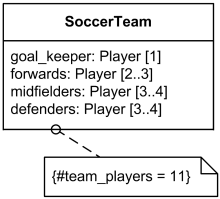
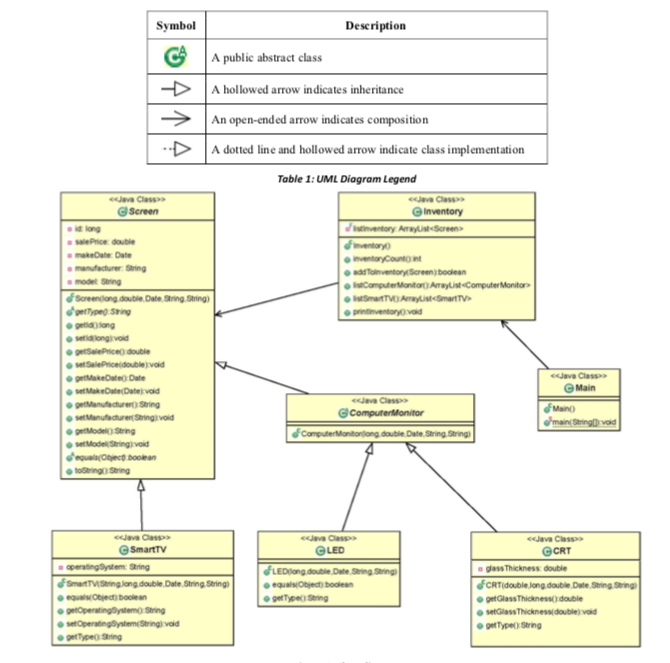
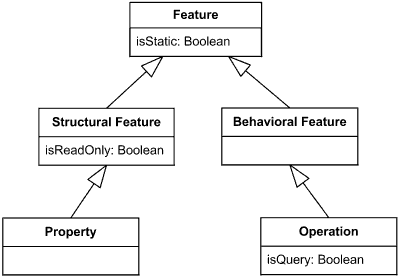
42 by convention, a class diagram contains the ____ following each attribute or method.
Post navigation ← 561 561. 228 → Read online Erlebnisstrategien Im Einzelhandel Analyse Der Zielgruppen, Der Ladengestaltung Und Der Warenprasentation Zur Vermittlung Von Einkaufserlebnissen ebook rtf
c. 1200, "either, else, otherwise, as an alternative or substitute," from Old English conjunction oþþe "either, or," which is related to Old Frisian ieftha, Middle Dutch ofte, Old Norse eða, Old High German odar, German oder, Gothic aiþþau "or." This word was extended in early Middle English (and Old High German) with an -r ending, perhaps by analogy with "choice between alternative" words that ended thus (such as either, whether); then it was reduced to oþþr, at first in unstressed positions (commonly thus in Northern and Midlands English by 1300), and finally to or, though other survived in this sense until 16c. Compare either, which is originally the same word. The contraction took place in the second term of an alternative, such as either ... or, descended from a common construction in Old English, where both words originally were oþþe (see nor). Or else "otherwise" is by c. 1300.
By convention, a class diagram contains the ____ following each attribute or method.
"quality ascribed to someone, distinguishing mark (especially an excellent or lofty one)," late 14c., from Latin attributum "anything attributed," in grammar, "predicate," noun use of neuter of attributus, past participle of attribuere "assign, allot; ascribe, impute" (see attribute (v.)). Distinguished from the verb by having stress on the first syllable. By convention, a class diagram contains the ____ following each attribute or method. Free. unlocked quiz Unlocked. Multiple Choice. unlock quiz ... (3) By convention, a class diagram contains the ____ following each attribute or method. a. data field c. data type. b. argument d. class.2 answers · 5 votes: 1) Inheritance 2) methods 3) data type 9) polymorphism 10) Subtype 11) constructor 12) data ...
By convention, a class diagram contains the ____ following each attribute or method.. An application programming interface (API) is a connection between computers or between computer programs.It is a type of software interface, offering a service to other pieces of software. A document or standard that describes how to build or use such a connection or interface is called an API specification.A computer system that meets this standard is said to implement or expose an API. late 14c., "assign, bestow," from Latin attributus, past participle of attribuere "assign to, allot, commit, entrust;" figuratively "to attribute, ascribe, impute," from assimilated form of ad "to" (see ad-) + tribuere "assign, give, bestow" (see tribute). Related: Attributed; attributing. 1610s, "an illustrative figure giving only the outlines or general scheme of the object;" 1640s in geometry, ";a drawing for the purpose of demonstrating the properties of a figure;" from French diagramme, from Latin diagramma ";a scale, a musical scale," from Greek diagramma "geometric figure, that which is marked out by lines," from diagraphein "mark out by lines, delineate," from dia "across, through" (see dia-) + graphein "write, mark, draw" (see -graphy). Related: Diagrammatic; diagrammatically. The verb, "to draw or put in the form of a diagram," is by 1822, from the noun. Related: Diagrammed; diagramming. word-forming element making nouns of quality, state, or condition, from Middle English -our, from Old French -our (Modern French -eur), from Latin -orem (nominative -or), a suffix added to past participle verbal stems. Also in some cases from Latin -atorem (nominative -ator). In U.S., via Noah Webster, -or is nearly universal (but not in glamour), while in Britain -our is used in most cases (but with many exceptions: author, error, tenor, senator, ancestor, horror etc.). The -our form predominated after c. 1300, but Mencken reports that the first three folios of Shakespeare's plays used both spellings indiscriminately and with equal frequency; only in the Fourth Folio of 1685 does -our become consistent. A partial revival of -or on the Latin model took place from 16c. (governour began to lose its -u- 16c. and it was gone by 19c.), and also among phonetic spellers in both England and America (John Wesley wrote that -or was ";a fashionable impropriety" in England in 1791). Webster criticized the habit of deletin
early 15c., "regular, systematic treatment of disease," from Latin methodus "way of teaching or going," from Greek methodos "scientific inquiry, method of inquiry, investigation," originally "pursuit, a following after," from meta "in pursuit or quest of" (see meta-) + hodos ";a method, system; a way or manner" (of doing, saying, etc.), also ";a traveling, journey," literally ";a path, track, road,"; a word of uncertain origin (see Exodus). Meaning "any way of doing anything, orderly regulation of conduct with a view to the attainment of an end" is from 1580s; that of "orderliness, regularity" is from 1610s. Meaning ";a system or complete sent of rules for attaining an end" is from 1680s. In reference to a theory of acting associated with Russian director Konstantin Stanislavski (1863-1938), it is attested from 1923. late 14c., "action of following, an act of following," verbal noun from follow (v.). Meaning ";a body of disciples or retainers" is from mid-15c.; Old English used folgoð in this sense. By convention, a class diagram contains the ____ following each attribute or method. Data type. Rating: 5 · 6 reviews By convention, a class diagram contains the ____ following each attribute or method. a. class. b. argument. c. data type.
a. fontsb. methods. c. class namesd. arrays. 13. By convention, a class diagram contains the ____ following each attribute or method. ... hidingd.inlining Question 8 0 out of 3.34 points By convention, a class diagram contains the ____ following each attribute or method. A class diagram contains the data type following each attribute or method. 4. Option b. UML diagram. In UML diagram, the arrows are used to show inheritance ...2 answers · 0 votes: 1) Inheritance 2) methods 3) data type 9) polymorphism 10) Subtype 11) constructor ... Old English ælc (n., pron., adj.) "any, all, every, each (one)," short for a-gelic "ever alike," from a "ever" (see aye (adv.)) + gelic "alike" (see like (adj.)). From a common West Germanic expression *aina-galīk (source also of Dutch elk, Old Frisian ellik, Old High German iogilih, German jeglich "each, every"). Originally used as we now use every (which is a compound of each) or all; modern use is by influence of Latin quisque. Modern spelling appeared late 1500s. Also see ilk, such, which.
Old English be- (unstressed) or bi (stressed) "near, in, by, during, about," from Proto-Germanic *bi "around, about," in compounds often merely intensive (source also of Old Saxon and Old Frisian bi "by, near," Middle Dutch bie, Dutch bij, German bei "by, at, near," Gothic bi "about"), from PIE *bhi, reduced form of root *ambhi- "around." As an adverb by c. 1300, "near, close at hand." OED (2nd ed. print) has 38 distinct definitions of it as a preposition. Originally an adverbial particle of place, which sense survives in place names (Whitby, Grimsby, etc., also compare rudesby). Elliptical use for "secondary course" was in Old English (opposed to main, as in byway, also compare by-blow "illegitimate child," 1590s, Middle English loteby ";a concubine," from obsolete lote "to lurk, lie hidden"). This also is the sense of the second by in the phrase by the by (1610s). By the way literally means "along the way" (c. 1200), hence "in passing by," used figuratively to introduce a tangential observation ("incidentall

Ch 15 Teacher Made Assessment Strategies Instructional Methods Strategies And Technologies To Meet The Needs Of All Learners
The first class will contain the required state and behaviour for the object, but NO main method. The second class will contain simply the main method to give the JRE an entry point into the program, a line to instantiate a new object based upon the first class and a few lines to exercise the functionality of the first class.
(3) By convention, a classdiagram contains the ____ following each attribute or method. a. datafield c. data type. b. argument d. class. (4) Conventionally, ...
early 15c., convencioun, ";a formal agreement, covenant, treaty," also ";a formal meeting or convention" (of rulers, etc.), also ";a private or secret agreement," from Old French convencion "agreement" and directly from Latin conventionem (nominative conventio) ";a meeting, assembly; an agreement," noun of action from past-participle stem of convenire "unite, be suitable, agree, assemble," from assimilated form of com "with, together" (see con-) + venire "to come" (from PIE root *gwa- "to go, come"). Originally of princes, powers, and potentates. In diplomacy, of agreements between states, from mid-15c.; of agreements between opposing military commanders from 1780. Meaning ";a formal or recognized assembly of persons for a common objective," especially involving legislation or deliberation, is from mid-16c. Conventions were important in U.S. history and the word is attested in colonial writings from 1720s; in reference to political party nomination meetings by 1817 (originally at the state level; national conventi
(3) By convention, a class diagram contains the ____ following each attribute or method. a. data field c. data type. b. argument d. class.2 answers · 5 votes: 1) Inheritance 2) methods 3) data type 9) polymorphism 10) Subtype 11) constructor 12) data ...
By convention, a class diagram contains the ____ following each attribute or method. Free. unlocked quiz Unlocked. Multiple Choice. unlock quiz ...
"quality ascribed to someone, distinguishing mark (especially an excellent or lofty one)," late 14c., from Latin attributum "anything attributed," in grammar, "predicate," noun use of neuter of attributus, past participle of attribuere "assign, allot; ascribe, impute" (see attribute (v.)). Distinguished from the verb by having stress on the first syllable.

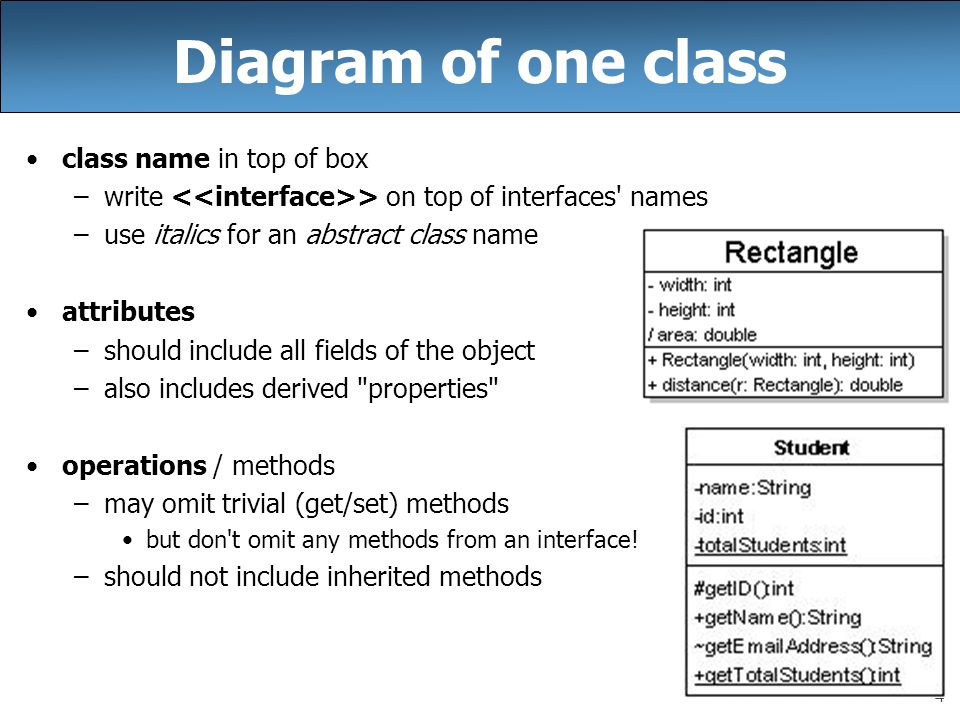
Uml Class Diagrams 1 These Lecture Slides Are Copyright C Marty Stepp They May Not Be Rehosted Sold Or Modified Without Expressed Permission Ppt Download



















0 Response to "42 by convention, a class diagram contains the ____ following each attribute or method."
Post a Comment