR MIRRORS - ppt download 2 CONCAVE MIRRORS All ray diagrams start with a center line and the mirror. 3 Next, put in the focal point (F) and the center of curvature (C) Note: F is always closer to the mirror 6 RAY DIAGRAM: R > do > f - draw a ray parallel to the center line to the mirror THEN through F - draw a ray through F to...
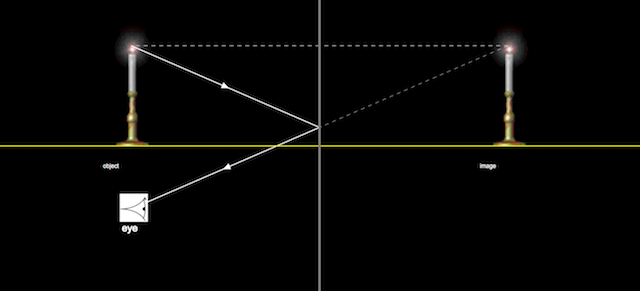
Ray diagram for mirror. Physics Tutorial: Ray Diagrams for Plane Mirrors This section of Lesson 2 details and illustrates the procedure for drawing ray diagrams. Let's begin with the task of drawing a ray diagram to show how Suzie will be able to see the image of the green object arrowin the diagram below. For simplicity sake, we will suppose that Suzie is viewing the image with her left eye closed. Thus, we will focus on how light travels from the two extremities of the object arrow (the left and right side) to the mirror and finally to Suzie's right eye as she sights at the image. The four steps of the process for drawing a ray diagram are listed, described and illustrated below. 1. Draw the image of the object. 2. Pick one extreme on the image of the object and draw the reflected ray that will travel to the eye as it sights at this point. 3. Draw the incident ray for light traveling from the corresponding extreme on the object to the mirror. 4. Repeat steps 2 and 3 for all other extremities on the object. Ray Diagrams - Mirrors - YouTube 121 - Ray Diagram - MirrorsIn this video Paul Andersen explains how ray diagrams can be used to determine the size and location of a reflected image. Ray di... Lesson Explainer: Drawing Ray Diagrams for Concave Mirrors | Nagwa Before starting to draw ray diagrams, it will be useful to first consider a concave mirror as a three-dimensional solid object. A concave mirror is a hollow curved object, like a bowl. A concave mirror is shown in the following figure. Convex Mirror - Ray diagram, Images Formed - with Steps ... 23.4.2020 · Convex Mirror - Ray diagram. Last updated at April 23, 2020 by . For a Convex Mirror, The focus and center of curvature is on the right side of the mirror So, there will only be 2 cases. They are Object is Placed at Infinity Object is Placed between Principal axis and Infinity
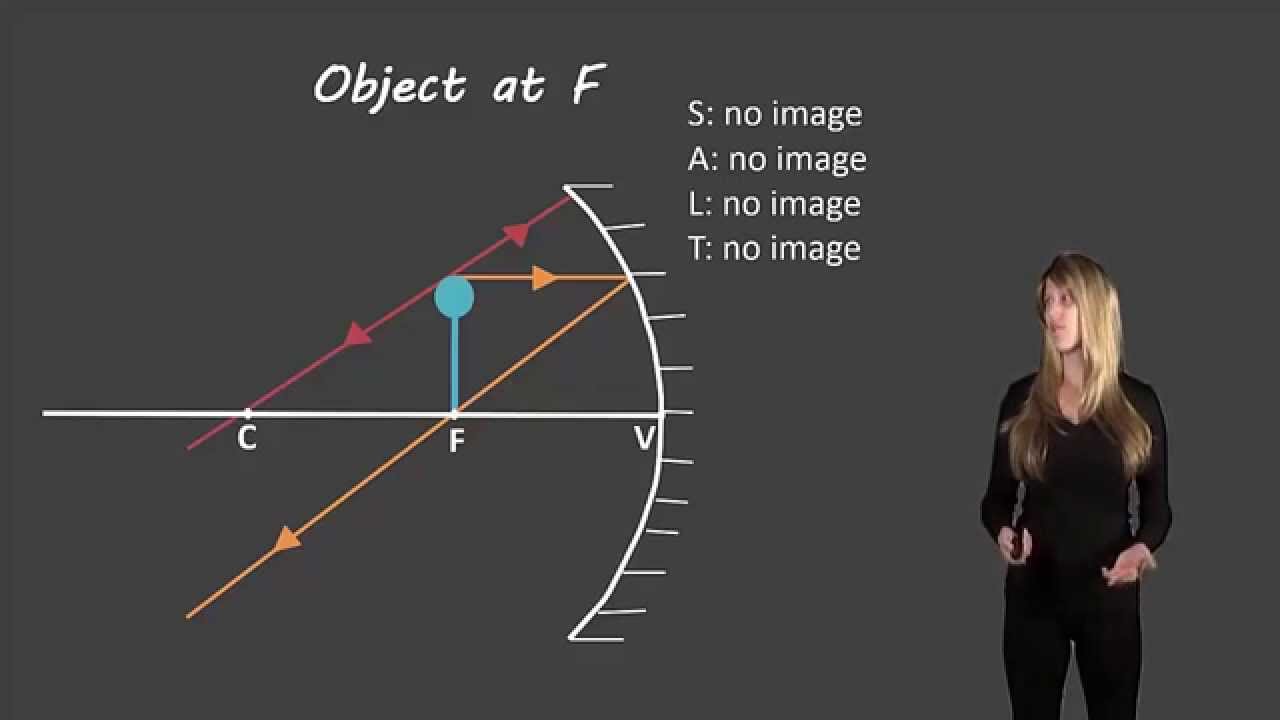
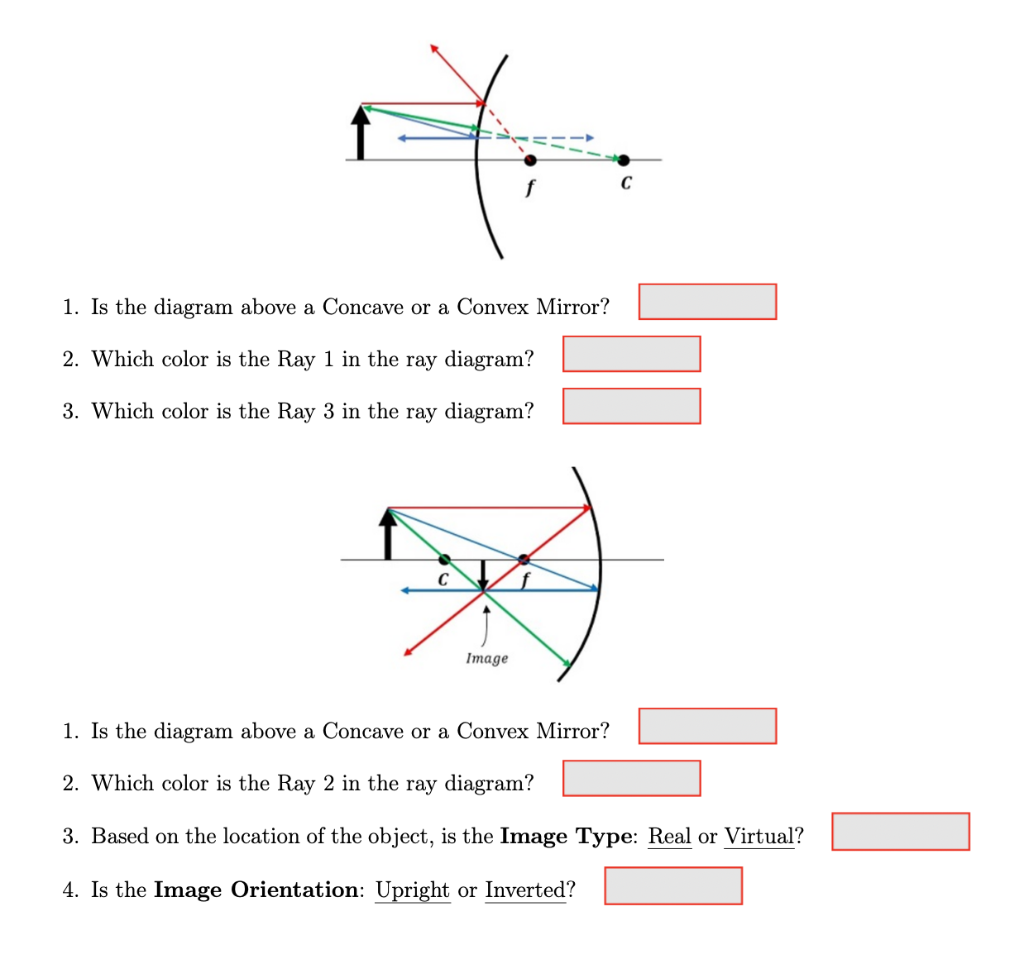
CC | Working with lenses and mirrors: how to draw a ray diagram Ray diagrams can look intimidating, but they don't have to be! In this blog post, we will tackle five examples of ray diagrams. Problem 4: choose the correct ray diagram. Now we have a concave mirror, which can either create a virtual upright image or a real inverted image depending on the... Plane mirror- Definition, Properties and Ray Diagram For flat mirrors, no light rays actually intersect at the point $P'$ (image point) but from the point of view of an observer appears that the light rays originate Now that the basics of image formation using a ray diagram in plane mirrors are reviewed, practice the following example. Example: two mirrors set... Mirrors | Boundless Physics | Ray Diagrams Concave Ray Diagram: This is a ray diagram of a concave mirror. The steps taken to draw are the same as those in a plane mirror. Convex Mirror Ray Diagram: A convex mirror with three rays drawn to locate the image. Each incident ray is reflected according to the Law of Reflection. What is the ray diagram for an object at focus in a concave mirror? Taking two principal rays, the ray diagram below (courtesy of Wikipedia) would be sufficient as an answer. But for emphasis, please consider a third ray emanating from the top of the object (as the other two) and direct it to the POLE of the mirror. The ray would reflect off the mirror following the Firs Law...
Ray Diagram For Convex Mirror - Wiring Diagram Source The ray 1 or the light beam 1 that come to the convex mirror are drawn parallel to the principal axis and touch the upper end of the object... Convex Mirrors. Ray Diagram for Convex Mirror - PDF Free Download Convex Mirrors Center of curvature and focal point both located behind mirror The image for a convex mirror is always virtual and upright compared also the kind of mirror used on the passenger side of many cars Ray Diagram for Convex Mirror Sign convention remains same REMEMBER focal point, f... Ray Diagrams (1 of 4) Concave Mirror - YouTube Shows how to draw ray diagrams and locate the image for concave mirrors. You can see a listing of all my videos at my website, ... Physics Tutorial: Ray Diagrams - Concave Mirrors Ray diagrams have been a valuable tool for determining the path taken by light from the object to the mirror to our eyes. In this section of Lesson 3 The diagram below shows two light rays emanating from the top of the object and incident towards the mirror. Describe how the reflected rays for these...
Concave and Convex Mirrors | Ray Diagram for Convex and Concave... Concave mirror: Concave mirror has a reflecting surface that caves inwards. The concave mirrors essentially converge light to only one prime focus point. This is why they are also known as converging mirrors. These mirrors are used for focusing light and the image that is formed by the concave...
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image by a ... Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image by a concave mirror for an object placed between its pole and focus. State three characteristics of the image.
Draw a ray diagram of a compound microscope. Write the ... Ray diagram of a compound microscope.When the final image is formed at the least distance of distinct vision,For the image formed at infinity, ue = feand By making focal length of the objective small, the magnifying power can be increased.
Convex mirror - Ray diagram rules Below are the ray diagram rules for convex mirrors, which allow you to predict where the light rays from an object will travel and then focus in the eye of an observer. Rule 1. Take a line from an object parallel to the principal axis and where it touches the convex mirror take another line to the principal...
Ray diagram in concave mirrors 1. Ray diagram construction for concave mirrors Presented by Obina Johnson Okeny. 2. Objectives: • To show how rays travel in order to form images Always draw me first I am the Object I am reflected parallel to the principal axis Now let us draw a ray diagram for an object at C Iamtheimage What is...
Ray Diagrams for Mirrors - Hyperphysics Mirror ray tracing is similar to lens ray tracing in that rays parallel to the optic axis and through the focal point are used. A third useful ray is that through the center of curvature since it is normal to the mirror and Move object inside focal length. Change to convex mirror. Ray diagrams for mirrors.
Concave Mirrors And Convex Mirrors - Image Formation, Ray ... Ray diagrams help us trace the path of the light for the person to view a point on the image of an object. Ray diagram uses lines with arrows to represent the incident ray and the reflected ray. It also helps us trace the direction in which the light travels. Plane Mirror vs Spherical Mirrors
Images formed by concave mirror using ray diagram - Class 10... Question 2 The image formed by concave mirror is seen to be real,inverted and of same size.What is the position of the object? Question 3 Where should an object be placed in front of a concave mirror so as to obtain highly enlarged image?
Spherical Mirrors - University Physics Volume 3 Use ray diagrams and the mirror equation to calculate the properties of an image in a spherical mirror. We will concentrate on spherical mirrors for the most part, because they are easier to manufacture than mirrors such as parabolic mirrors and so are more common.
PPT - Ray Diagrams in Concave Mirrors PowerPoint Presentation... Ray Diagrams - . outline. reflection mirrors plane mirrors spherical mirrors concave mirrors convex mirrors refraction. Ray Diagrams - . a ray of light is Diagram of the Elements of the Curved Mirror. 2 Rules for Concave Mirrors: 1. Any incident ray traveling parallel to the principal axis on the way to...
Ray Diagrams for Mirrors - GeoGebra Ray Diagrams for Mirrors. Author: Chris Luke. Topic: Diagrams. Next. Concave and Convex Mirrors. New Resources.
Image Formation by Spherical Mirrors: Videos, Ray Diagrams... Ray diagrams are used to depict the image formation by tracing the path of light rays i.e. incident rays and reflected rays. They are drawn in order for A ray of light passing through the center of curvature of any mirror is reflected back along the same path. Any incident ray which isn't parallel to the...
Curved mirror - Wikipedia A convex mirror or diverging mirror is a curved mirror in which the reflective surface bulges towards the light source. Convex mirrors reflect light outwards, therefore they are not used to focus light. Such mirrors always form a virtual image, since the focal point (F) and the centre of curvature (2F) are both imaginary points "inside" the mirror, that cannot be reached.
Concave Mirror ray diagram – GeoGebra Concave Mirror ray diagram. Author: Ray Tuck. This simulation shows a ray diagram for a concave mirror. Change the object position by dragging the yellow circle. Check the check boxes to show the distances S o and S i; F is the focal point. Light rays are shown in red, extensions to rays are shown as green dashed lines.
Plane Mirror: Definition, Ray Diagram, Uses and Applications Image formation by a plane mirror using a ray diagram. A plane mirror is a mirror that has a flat reflecting surface without any inward or outward curve. A ray of light falling on a plane mirror is reflected at the same angle as the angle of incidence.
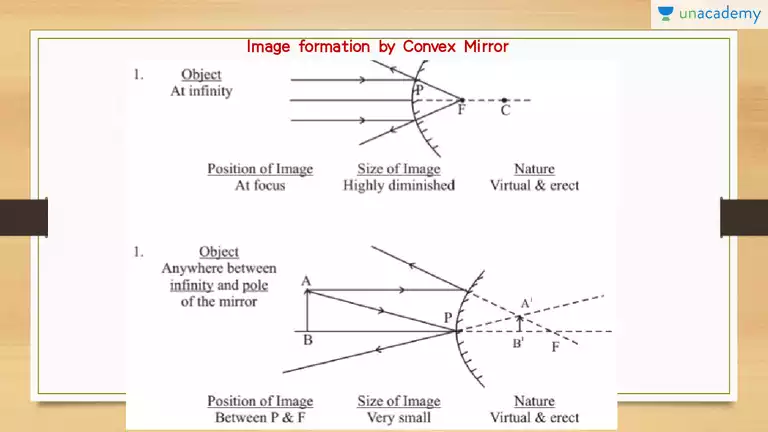
Physics Tutorial: Ray Diagrams - Convex Mirrors In the first section of Lesson 4, we learned that light is reflected by convex mirrors in a manner that a virtual image is formed. We also learned that there are two simple rules of reflection for convex mirrors. These rules represent slight revisions of the two rules given for concave mirrors. The revised rules can be stated as follows: Some students have difficulty understanding how the entire image of an object can be deduced once a single point on the image has been determined. If the object is merely a vertical object (such as the arrow object used in the example below), then the process is easy. The image is merely a vertical line. This is illustrated in the diagram below. In theory, it would be necessary to pick each point on the object and draw a separate ray diagram to determine the location of the image of that point. That would require a lot of ray diagrams as illustrated in the diagram below. Fortunately, a shortcut exists. If the object is a vertical line, then the image is also a vertical line. For our purposes, we will only deal with the simpler situations in which the object is a vertical line that has its bottom located upon the principal axis. For such simplified situations, the image is a vertical line with the lower extremity located upon the principal axis.
Ray Diagrams for Plane Mirrors - Physics Classroom • Ray diagrams are based on the premise that to view an object in a mirror, one must sight along a line at the image of the object. When one does, light travels along that line to your eye. • Ray diagrams can be drawn for all types of mirrors. This video focuses on plane mirrors. Proceure for Drawing Ray Diagram Step 1 Locate the Image:
Ray diagrams mirrors | Видео Light: Ray diagrams for mirrors: Concave mirror part 1Подробнее. concave mirrors ray diagrams #ncertphysics#cbsephysics10thclass#light#refelctionПодробнее. Rules to draw ray diagrams using convex mirrorПодробнее. Ray diagrams of concave mirror in english.Подробнее.
Convex & concave mirror ray diagrams (video) | Khan Academy Let's explore the ray tracing technique to figure out the properties of images when things are kept in front of a concave or a convex mirror.
How to Draw a Ray Diagrams for Convex Mirrors While making ray diagrams, these two rules are important for students. The purpose of drawing ray diagrams is to find the location, size, direction, and type of image formed by a convex mirror. The steps involved in drawing ray diagrams are quite simple and easy to understand.
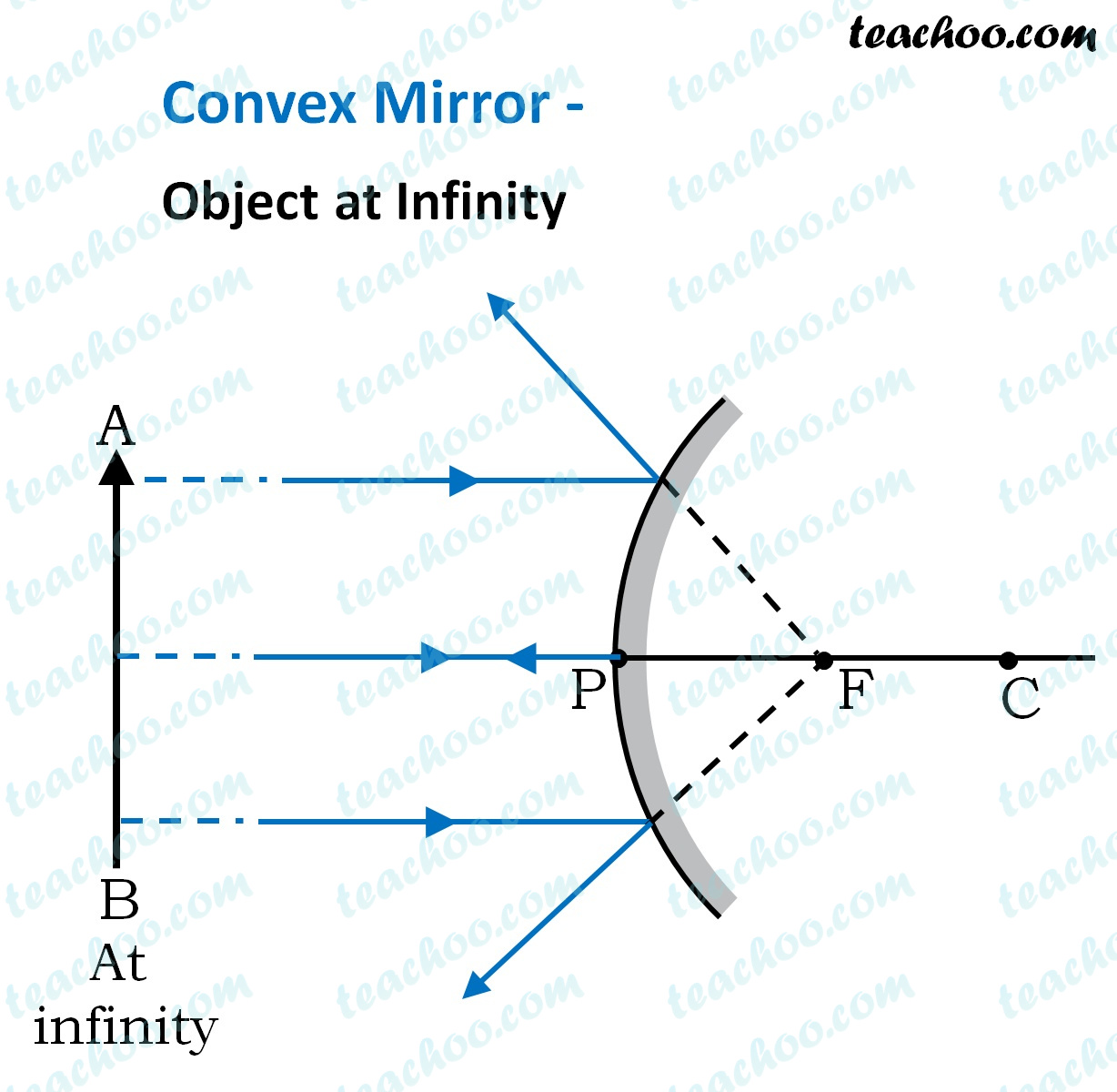
Concave Mirror - Ray diagram, Image Formation, Table For a Concave mirror, object can be kept at different positions. Hence, we take different cases. Case 1 - Object is Placed at infinity. In this Case, Object AB is kept far away from mirror (almost at infinite distance). So, we draw rays parallel to principal axis.
Mirror ray diagrams : Mcat Making a ray diagram takes a LONG time. Here's some mnemonics that'll score you the bulk of the points. For convex lenes and concave mirrors: if object is behind focal point think "Behind the RIM" (real, inverted and magnified)
Ray Diagrams for Images formed by concave & convex mirrors... Image formation by spherical mirrors is an interesting topic of the Light chapter. Here along with the ray diagram, you will get the related details like Object position, image position, and nature of the image.
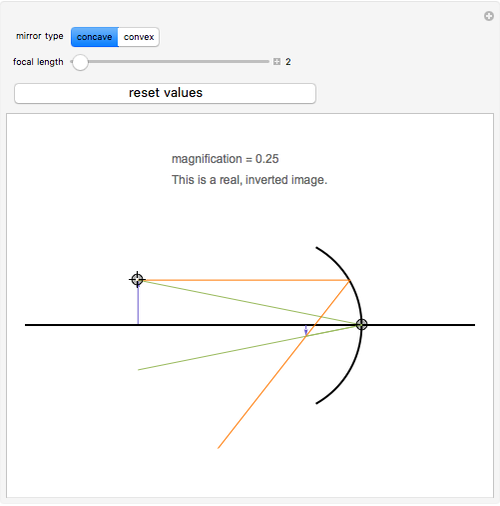
Ray Diagrams for Spherical Mirrors - Wolfram Demonstrations Project This Demonstration lets you visualize the ray diagrams for concave and convex spherical mirrors. By manipulating the object and mirror locations, you can create real or virtual images. The ray parallel to the principal axis and the ray that hits the center of the mirror are drawn.
RAY DIAGRAMS FOR MIRRORS - ppt download 2 CONCAVE MIRRORS All ray diagrams start with a center line and the mirror. 3 Next, put in the focal point (F) and the center of curvature (C) Note: F is always closer to the mirror 6 RAY DIAGRAM: R > do > f - draw a ray parallel to the center line to the mirror THEN through F - draw a ray through F to...
Convex Mirror image formation- Conditions, Ray Diagram, Uses Ray diagrams are necessary for understanding the formation of an image by a convex mirror. For constructing ray diagrams and to learn the image formation, we should consider at least two incident rays coming from the object.
Drawing ray diagrams for plane mirrors - Mini Physics - Learn Physics This is a short tutorial on how to draw ray diagrams for plane mirrors. Click on the images to view a larger version. Initially, we have an object in front of a Lines joining the object to the positions of the reflected rays on the mirror represent the incident rays. Properties of image formed in plane mirror



![18.3 Images Formed by Curved Mirrors [Prev Section] [Next ...](https://ux1.eiu.edu/~cfadd/3050/Adventures/chapter_18/x_18.10.jpg)
















0 Response to "41 ray diagram for mirror"
Post a Comment