42 consider the circuit diagram depicted in the figure.
Voltage divider circuit with or without load. Consider the circuit shown below on the left side. It is easy to see that i = v. g. R. 1 +R. 2. and v. out ... It is easy to solve the above circuit. The solution is depicted in the first figure on ... from the simple circuit of Figure 4 to the circuit of Figure 3, and so on. ...
Consider this diagram. Let us assume that it describes a series circuit containing a resistor, a capacitor, and an inductor. The current in the circuit has amplitude , as indicated in the figure. Which of the following choices gives the correct respective labels of the voltages across the resistor, the capacitor, and the inductor?
Problem 1: Consider the circuit depicted in the attached figure. The voltage source is an AC source of frequency f = 55 Hz. R, Randomized Variables C, R1 = 103 Q R2 = 162 Q C1 = 6.5 µF C2 = 9.5 µF V C2 R2 L = 0.77 H Part (a) Given the above circuit, write an expression for the total impedance Z for the circuit as a complex number.
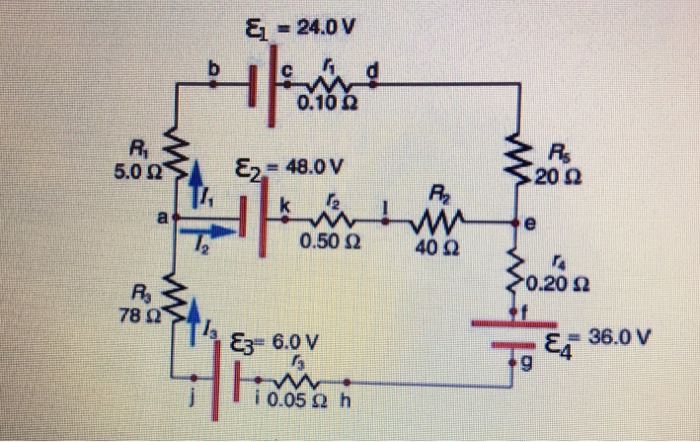
Consider the circuit diagram depicted in the figure.
Figure P 5.42 0.2 H *P5.42. Find the phasors for the current and for the voltages of the circuit shown in Figure P5.42. Construct a phasor diagram showing Vs, I, v R. and VL. What is the phase relationship between Vs and I?
Figure 6.13. State-assigned table for the sequential circuit in Figure 6.12. Present Next state state Outputs A 00 00 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 B 01 10 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 C 10 11 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 D 11 00 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 1
Consider the circuit shown in Figure (a). i L(0-) = 0, and v R(0-) = 0. But, -v R(0-) + v C(0-) + 10 = 0, or v C(0-) = -10V. (a) At t = 0+, since the inductor current and capacitor voltage cannot change abruptly, the ...
Consider the circuit diagram depicted in the figure..
Consider the circuit diagram depicted in the figure. 0 ω r 3 16. For the action depicted in the figure figure 2 indicate the direction of the induced current in the loop clockwise counterclockwise or zero when seen from the right of the loop. Now consider a diagram describing a parallel ac circuit containing a resistor a capacitor and an inductor.
For the action depicted in the figure, (Figure 2) indicate the direction of the induced current in the loop (clockwise, counterclockwise or zero, when seen from the right of the loop). The face of the south pole will become the north pole, so there will be a force of attraction between them, which makes the motion of the coil opposed.
Figure 12.2.2 (a) Time dependence of IR (t) and VR (t) across the resistor. (b) Phasor diagram for the resistive circuit. The behavior of IR (t)and can also be represented with a phasor diagram, as shown in Figure 12.2.2(b). A phasor is a rotating vector having the following properties: VR (t) (i) length: the length corresponds to the amplitude.
View (3) Problem 30 Consider the circuit diagram in the figure. E1 = 18V.docx from AA 1 (3%) Problem 30: Consider the circuit diagram in the figure. E1 = 18V R Ez = 45 Otheexpertta.c 50% Part (a)
Suppose that these systems are connected in series as depicted in Figure P3.10. Find the input-output relation for the overall interconnected system. Is this sys tem linear? Is it time-invariant? x[n] System 1 - System 2 System 3 y[n] Figure P3.10 (d) Consider a second series interconnection of the form of Figure P3.10 where the
Consider the circuit diagram depicted in the figure. a. What equation do you get when you apply the loop rule to the abcdefgha, in terms of the variables in the figure?
2. 27.3.2 (7, ex) Consider the circuit diagram depicted in the figure. (a) What equation do you get when you apply the loop rule to the loop abcdefgha, in terms of the variables in the figure? (b) If the current through the top branch is I2 = 0.085 A, what is the current through the bottom, I3, in amps? (c) Find the current through R 1 and the resistance of R 1.
Answer to: For the circuit shown in the figure, V1 = 14.6 V and V2 = 9.4 V. Determine the current in the 4.0 ohm resistor. By signing up, you'll...
P 5.2-2 Consider the circuit of Figure P 5.2-2. Find i a by simplifying the circuit (using source transformations) to a single-loop circuit so that you need to write only one KVL equation to find i a. Figure P 5.2-2 . Solution: Finally, apply KVL: 16 10 3 4 0 2.19 A aa 3 a
Transcribed image text: Consider the circuit diagram depicted in the figure. What equation do you get when you apply the loop rule to the loop abcdefgha, in terms of the variables in the figure? If the current through the top branch is I_2 = 0.47 A, what is the current through the bottom.
A) Consider the combination of capacitors shown in the diagram, where C 1 = 3.00 μF, C 2 = 11.0 μF, C 3 = 3.00 μF, and C 4 = 5.00 μF.. Find the equivalent capacitance C A of the network of capacitors. Express your answer in microfarads. B) Two capacitors of capacitance C 5 = 6.00 μF and C 6 = 3.00 μF are added to the network, as shown in the diagram. Find the equivalent capacitance C B ...
Answer to Solved (10%) Problem 10: Consider the circuit diagram. Transcribed image text: (10%) Problem 10: Consider the circuit diagram depicted in the figure. E1 = 18 V 250 R 0.522 E2-45V 50% Part (a) What equation do you get when you apply the loop rule to the loop abcdefgha, in terms of the variables in the figure?
91% (345 ratings) Problem Details. Consider the circuit diagram depicted in the figure. Part (a) What equation do you get when you apply the loop rule to the loop abcdefgha? Part (b) If the current through the top branch is I2 = 0.49 A, what is the current through the bottom I3, in amps? Frequently Asked Questions.
In this problem, we will consider the following situation as depicted in the diagram: A block of mass m slides at a speed v along a horizontal smooth table. It next slides down a smooth ramp, descending a height h, and then slides along a horizontal rough floor, stopping eventually. Assume that the block slides slowly enough so that it
Transcribed image text: (10%) Problem 5: Consider the circuit diagram depicted in the figure 0.5 Ω R2 2.5 Ω /2 R 1.5Ω 0.5 Ω 50% Part (a) what equation do you get when you apply the loop rule to the loop abcdergha, in terms of the variables in the figure? Grade= 100% Correct Answer Student Final Submission Feedback Correct! 012 R2+ 112 T3 R3 +32-62 0- 1-(Ti +R2) I2+(R3r2)13 2 Grade Summary ...
Consider the circuit diagram depicted in the figure. What equation do you get when you apply the loop rule to the loop abcdefgha? If the current through the top branch is I_2 = 0.49 A. what is the current through the bottom, I_3, in amps?
Consider the circuit shown in the figure below where c1 400 µf c2 700 µf and δv 180 v. 180 v v r 4 400 r 1 200 r 2 300 3 100 label the voltage v 180 v and the resistors. Calculate the power delivered to each resistor in the circuit shown in figure p2131. Consider the following circuit diagram.
Question. Consider the circuit diagram depicted in the figure. What equation do you get when you apply the loop rule to the loop abcdefgha, in terms of the variables in the figure? 0 = If the current through the top branch is I_2 = 0.69 A, what is the current through the bottom, I_3, in amps?
Consider a series RC circuit as in the figure below for which R = 1.00 MΩ, C = 5.00 µF, and ε = 30.0 V. Find (a) the time constant of the circuit and (b) the...
They depict every component in a circuit, the component's technical information (such as its ratings), and how each component is wired into the circuit. Block diagrams are the simplest type of drawing.
Consider the circuit diagram depicted in the fgure. It is known that two battery internal resistors r1and r2 are both 0.2Ω· = 12V and & = 24V. R2 16Ω 2. and Rs 262, but Ri is unknown. Caution: Current directions.
Sample Circuit We consider the ... Consider the circuit shown in Figure P28.9. Find (a) the current in the 20.0-Ω resistor and (b) the ... Draw the circuit diagram and assign labels and symbols to all known and unknown quantities. Assign directions to the currents.
Figure 12.2.2 (a) Time dependence of IR (t) and VR (t) across the resistor. (b) Phasor diagram for the resistive circuit. The behavior of IR (t)and can also be represented with a phasor diagram, as shown in Figure 12.2.2(b). A phasor is a rotating vector having the following properties: VR (t) (i) length: the length corresponds to the amplitude.

0 Response to "42 consider the circuit diagram depicted in the figure."
Post a Comment