45 converging lens ray diagram
Name the lens and draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image. Solution 16. If a lens forms an upright and diminished image of an object placed at its focal point, then it is a concave lens. Question 17. Draw a ray diagram to show how a converging lens is used as a magnifying glass to observe a small object.
Solved 1 Draw The Ray Diagram For A Parallel Beam Of Light Chegg. Explain With A Suitable Diagram How Concave Mirror Converges Parallel Beam Of Light Rays Mark Clearly The Pole Focus And Centre Curvature In This. A Parallel Beam Of Light Is Incident On Diverging Lens Focal Length 12 Cm The Emergent Pes Through Converging 20 Placed Coaxial With It.
It's also called a converging lens because it makes light rays come together (converge). Looking at things through a convex lenses makes them appear bigger—so convex lenses are used in things like magnifying glasses. Another kind of lens curves the opposite way, with the middle thinner than the outside. This is called a concave lens.
Converging lens ray diagram
Draw a ray diagram showing how reflection and refraction produce all these images. (e) Fig. 12 represents a stone S at the bottom of a pond of water. Using the two rays, as shown, complete the ray diagram to show where the image of the stone appears when viewed from E. (f) What is a ''mirage'? Explain with the help of a diagram.
(a) An object is placed 10 cm from a lens of focal length 5 cm. Draw the ray diagrams to show the formation of image if the lens is (i) converging, and (ii) diverging. (b) State one practical use each of convex mirror, concave mirror, convex lens and concave lens.
Concave Mirror Ray Diagram Worksheet Answers. Bernadina Bailly. February 8, 2021. The method is applied to the task of drawing a ray diagram for an object located beyond the center of curvature c of a concave mirror. 10 draw a ray diagram for a 30 cm tall object placed 100 cm from a converging lens having a focal length of 150 cm.
Converging lens ray diagram.
Draw a ray diagram for the following situation involving a diverging lens. 11 draw a ray diagram for a diverging lens that has a focal length of 108 cm when an object is placed 324 cm from the lenss surface. Ray diagrams for converging lens you are here trick to drawing ray diagrams for converging lens. 12 draw a ray diagram for an object.
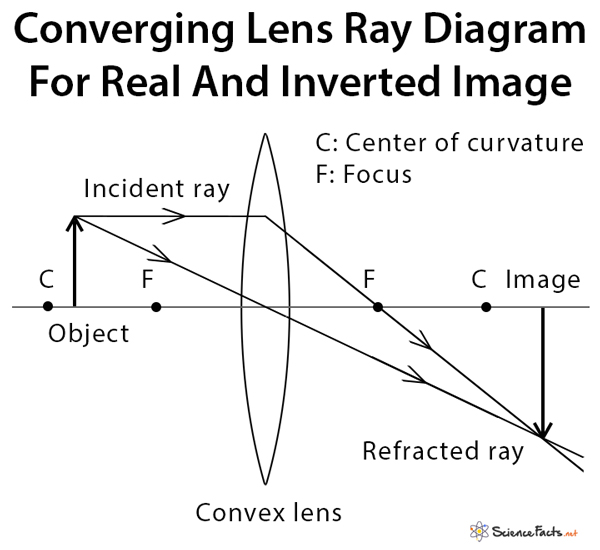
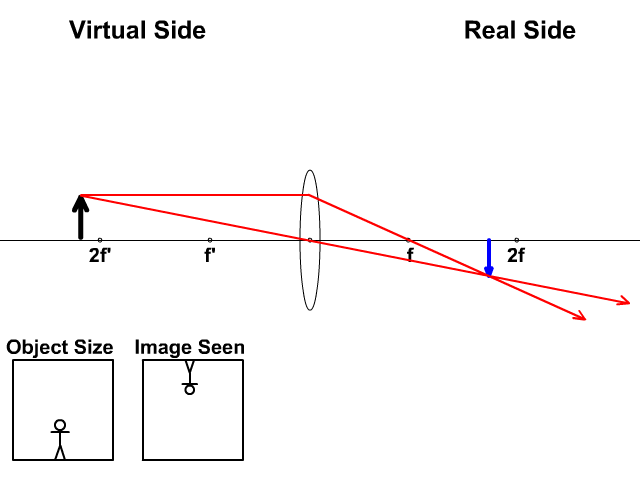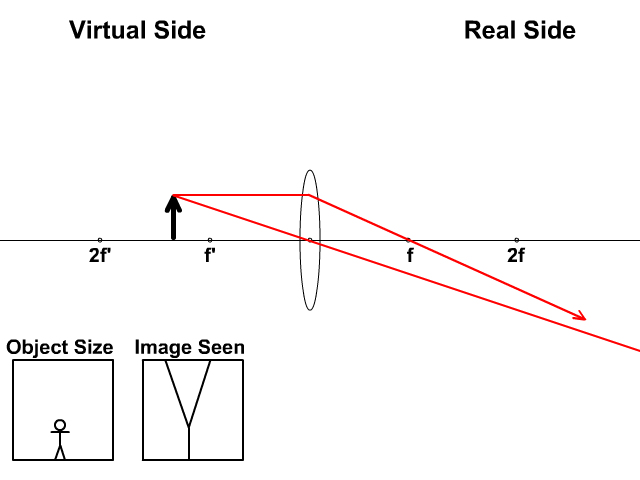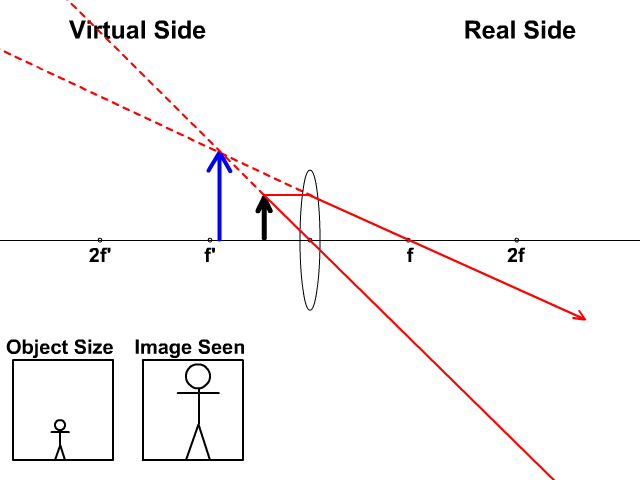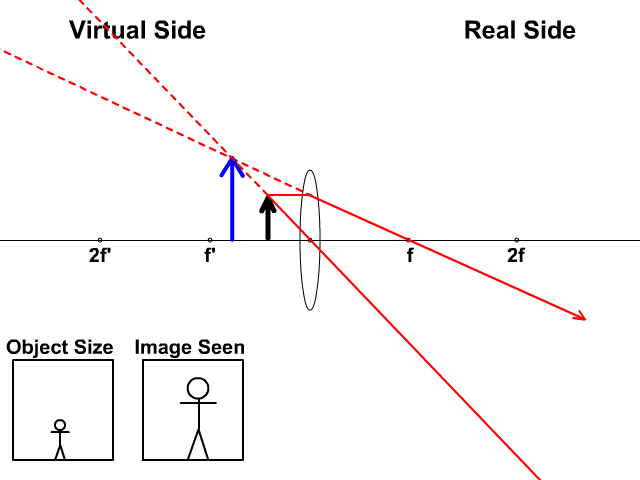
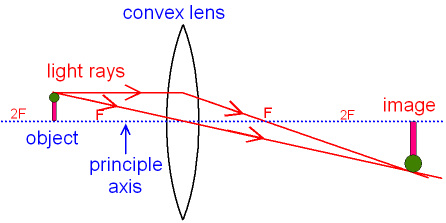
An object 5 cm in length is held 25 cm away from a converging lens of focal length 10 cm. Draw the ray diagram and find the position, size and the nature of the image formed. Answer: Given h = 5 cm u = -25 cm f = 10 cm To find v = ? h 1 = ? From the lens formula
A spherical lens has two Centre of Curvature.. Focus (F): It is the point on the axis of a lens to which parallel rays of light converge or from which they appear to diverge after refraction. Focal length: Distance between Optical Centre and Focus. Concave lens: Diverging lens. Convex lens: Converging lens
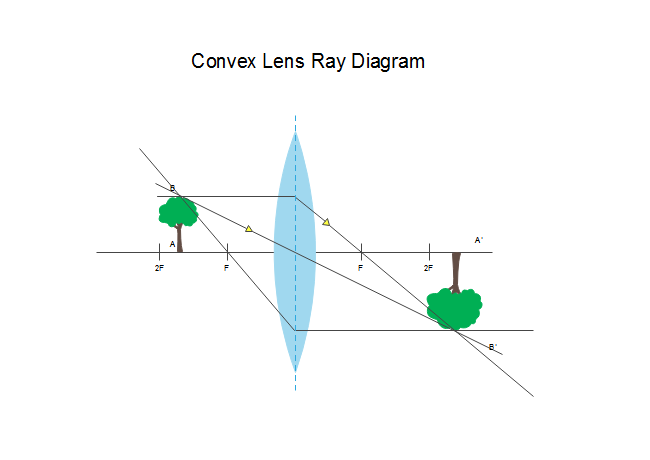
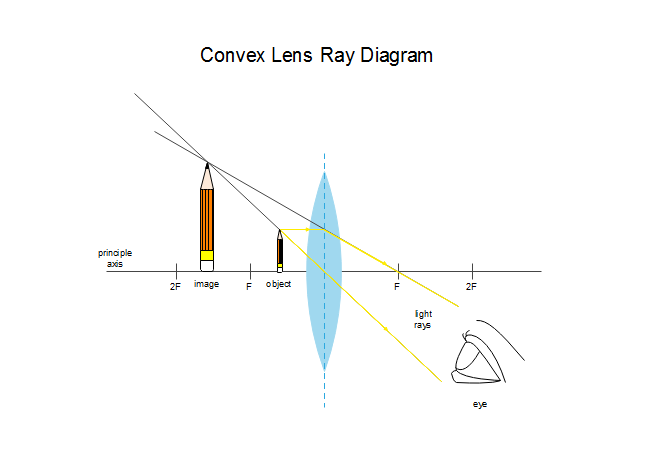
The method of drawing ray diagrams for double convex lens is described below. The description is applied to the task of drawing a ray diagram for an object located beyond the 2F point of a double convex lens. 1. Pick a point on the top of the object and draw three incident rays traveling towards the lens.
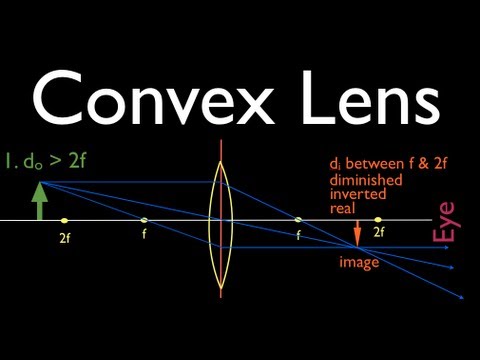
(a) A thin diverging lens (b) A thin converging lens (c) A thick diverging mirror (d) A thick converging mirror. A real image of same size as that of object is formed by a convex lens. The object musty be at a distance of (a) υ < ƒ (b) υ = ƒ (c) ƒ < υ < 2ƒ (d) υ < 2ƒ
Related Doubts (a) Find the position and size of the virtual image formed when an object 2 cm tall is placed 20 cm from:(i) a diverging lens of focal length 40 cm.(ii) a converging lens of focal length 40 cm.(b) Draw labelled ray diagrams to show the formation of images in case (i) and (ii) above (The diagrams may not be according to scale).
Worksheets are ray diagrams for convex mirrors, converging diverging lenses ray diagrams, physics, concave mirrors, grade 8 science ray diagrams for convex mirrors, 1 1 1 h d i i in every problem draw a ray i o f h d o o, ray diagrams for concave mirrors, diverging converging lens work. Last, describe the image formed (inverted or upright ...
Ray Diagrams for Concave Lenses The ray diagrams for concave lenses inside and outside the focal point give similar results. Ray Diagrams 3 of 4 Concave and Convex Lenses and Mirrors. A lens is an optical device which transmits and refracts light converging or diverging the beam.
A thin converging lens is used to produce on a screen a focused image of a candle. Diagram shows image formation of an object on a screen by a converging lens. The ray diagram in Figure 13 shows that the image is on the same side of the lens as the object and hence cannot be projectedit is a virtual image. Note that the image is closer to the lens.
Figure 25.6. 2: Sunlight focused by a converging magnifying glass can burn paper. Light rays from the sun are nearly parallel and cross at the focal point of the lens. The more powerful the lens, the closer to the lens the rays will cross. The greater effect a lens has on light rays, the more powerful it is said to be.
A worksheet to construct ray diagrams to show where images are formed by a converging convex lens and a diverging concave lens. Draw a ray diagram and use the information from the ray diagram to fill in the box. Aimed at aqa gcse physics. 10 draw a ray diagram for a 3 0 cm tall object placed 10 0 cm from a converging lens having a focal length ...
13+ Convex Lens Ray Diagram. This set of 3 rays is a standard way of simplifying the. Any incident ray traveling parallel to the principal axis of a converging lens will refract through the lens and travel. To draw these ray diagrams, we will have to recall the three rules of refraction for a double convex lens: Wikipedia] the example ray ...
14+ Diverging Lens Ray Diagram. Examples are given for converging and diverging lenses and for the cases where the object is inside and outside the principal focal length. Ray tracing for concave or diverging lens draw different ray diagrams with the object at different places in relation to the focus and find out where the image appears.
Previously in Lesson 5, ray diagrams were constructed in order to determine the location, size, orientation, and type of image formed by double concave lenses (i.e., diverging lenses). The ray diagram constructed earlier for a diverging lens revealed that the image of the object was virtual, upright, reduced in size and located on the same side ...
To focus a camera on objects at different distances, the converging lens is moved toward or away from the film, so a sharp image always falls on the film. A camera with a telephoto lens (f = 200.0 mm) is to be focused on an object located first at a distance of 3.5 m and then at 50.0 m.
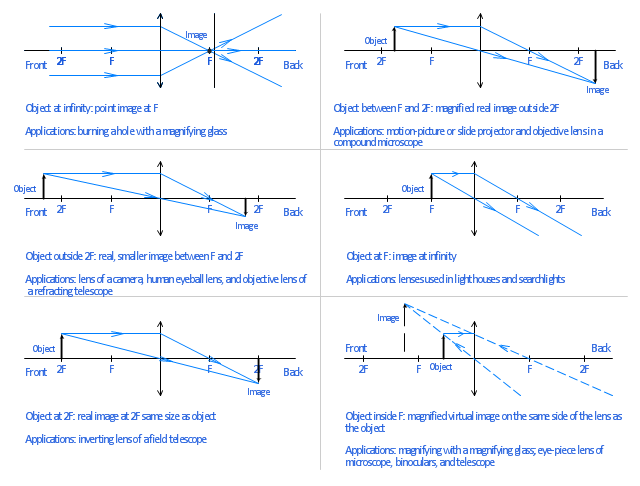
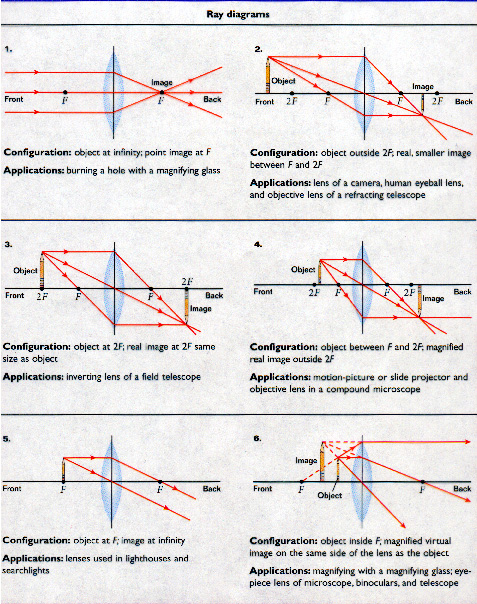
Ray Diagram for Convex and Concave Lens The nature of the image formed by a convex lens varies as the distance of the object from the lens changes. However, with a concave lens, we always get virtual, upright, and diminished images (regardless of the distance of the object from the lens).
Which diagram shows image formation of an object on a screen by a converging lens?Answer -While drawingray diagram, we follow these rulesA rayparallel tothe principalaxiswill pass through the principal focus.A raypassing throughthe principalfocuswill become parallel to the principal axis.A raypassin
Ray Diagrams for Lenses. Three principal rays can be used to locate and size the image formed by a single lens, with examples for converging and diverging lenses. The three principal rays are:. A ray from the top of the object proceeding parallel to the centerline perpendicular to the lens, passing through the principal focal point beyond the lens.
Oct 30, 2014 — SS: Ray Diagrams For Converging Lens · There is one ray of light passing through the center of the lens. · 2 rays are enough to determine the ...
Open 9+ pages ray diagrams for converging lenses answers analysis in Doc format. 9Ray Diagrams for Lenses. Description of how to draw ray diagrams for diverging lenses for grade 10 science. Teachers are granted permission to use them freely with their students and to use it as part of their curriculum.
5) virtual, inverted, and diminished. Page 7. A real image is formed by a converging lens. If a weak ...15 pages
In each diagram use an arrow 10 cm tall pointing upwards as the object. Ray 3 passes straight through the center of the lens. Concave And Convex Mirrors Ray Diagram For Convex And Concave Mirror. Converging mirror ray diagram. The method is applied to the task of drawing a ray diagram for an object located […]
The image formed by a single lens can be located and sized with three principal rays. Examples are given for converging and diverging lenses and for the cases ...
Converging Lens Ray Diagram. Written By Pelvic Diagram Wednesday, May 26, 2021. Edit. Converging Lens Ray Diagram. Here are ray diagrams for the four cases from the video plus one more. The image formed by a single lens can be located and sized with three principal rays. Solved: Converging & Diverging Lenses Ray Diagrams DIRECTI ...
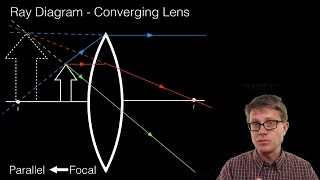
Converging Lens es A convex lens is a converging lens which bends light ray s into focus. The focal length, f, is the distance to the focal point where parallel ray s converge as shown. A Ray Diagram is a simple picture using only 2 or 3 light ray s reflected off an object to visualize how images are formed.
Step-by-Step Method for Drawing Ray Diagrams · 1. Pick a point on the top of the object and draw three incident rays traveling towards the lens. · 2. Once these ...
Convex Lens - Ray diagram. Last updated at Nov. 18, 2021 by Teachoo. For a Convex Lens, object can be kept at different positions Hence, we take different cases Case 1 - Object is Placed at infinity In this Case, Object is kept far away from lens (almost at infinite distance)





















---teachoo.png)





0 Response to "45 converging lens ray diagram"
Post a Comment