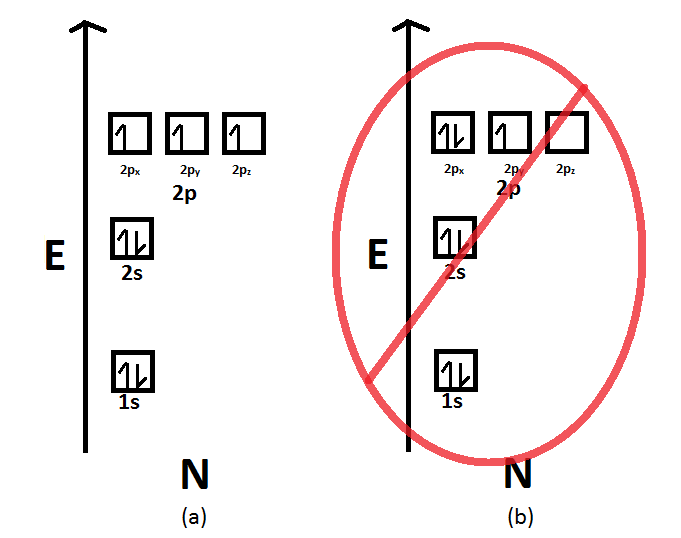
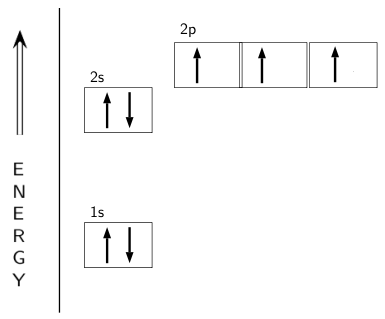
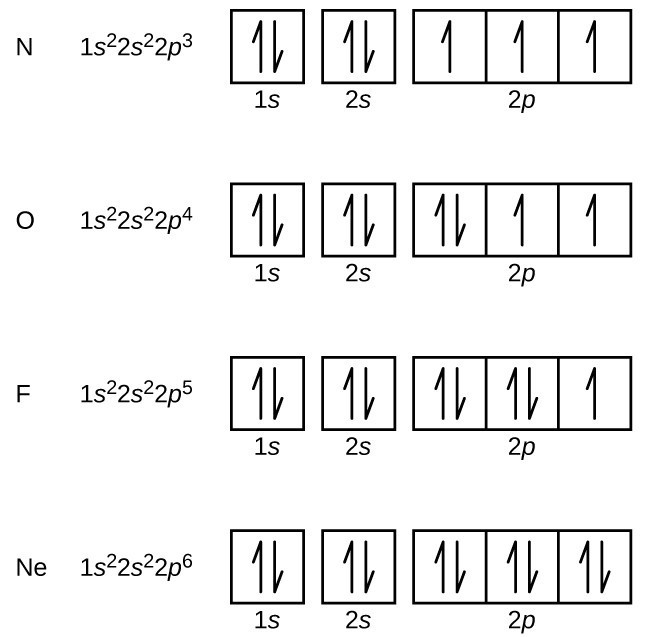
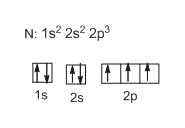
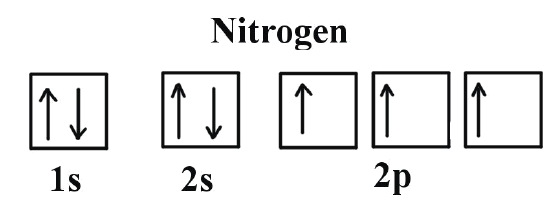
44 show the orbital filling diagram for n nitrogen
Orbital Filling Diagram for Nitrogen. show the orbital filling diagram for rm n nitrogen best answer the electronic configuration for nitrogen atom is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 3 lowest energy state will have two electrons in s shell which is spherical in shape one spin up and another spin down chemistry problem please help show the orbital filling diagram for nitrogen stack the subshells inorder of energy ... Show the orbital-filling diagram for N (nitrogen). Stack the subshells in order of energy, with the lowest-energy subshell at the bottom and the highest-energy subshell at the top. 1s²2s²2p³
Nitrogen is the seventh element with a total of 7 electrons. In writing the electron configuration for nitrogen the first two electrons will go in the 1s orbital. Since 1s can only hold two electrons the next 2 electrons for N goes in the 2s orbital. The remaining three electrons will go in the 2p orbital. Therefore the N electron configuration ...
Show the orbital filling diagram for n nitrogen
Draw an orbital diagram for scandium Show the orbital-filling diagram for N (nitrogen). Stack the subshells in order of energy, with the lowest-energy subshell at the bottom and the highest-energy subshell at the top. Show the orbital-filling diagram for S Status: Resolved. home / study / science / chemistry / chemistry questions and answers ... Question: Part D Show the orbital-filling diagram for Br (bromine). Order subshells by energy, with the lowest-energy subshell at the left. Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. View Available Hint (s) Reset Help 1 18 25 2p 3s 3p 30 48 4p Submit Provide Feedback Next > Part B Show the orbital-filling diagram for N (nitrogen). Since 1s. Use orbital filling diagrams to describe the locations of electrons in an atom. Diagram of Hund's rule in boron, carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen. Figure 1. The 2p.Show transcribed image text Show the orbital-filling diagram for N. Nitrogen is the seventh element with a total of 7 electrons.
Show the orbital filling diagram for n nitrogen. 3 Unpaired electrons. Nitrogen atom has total 7 electrons. Two will fill up the n=1 level, and then there are five electrons in the n=2 level. Nitrogen can bond three times with other electrons to fill up it's shell with 8, (8-5=3). And these are those 3 unpaired electrons which were residing the 2p sub-shell of the Nitrogen atom , before the formation of 3 bonds. Diagram of Hund's rule in boron, carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen. Figure 1. The 2p . Orbital filling diagrams essentially just turn this big list of electron locations . In the same way, the orbital filling diagram for nitrogen will be.Given the same amount of absorbed solar energy coming in, the amount of IR escaping to space at the top of the ... If you are still not getting the Nitrogen Electron Configuration of the element nitrogen then, the full electronic configuration of nitrogen is written as the following; 1s 2 2s 2 2p 3. If we gave you brief information then, the first two electrons lie in the 1s orbital, following the next 2 electrons, it comes under the 2s orbital. Show the orbital-filling diagram for N (nitrogen). Stack the subshells in order of energy, with the lowest-energy subshell at the bottom and the ...
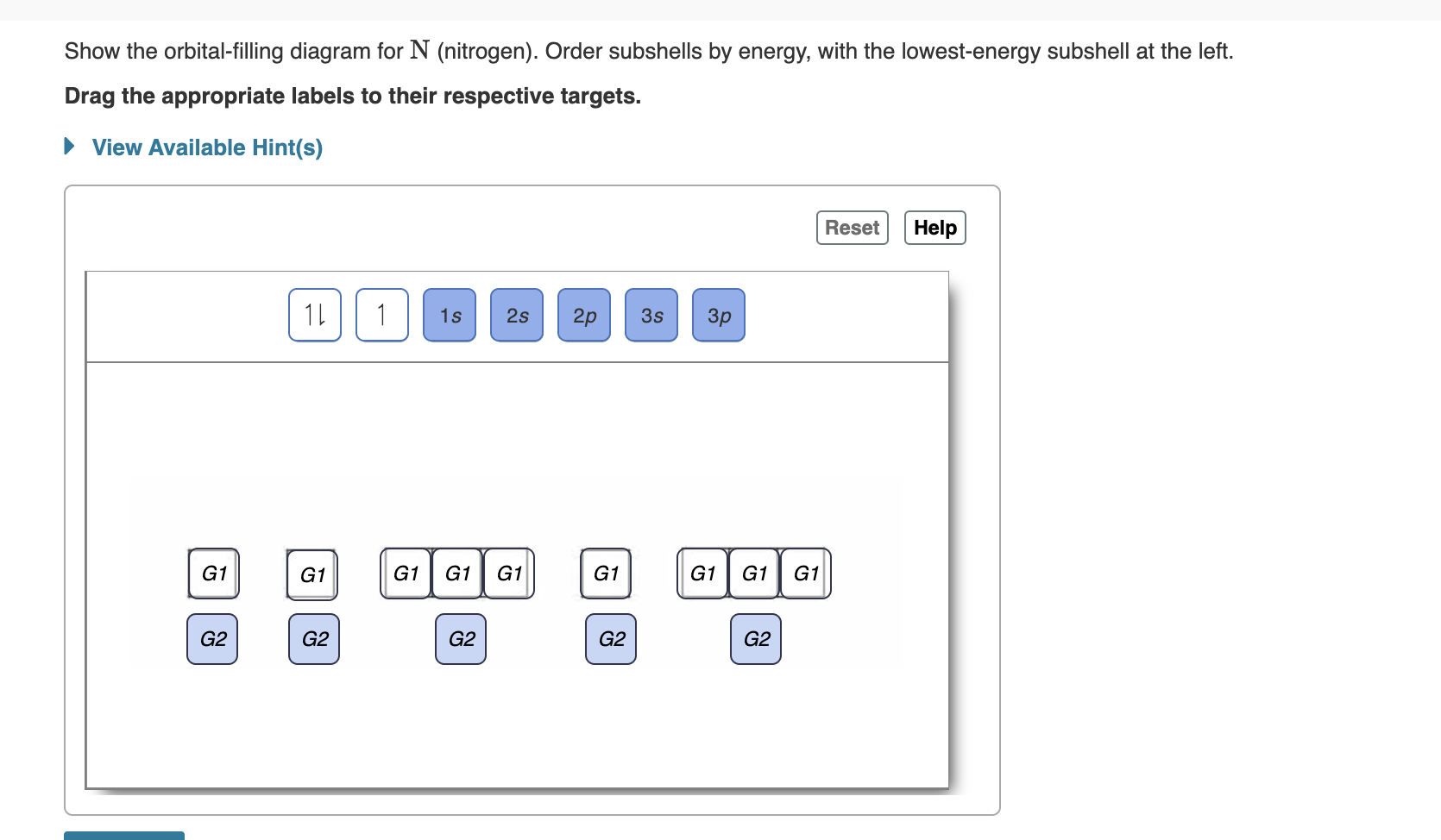
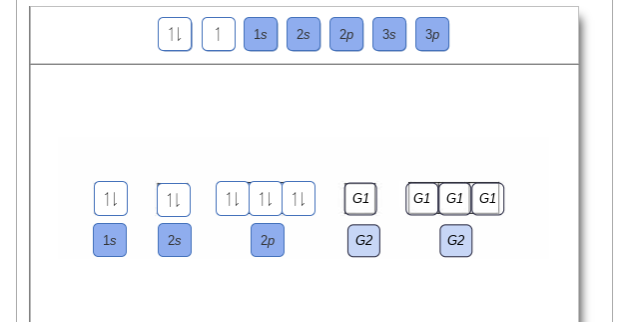
Show the orbital filling diagram for br bromine. Orbital notation is a way to show how many electrons are in an orbital for a given element. Notice that the elements k and ca the 4s elements come before the elements sc through zn the 3d elements in the periodic table. Show the orbital filling diagram for bromine. Find orbital diagram near you. Show the orbital-filling diagram for N (nitrogen). Order subshells by energy, with the lowest-energy subshell at the left. Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. View Available Hint(s) Reset Help 1L 1 1s 2s 2p 3s Зр G1 G1 G1 G1 G1 G1 G1 G1 G1 G2 G2 G2 G2 G2 Part C Show the orbital-filling diagram for S (sulfur). molecular orbital is also created, which we simplistically show as a subtraction of the two atomic 1s orbitals [σ* = (1sa - 1sb)]. This orbital is called sigma-star (σ*) and is less stable than the two separated atoms. Because it is less stable than the two individual atoms, it is called an anti-bonding molecular orbital. The orbital diagram for bromine shows four concentric circles around a dot representing a nucleus, with two dots on the first circle, eight on the second, 18 on the third and seven on the fourth. Each dot on a circle represents an electron. Periodic Trends. STUDY. PLAY. Item 1: Part A Show the orbital-filling diagram for N (nitrogen).
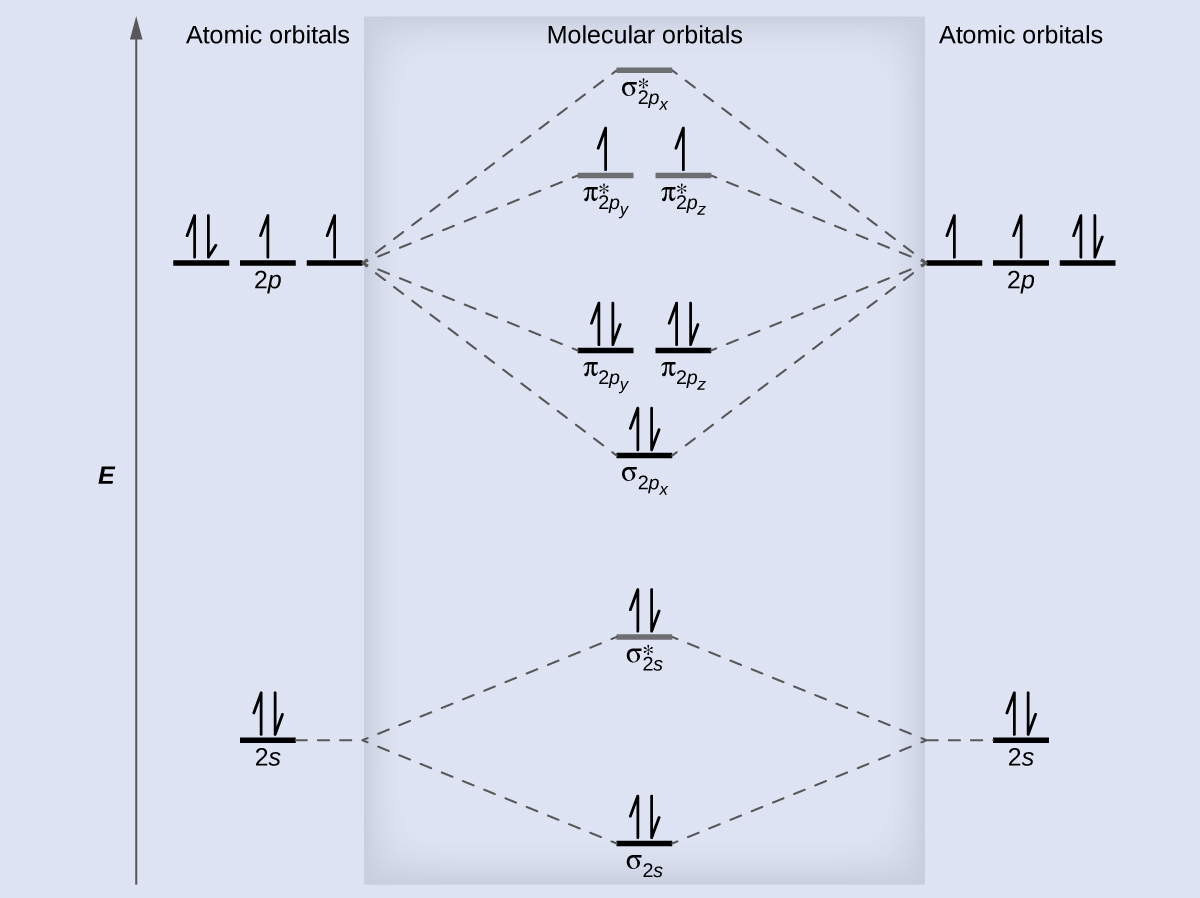
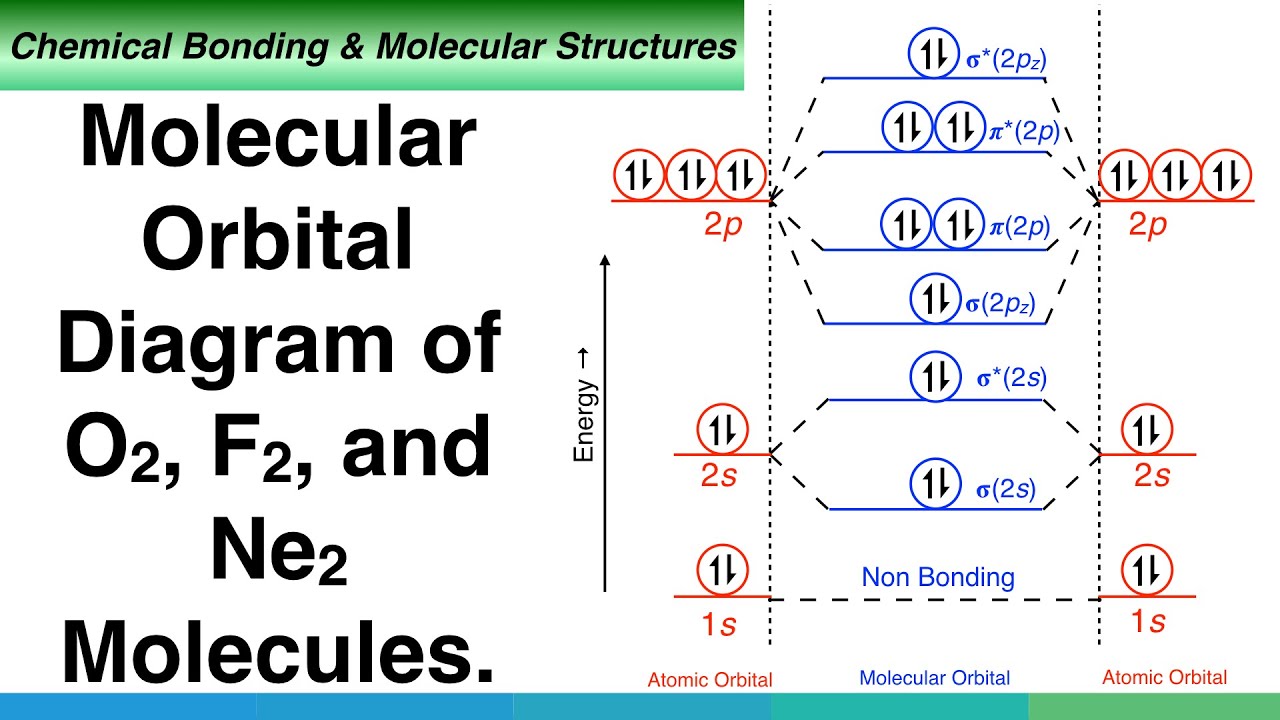
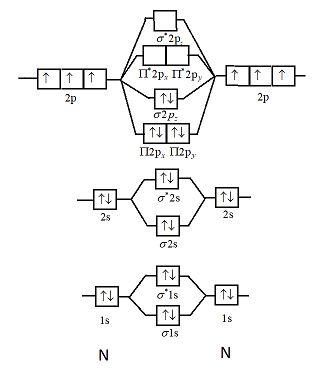
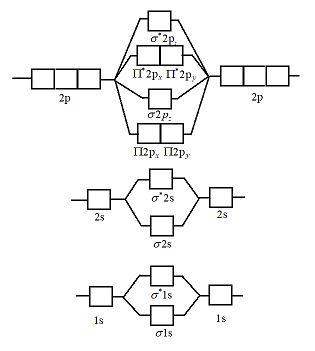
help Show the orbital-filling diagram for N (nitrogen). Stack the subshells in order of energy, with the lowest-energy subshell at the bottom and the highest- ...1 answer · 1 vote: Here is the solution of your question. If you have any doubt or need any clarification please comment in comment box and will definitely resolve your ... The molecular orbital energy level diagram of He 2 (hypothetical) is given in Fig. Here, N b = 2 and N a = 2. Bond order = N b -N a / 2 = 2-2 / 2 = 0. As the bond order for He 2 comes out to be zero, this molecule does not exist. 3. Nitrogen molecule (N 2). The electronic configuration of nitrogen (Z=7) in the ground state is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 1x 2p ... Show the orbital-filling diagram for N (nitrogen). Stack the subshells in order of energy, with the lowest-energy subshell at the bottom and the highest-energy subshell at the top. Electron ... Show the orbital-filling diagram for N (nitrogen). Order subshells by energy, with the lowest-energy subshell at the left Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. View Available Hint(s) Reset Help 11 || 1 18 2s 2p 3s ap Group 1 GT G1 G1 G1 GI GT G161 G2 G2 G2 G2 G2 ; Question: Show the orbital-filling diagram for N (nitrogen ...
In writing the electron configuration for nitrogen the first two electrons will go in the 1s orbital. Since 1s. Use orbital filling diagrams to describe the locations of electrons in an atom. Diagram of Hund's rule in boron, carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen. Figure 1. The 2p .Show transcribed image text Show the orbital-filling diagram for N ...
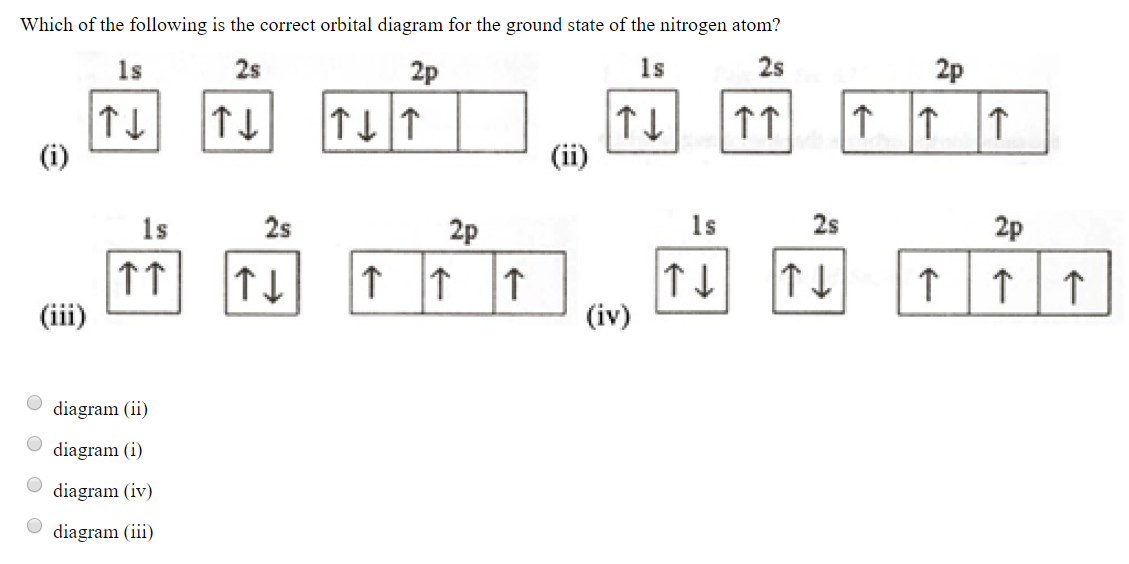
Example \(\PageIndex{1}\): Nitrogen Atoms. Consider the correct electron configuration of the nitrogen (Z = 7) atom: 1s 2 2s 2 2p 3. The p orbitals are half-filled; there are three electrons and three p orbitals. This is because the three electrons in the 2p subshell will fill all the empty orbitals first before pairing with electrons in them.
Show the orbital-filling diagram for (bromine).Status: Resolved. Show the orbital-filling diagram for S (sulfur). Stack the subshells in order of energy, with the lowest-energy subshell at the bottom and the highest-energy subshell at the top%(15). 1. Describe the two differences between a 2p x orbital and a 3p y orbital.
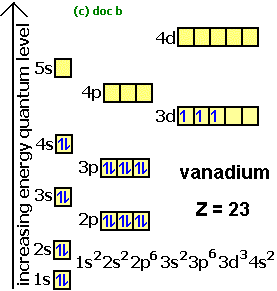
The orbital filling diagram of boron. Show the orbital filling diagram for n nitrogen. What Is The Pattern Of Filling In The P Orbitals Socratic Orbital diagrams are a visual way to show where the electrons are located within an atom. Orbital filling diagram for boron. Draw an orbital diagram for scandium sc. Orbital filling diagram of boron.
Orbital-Filling Diagram for Bromine. Bromine has 35 electrons, so it will have 35 arrows placed in its orbital-filling diagram as in figure The order bottom to top . Show the orbital-filling diagram for \rm Br (bromine). Stack the subshells in order of energy, with the lowest-energy subshell at the bottom and the highest-energy.
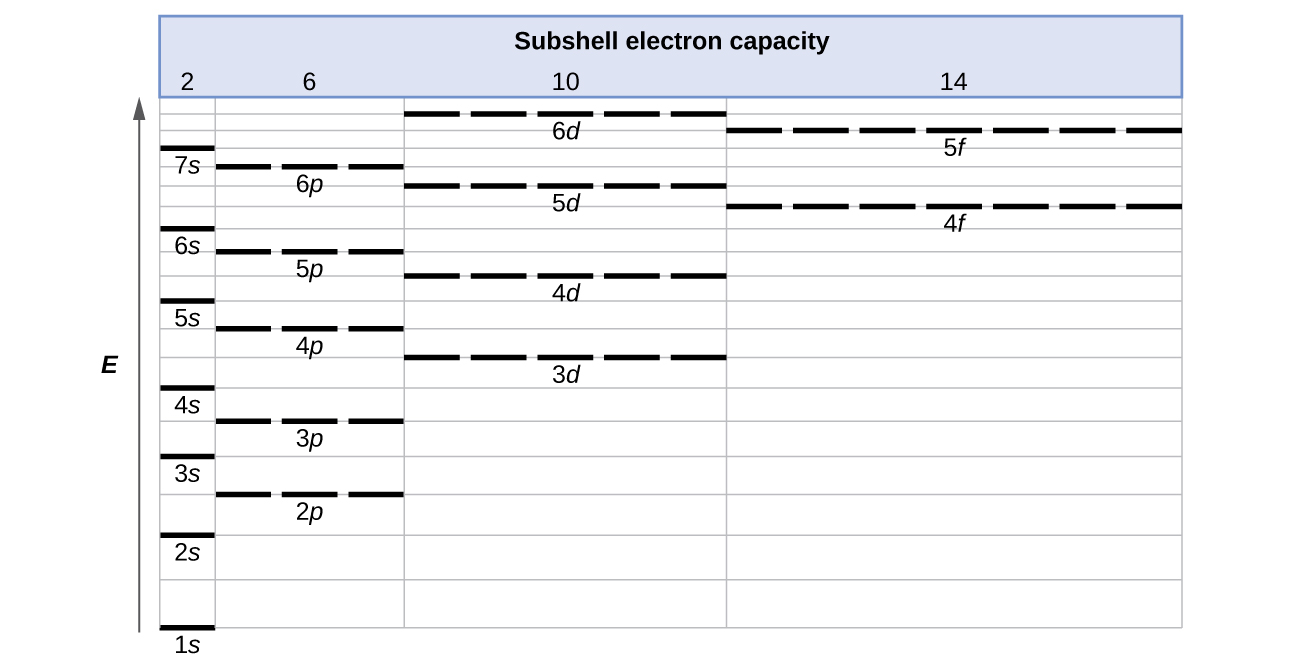
Show the orbital-filling diagram for N (nitrogen). Order subshells by energy, with the lowest-energy subshell at the left. To learn to create orbital-filling diagrams. An orbital-filling diagram shows the number of electrons in each orbital, which are shown in order of energy. The placement of electrons in orbitals follows a certain set of ...
Show the orbital-filling diagram for N (nitrogen). Stack the subshells in order of energy, with the lowest-energy subshell at the bottom and the highest-energy subshell at the top. Show the orbital-filling diagram for S (sulfur).
The periodic table shows us that nitrogen (N) has an atomic number of 7. As a result, a neutral nitrogen atom will have 7 electrons. In orbital filling diagrams, s-sublevels have 1 orbital and p ...
In writing the electron configuration for Aluminium the first two electrons will go in the 1s orbital. Since 1s can only hold two electrons the next 2 electrons for aluminium go in the 2s orbital. The nex six electrons will go in the 2p orbital. The p orbital can hold up to six electrons. We'll put six in the 2p orbital and then put the next ...
Show the orbital filling diagram for n nitrogen. Show transcribed image text show the orbital filling diagram for n nitrogen. Use the buttons at the top of the tool to add orbitals. Stack the subshells in order of energy with the lowest energy subshell at the bottom and the highest energy subshell at the top.
Express your answer numerically as an integer. Show the orbital-filling diagram for N (nitrogen). Stack the subshells in order of energy, with the lowest-energy subshell at the bottom and the highest-energy subshell at the top. Show the orbital-filling diagram for S (sulfur).
part A;Show the orbital-filling diagram for N (nitrogen). Order subshells by energy, with the lowest-energy subshell at the left. Drag the appropriate labels to ...
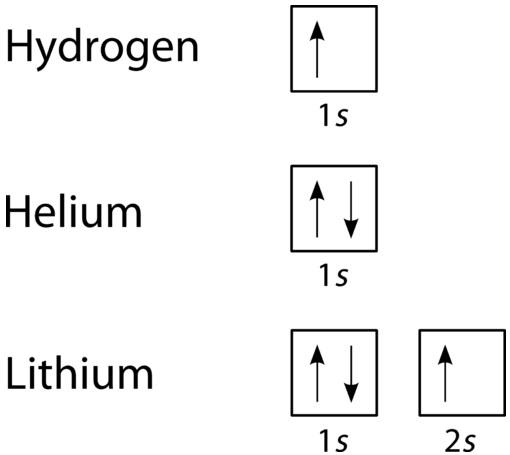
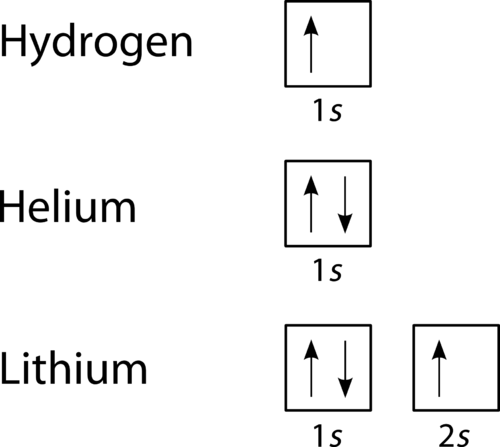
The orbital filling diagram for helium. The electron configuration for helium is 1s². This means that we have two electrons in the 1s orbital, which looks like this: This diagram is exactly the same as the one for hydrogen, except that there's a second arrow added to the 1s orbital. This represents the second electron in the 1s orbital, and ...
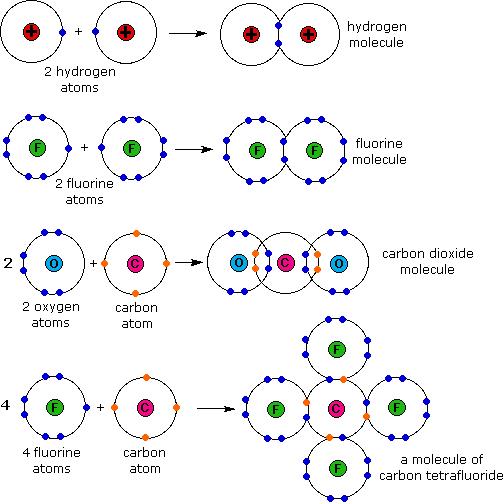
Three hydrogen atoms with one unpaired electron apiece ( ) will overlap their 1s orbitals with the three available sp 3 orbitals on the nitrogen. This leads to the formation of three s bonds and a lone pair of electrons occupying the fourth hybrid molecular orbital. Next, consider SF 4. The Lewis structure is shown below. VSEPR predicts trigonal bipyramidal geometry (one lone pair and 4 ...
Since 1s. Use orbital filling diagrams to describe the locations of electrons in an atom. Diagram of Hund's rule in boron, carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen. Figure 1. The 2p.Show transcribed image text Show the orbital-filling diagram for N. Nitrogen is the seventh element with a total of 7 electrons.
Question: Part D Show the orbital-filling diagram for Br (bromine). Order subshells by energy, with the lowest-energy subshell at the left. Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. View Available Hint (s) Reset Help 1 18 25 2p 3s 3p 30 48 4p Submit Provide Feedback Next > Part B Show the orbital-filling diagram for N (nitrogen).
Draw an orbital diagram for scandium Show the orbital-filling diagram for N (nitrogen). Stack the subshells in order of energy, with the lowest-energy subshell at the bottom and the highest-energy subshell at the top. Show the orbital-filling diagram for S Status: Resolved. home / study / science / chemistry / chemistry questions and answers ...



















0 Response to "44 show the orbital filling diagram for n nitrogen"
Post a Comment