40 b2 molecular orbital diagram
Molecular orbital : A molecule in which all the electrons are paired, is called diamagnetic. | Online Chemistry tutorial IIT, CBSE Chemistry, ICSE Chemistry, engineering and medical chemistry entrance exams Molecular orbital diagram of C2 molecule : Number of electrons in C2 molecule = 12.
The molecular orbital theory is one of the most productive models of chemical bonding. It is the basis of quantitative calculations, including those regarding the computer-generated images. The bonding and anti-bonding orbitals are usually depicted by the molecular orbital diagram.
Molecular orbital theory uses group theory to describe the bonding in molecules; it comple-ments and extends the introductory bonding models in Chapter 3 . In such interactions are so weak, we will not include them in other molecular orbital. energy level diagrams. Additional labels describe the orbitals.
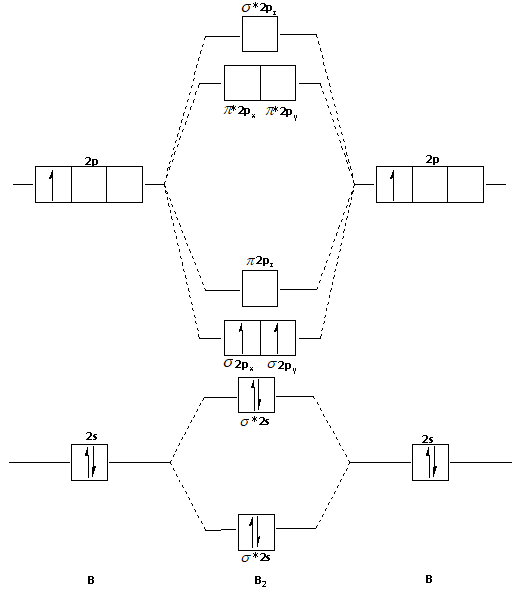
B2 molecular orbital diagram
Molecular Orbital Theory- To simplify things, we will consider the interaction of the orbitals containing valence electrons to create molecular orbitals. Have you ever thought about how sigma and pi bonds are formed? What is the difference between diamagnetic and paramagnetic behaviour?
Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The first major step is understanding the difference between two major theories: Valence Bond Theory and Molecular Orbital Theory. Valence Bond Theory proposes that electrons are localized between two atoms.
Molecular orbital diagrams are diagrams of MO energy levels, shown as short horizontal lines in the center. Atomic orbitals (AO) energy levels are shown for comparison. Lines, often dashed diagonal lines, connect MO levels with their constituent AO levels.
B2 molecular orbital diagram.
The molecular orbital diagram representing this order of energy levels is shown in fig. For example, homonuclear diatomic molecules of second row elements like Li 2 , Be 2 , B 2 , C 2 , N 2 , the σ 2p z MOs is higher in energy than π 2px and π 2py MOs.
This second orbital is therefore called an antibonding orbital. This scheme of bonding and antibonding orbitals is usually depicted by a molecular orbital diagram such as the one shown here for the dihydrogen ion H2+.
In molecular orbital (MO) approach - overlap orbitals for the whole molecule -bonding is therefore DELOCALISED. We will look first at DIATOMIC MOLECULES and only later move on to POLYATOMIC MOLECULES. Molecular Orbital Energy Level Diagram for a Heteronuclear Diatomic.
Figure 9-2 Molecular orbital (MO) diagram for the combination of the 1s atomic orbitals on two identical atoms (at the left) to form two MOs. The solid lines represent the relative energies of the indicated atomic and molecular orbitals. (a) The diagram for H2, He2, Li2, Be2, B2, C2, and N2...
Bond Order. The filled molecular orbital diagram shows the number of electrons in both bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals. Eight possible homonuclear diatomic molecules might be formed by the atoms of the second period of the periodic table: Li 2 , Be 2 , B 2 , C 2 , N 2 , O 2 , F 2 , and Ne 2...
• Because the energy of the two electrons is lower than the energy of the individual atoms, the molecule is stable. Figure 9.26: (a) The molecular orbital energy-level diagram for the H2 molecule. (b) The shapes of the molecular orbitals are obtained by squaring the wave functions for MO1 and...
Bond Order. The filled molecular orbital diagram shows the number of electrons in both bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals. Eight possible homonuclear diatomic molecules might be formed by the atoms of the second period of the periodic table: Li2, Be2, B2, C2, N2, O2, F2, and Ne2.
answered. Molecular orbital diagram of B2. 1. See answer. priyesharma02. Ambitious. 60 answers. 7.2K people helped. molecular orbita diagram of B2. eddibear3a and 58 more users found this answer helpful.
The molecular orbital energy diagram predicts that He2 will not be a stable molecule, since it has equal numbers of bonding and antibonding Eight possible homonuclear diatomic molecules might be formed by the atoms of the second period of the periodic table: Li2, Be2, B2, C2, N2, O2, F2, and Ne2.
A bare molecular orbital diagram is presented and you must drag the correct orbitals and labels onto the diagram. The diagram is then completed by filling the energy levels with the correct number of electrons. The following molecules are currently available: Molecules of the First Row
Be sure your diagram contains all of the electrons in the ion, including any core electrons Energy. This problem has been solved! See the answerSee the answer.
Why is this not the case in the ceb2 mo. The molecular orbital diagram for ceo2 says that the sigma 2p bonding molecular orbital is lower i...
A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the s...
Jun 30, 2020 · So the bond order of B2 is equal to 1, which you can get by drawing the molecular orbital diagram and performing the equation Bond Order = . 5 * (# of bonding electrons - # of antibonding electrons). However, when you draw the Lewis structure of B2, you get a triple bond.
6 in all have to be accommodated in various molecular orbitals in the increasing order of their energies. Notice how the σ from the 2p beha...
In picture 1 we show the molecular orbital structure of F2. In picture 2 we show the overlapping p orbitals, which form the bond between the two fl uorine atoms, in red and green gradients. The dashed lines show the remaining p orbitals which do not take part in the bonding. σ z y x σ* x y z Construct the molecular orbital diagram for ...
Determine the number of sigma and pi. Molecular orbital diagram of b2. I2 Mo Diagram Empat Stanito Com Molecular...
Nov 11, 2016 · So the bond order of B2 is equal to 1, which you can get by drawing the molecular orbital diagram and performing the equation Bond Order = .5 * (# of bonding electrons - # of antibonding electrons). However, when you draw the Lewis structure of B2, you get a triple bond. I always thought bond order corresponded to the number of bonds.
The spatial and energetic properties of electrons are described by quantum mechanics as atomic or molecular orbitals that contain these ele...
Nov 30, 2021 · Molecular orbital diagram practice worksheet. ... What is the bond order for B2? (4 bondingIn this worksheet, we will practice using particle-in-a-box and node-counting arguments to predict molecular orbital diagrams for conjugated molecules. Draw the molecular orbital energy level diagram for F 2. Molecular Orbitals of the Second Energy Level.
A molecular orbital diagram or mo diagram is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of mol...
A molecular orbital diagram or mo diagram is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals lcao method in particular.
The valence molecular orbital diagram for the anion B2- is given. - B2- has a shorter bond than B2-The molecular orbital bond order is equal to 3/2.-B2- is paramagnetic. The MO diagram for the hydroxide ion -OH is shown.-The MO bond order is given by 2/2=1-there are 3 nonbonding MO's in this species
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular.
Nov 11, 2014 · Re: M.O. Diagram for B2 Post by Chem_Mod » Tue Nov 11, 2014 11:21 pm As discussed in class the MO diagram for B 2 shows that it has two unpaired electrons (which makes it paramagnetic) and these electrons are in bonding molecular orbitals resulting in …
I have a homework problem asking me to construct the molecular orbital diagram for methylene chloride, and I am not too sure what to do next. I have determined that all of the orbitals transform as follow: C 2S=A1 C 2Pz=A1 C 2Py=B2 C 2Px=B1 2H 1S=A1+B2 2Cl 3S=A1+B1 2Cl 3Pz=A1+B1 2Cl 3Py=A2+B2 2Cl 3Px=A1+B1 My thoughts were to construct the MO for the CH2 side, then add the two chlorines from there. Let me know if you have any pointers. thank you
The molecular orbital diagram for diboron (B 2. 2. ) is given below: As you can see, there are a total of 4 molecular bonding orbitals used to create this molecule. The magnetism of these molecules depends on the presence or absence of unpaired electrons in their Molecular Orbital diagram.
Molecular orbital diagram practice worksheet
At the moment I'm learning about molecular orbital diagrams for homonuclear molecules, namely: B2, C2, N2, O2, F2, and Ne2. I understand that the energy of the 2p sigma bond is at a higher level for B2, C2, and N2, leading to the 2p sigma bond and the 2p pi bond switching places in the MO diagram (with 2p pi bond appearing under 2p sigma bond) for B, C, and N but not for O, F, or Ne. My lectures state that this is due to s and p mixing and my textbook states that it is due to electron repulsion ...
the valence molecular orbital diagram for the anion B2- is given. Which of the following options correctly interpret this diagram? - B2- has a shorter - the MO diagram shows the relative energy and number of electrons in each MO - The MO diagram can be used to calculate bond order and predict...
This video discusses how to draw the molecular orbital (MO) diagram for the B2 (boron) molecule. The bond order of the boron molecule is also calculated and...
Procedure to draw the molecular orbital diagram of CN. 1. Find the valence electron of each atom in the CN molecule. Clearly, carbon has 4 valence electrons and nitrogen has 5. 2. Find if the molecule homo-nuclear diatomic molecular orbital or hetero-nuclear diatomic molecular orbital. Clearly, CN …
Before we can draw a molecular orbital diagram for B₂, we must find the in-phase and out-of-phase overlap combinations for boron's atomic orbitals. Then we rank them in order of increasing energy. We can ignore the #1s# orbitals, because they do not contain the valence electrons.
Oct 17, 2018 · Explain why the relative energy levels diagrams for Li2, Be2, B2, C2, N2 are different The molecular orbital theory of Li2 to F2 gives a graphical explanation. Energy level diagram for Molecular orbitals. May 25, By Mrs Shilpi Nagpal 9 . It is paramagnetic in nature. 6)Li2. Molecular orbital energy level of Li2.Molecular orbitals of Li 2, Be 2 ...

0 Response to "40 b2 molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment