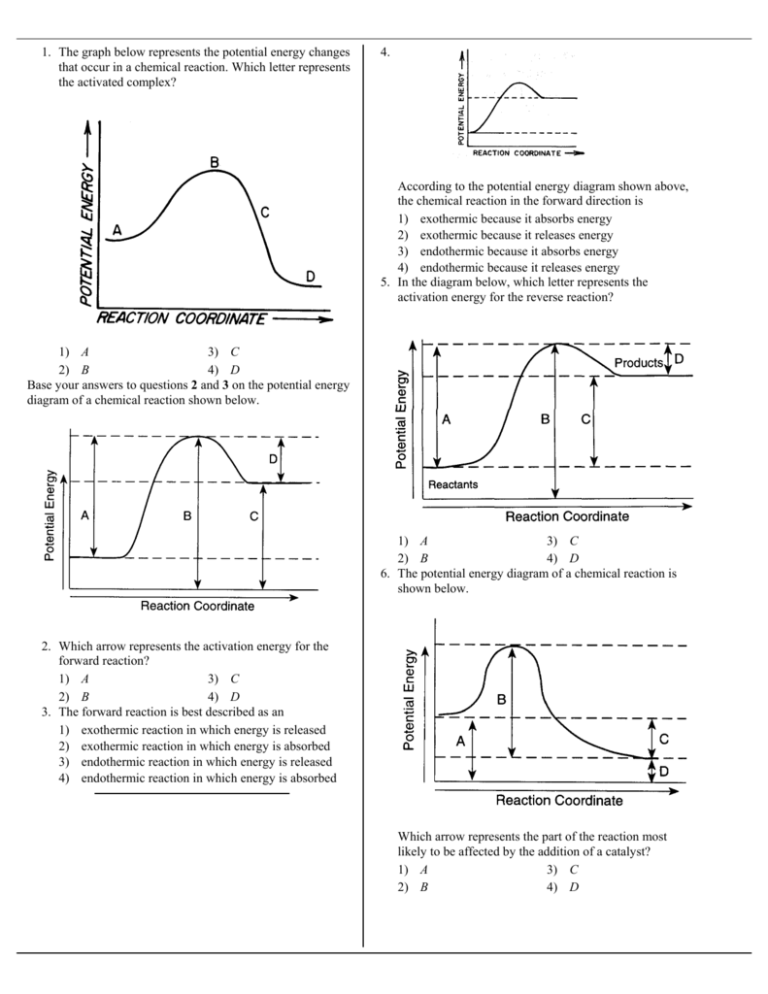
40 labeled reaction coordinate diagram
Chemistry questions and answers. Label the following reaction coordinate diagram. Energy Reactant (s) Transition State Product (s) Activation Energy (forward) Transition State Activation Energy (forward) Energy Enthalpy of Enthalpy of Reaction Product (s) Reaction AHrxn Reactant (s) Reaction Coordinate Reaction Coordinate Reset Zoom. 1! Energy/Reaction Coordinate! Diagrams! Thermodynamics, Kinetics ! Dr. Ron Rusay" A Reaction Coordinate (Energy) Diagram Thermodynamic Quantities Gibbs standard free energy change (ΔGo) Enthalphy (ΔHo): the heat given off or absorbed during a reaction
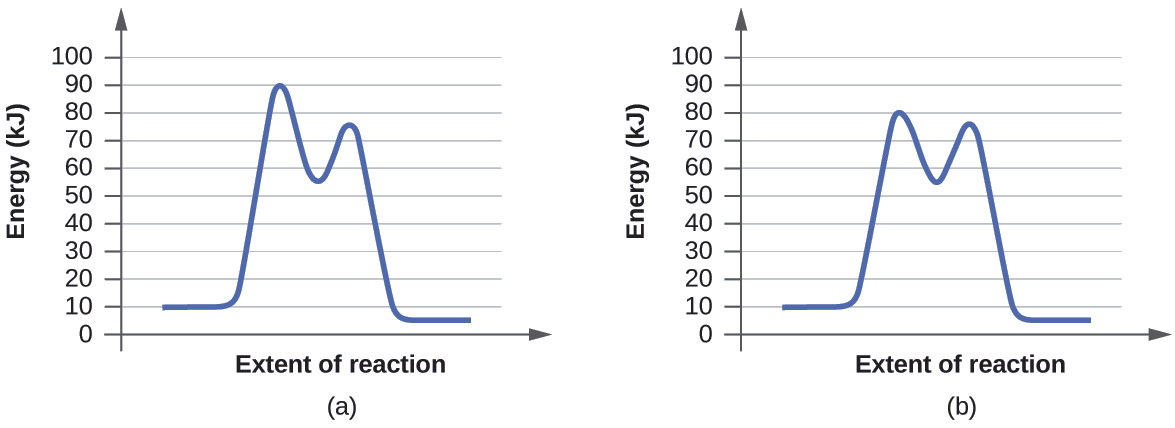
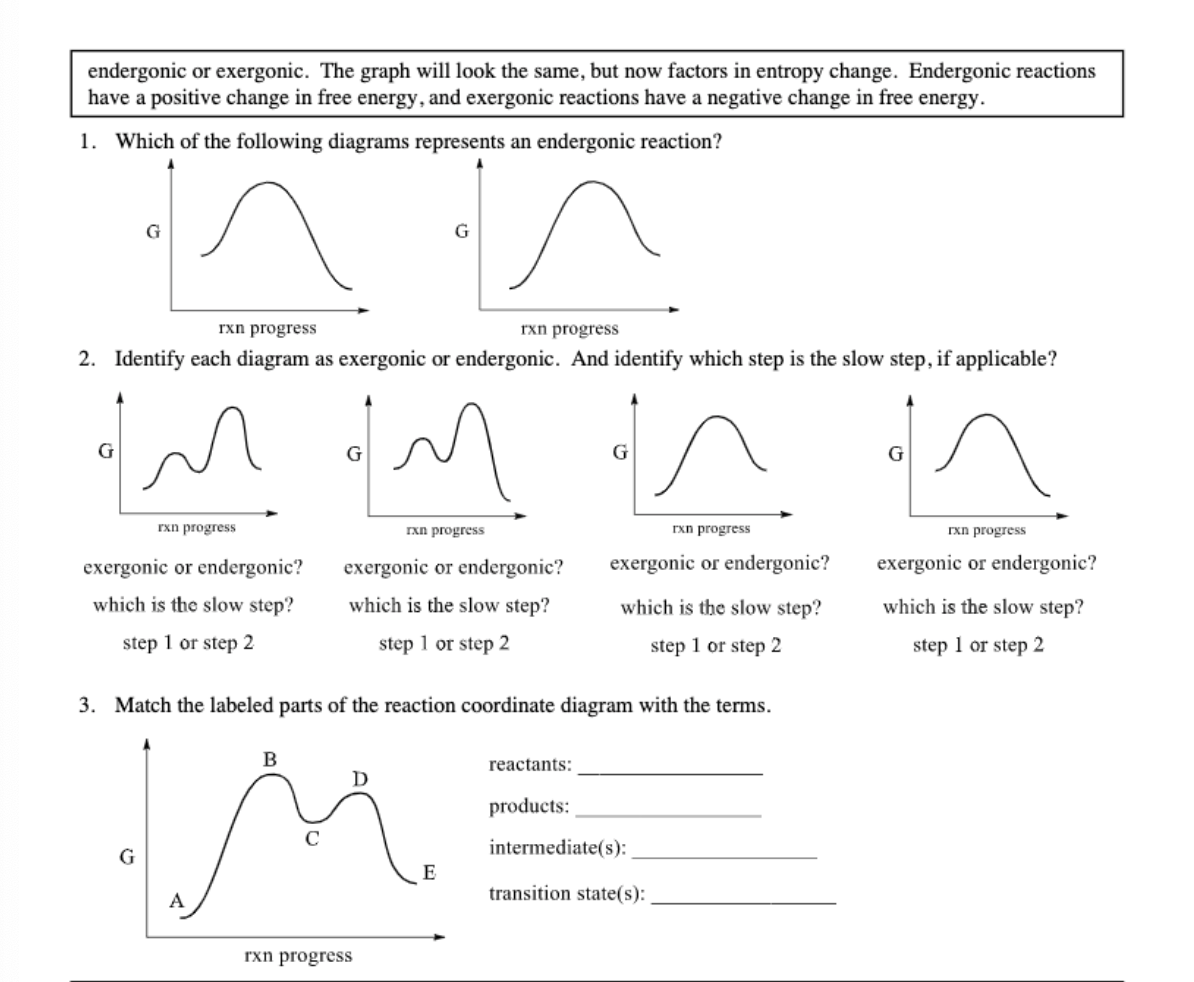
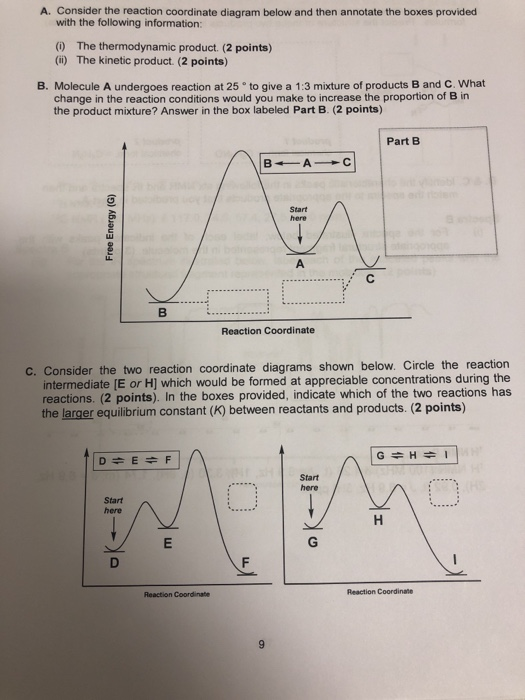
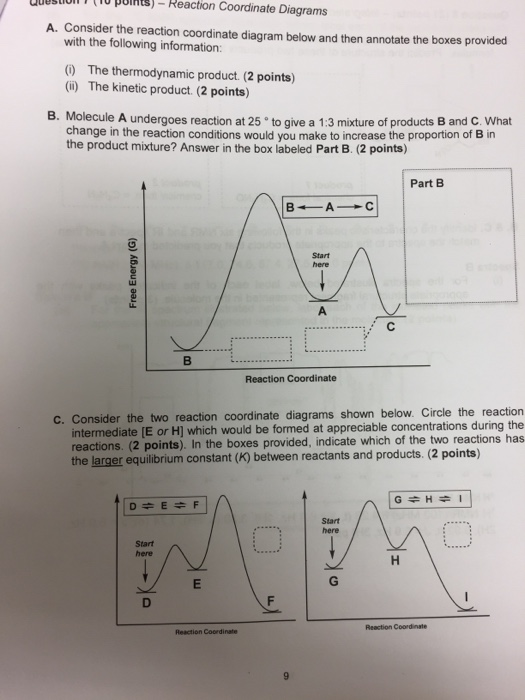
Draw a properly labeled reaction coordinate diagram for a reaction with the following. criteria: make sure to clearly indicate Î G and any activation energies (for the forward reaction) as well as all intermediates and transition states. a) exergonic 3 step reaction. b) the first step is the rate-determining step

Labeled reaction coordinate diagram
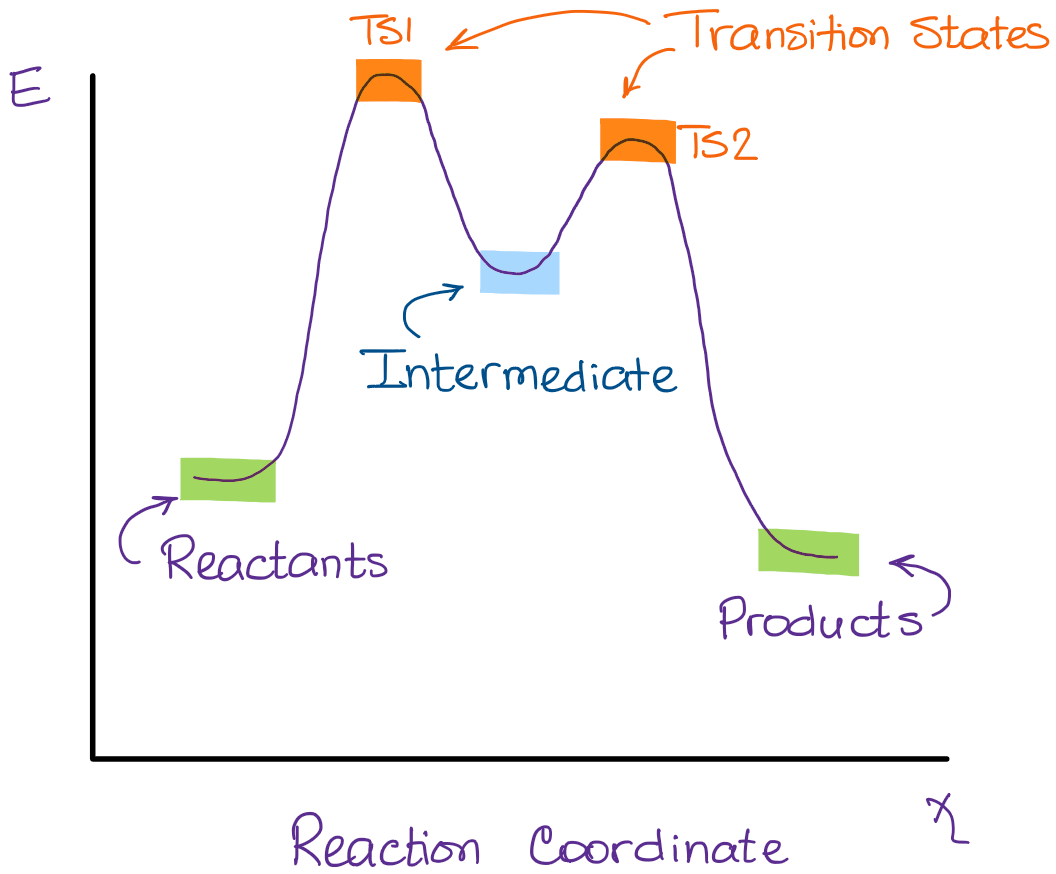
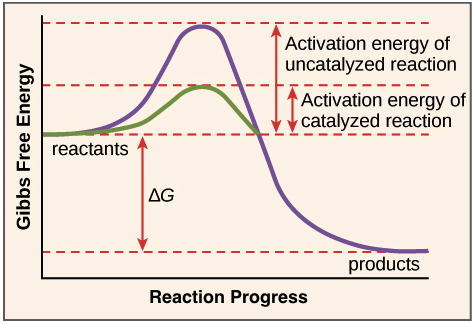
Reaction coordinate diagrams. The intrinsic reaction coordinate (IRC), derived from the potential energy surface, is a parametric curve that connects two energy minima in the direction that traverses the minimum energy barrier (or shallowest ascent) passing through one or more saddle point(s). However, in reality if reacting species attains enough energy it may deviate from the IRC to some extent. Labelthe following reaction coordinate diagram by matching betweenletters and numbers: Answer +20. Watch. 1. answer. 0. watching. 31. views. For unlimited access to Homework Help, a Homework+ subscription is required. Jean Keeling Lv2. 10 Aug 2019. Unlock all answers. Get 1 free homework help answer. Unlock ... One such reaction is catalytic hydrogenation, the process by which hydrogen is added across an alkene C=C bond to afford the saturated alkane product. A comparison of the reaction coordinate diagrams (also known as energy diagrams) for catalyzed and uncatalyzed alkene hydrogenation is shown in Figure 1. Figure 1.
Labeled reaction coordinate diagram. Label the following reaction coordinate diagram by matching between letters and numbers: (diagram in kinetics pt 2 folder in energy diagram folder on desktop) 1- J ... -Label the multi-step reaction energy diagram below using the letters corresponding to the labels on the left. There are more labels than needed; each label can be used only once. c) Using a reaction coordinate diagram and the Hammond postulate, plot if you would expect an early or late transition state for the first step (A to B) of this reaction. Label this plot "C". (2 points) PE Reaction coordinate d) Based on your answer to part (c), what range would you expect the β LG values fall within? Explain your answer. About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators ... Solved Label The Following Reaction Coordinate Diagram By. Click Images to Large View Solved Label The Following Reaction Coordinate Diagram By. Solved Use The Molecular Orbital Energy Diagram Below To. Click Images to Large View Solved Use The Molecular Orbital Energy Diagram Below To.
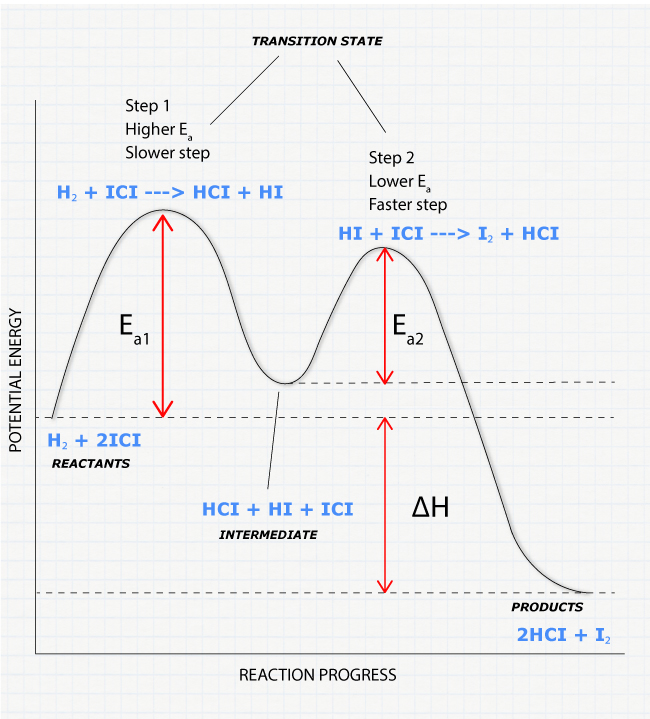
Draw a reaction coordinate diagram for this reaction as above but add the activation energy, E a, for the catalyzed reaction on the appropriate curve in this diagram and label it. This is a bit more subtle since .Types of catalysts (article) | Kinetics | Khan AcademySection The Rate of a Reaction Use curved arrows to show the mechanism and the conversion between resonance structures. Make sure to add any missing charges. Note the use of a generic base in the last step. b) Label the reaction coordinate diagram for a typical EAS reaction shown below by correctly placing the letter for each structure on the diagram. Reaction Coordinate Diagram of Ozone Photolysis The reaction coordinate diagram for the ozone photolysis reaction is a little different from those above because this is an endothermic reaction . Together, the products O 2 and atomic O, have a higher energy than the reactant O 3 and energy must be added to the system for this reaction. transition state theory is given. A reaction energy diagram (Figure 1) is presented on the chalk board (complete with axes labeled: potential energy vs. reaction coordinate (or reaction progress)). The activation energy, Ea, (the change in energy from reactants to the top of the "hill") is labeled.
Transcribed image text: A reaction coordinate diagram is shown below for the reaction of A to form E. Answer the following question. Identify the transition state(s ... 34. (a) On the reaction coordinate diagram shown below, label the transition state and the overall free-energy change (∆G) for the endergonic (+∆G) reaction? (c) Draw a second curve showing the energetics of the reaction if it were enzyme-catalyzed. (8 pts) Free energy, G Reaction coordinate (AÆB) Products (B) Reactants (A) Page 7 Reaction coordinate Transition state ΔG 1 ‡ ΔG 1 ‡' ΔG -1 ‡' ΔG -1 ‡ ΔG° G A G P Initial state Final state Fig. 4.2 A free energy (G) diagram for a simple reversible exothermic reaction A↔P(solid and broken lines). G A and G P represent the average free energies per mole for the reactant A and the product P, the initial and ... Problem Details. Label the following reaction coordinate diagram by matching between letters and numbers: All Chemistry Practice Problems Energy Diagram Practice Problems. Q. A reaction coordinate diagram is shown below for the reaction of A to form E. Answer the following questions.i) Identify the transition state (s)?ii) W...
1i. Draw an energy vs reaction coordinate diagram to illustrate a reaction in which the energy of the products is greater than the energy of the reactants. Label all quantities as per Fig. 1. See diagram (3) in sample exercise 14.10 on pg 595 of Brown and LeMay, 11th ed.
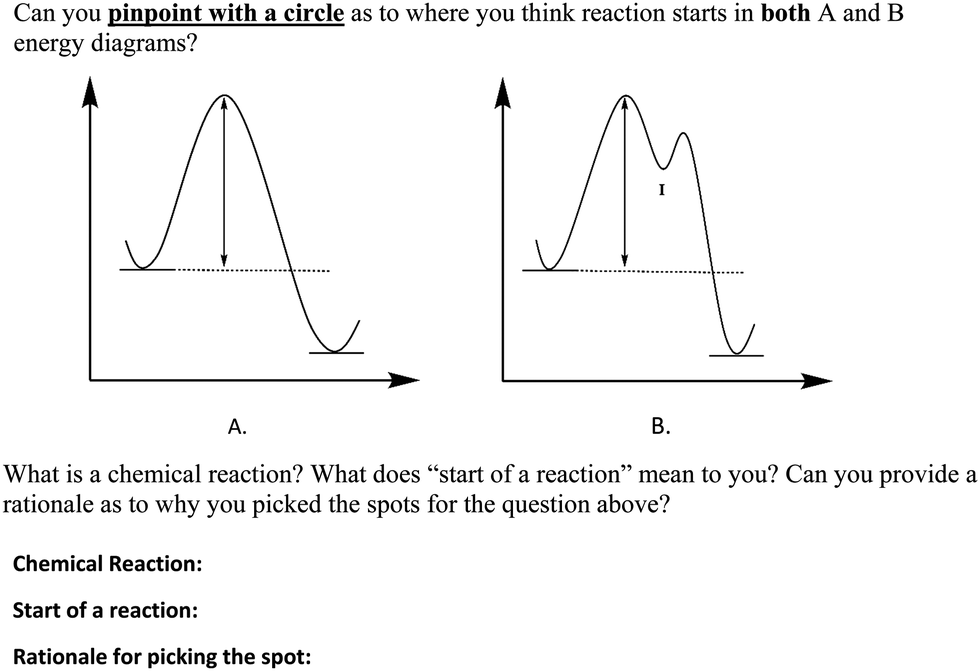
1. Draw and label a pair of axes. Label the vertical axis "Potential Energy" and the horizontal axis "Reaction Coordinate". 2. Draw and label two short horizontal lines to mark the energies of the reactants and products. 3. Draw the energy level diagram. There must be a hump in the curve to represent the energy level of the activated complex. 4.
gram to represent the heat of the reaction. Label the arrow AH. The potential energy diagram of a chemical reaction is shown below. 200 - 150 100 - 50 (a) (b) (c) Reaction Coordinate Does this potential energy diagram represent an exothermic or an endothermic reactio ? [Explain why.] What is the minimum amount of energy

From The Above Diagram Which Labeled Arrow A B C D Represents The Activation Energy For The Reverse Reaction
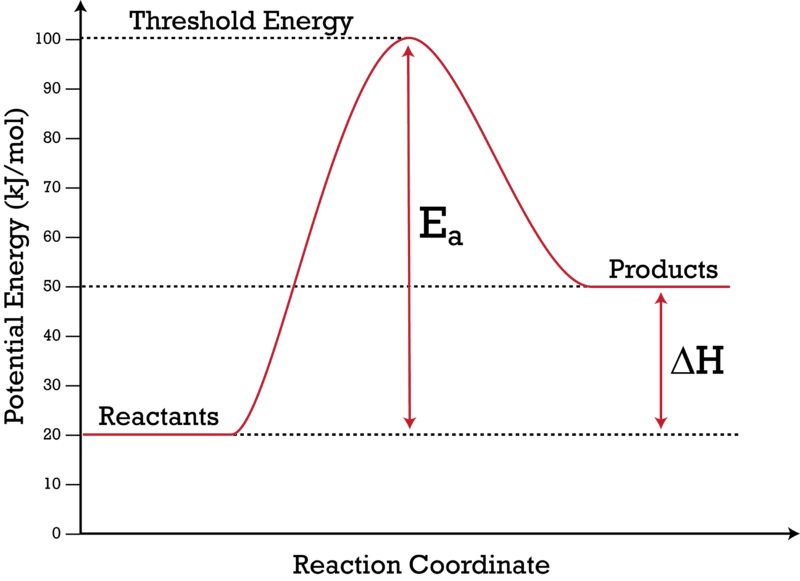
8. A lit fuse was required to initiate the reaction in the flare. Use this information, along with your previous results to correctly label the reaction coordinate diagram shown below. Use these symbols to label each item in your diagram: reactants (R), products (P), reaction enthalpy (AH), and activation energy (Ea).
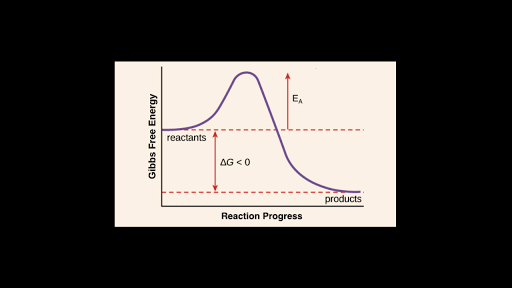
The fully filled in reaction coordinate diagram is displayed below. The arrow marked in the question represents the activation energy, which is the energy barrier that must be overcome in order for the reactants to form products. This reaction is also exothermic because the energy of the products is lower than that of the reactants.
Construct the gas phase Reaction Coordinate Diagram for the Cl + CH3Cl SN2 reaction by plotting the relative energy in kJmol 1 versus Cl + C | {z} Distance H3 Cl. Place the Reaction Coordinate Diagram on the graph provided below and plot the energies on a relative energy scale. Label the various species along the reaction pathway. 0 5 10 15 20 ...
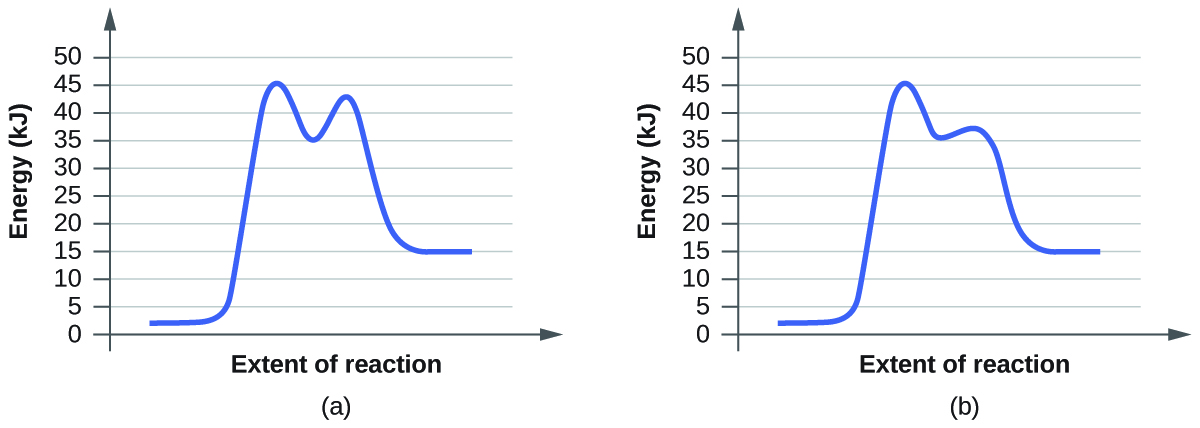
much more rapid. Draw and correctly label reaction coordinate diagrams that represent each of the two situations and describe how each diagram reflects the thermodynamics and kinetics of the situation. Your diagrams should bear some resemblance to the picture at the right and meet the following requirements: 1) the axes
126 MHR Chemistry 12 Solutions Manual 978 --07-106042-4 13. Consider the reaction below: C + D → CD E a(fwd) = +61 kJ, E a(rev) = +150 kJ Draw and label a potential energy diagram for this reaction. Calculate and label
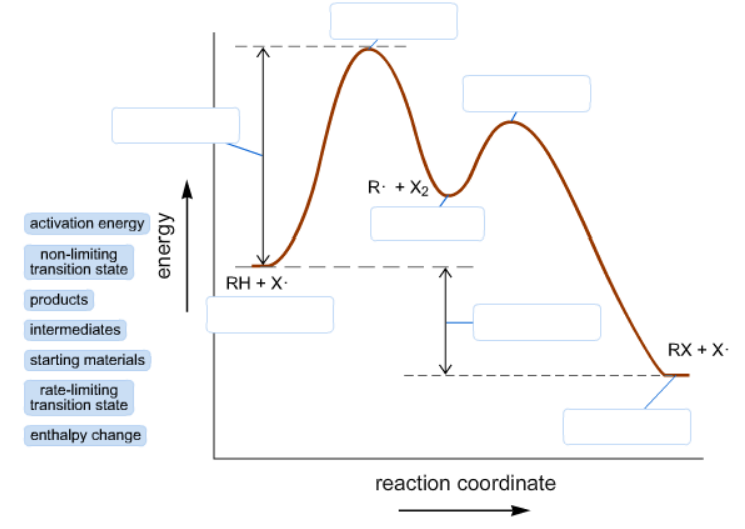
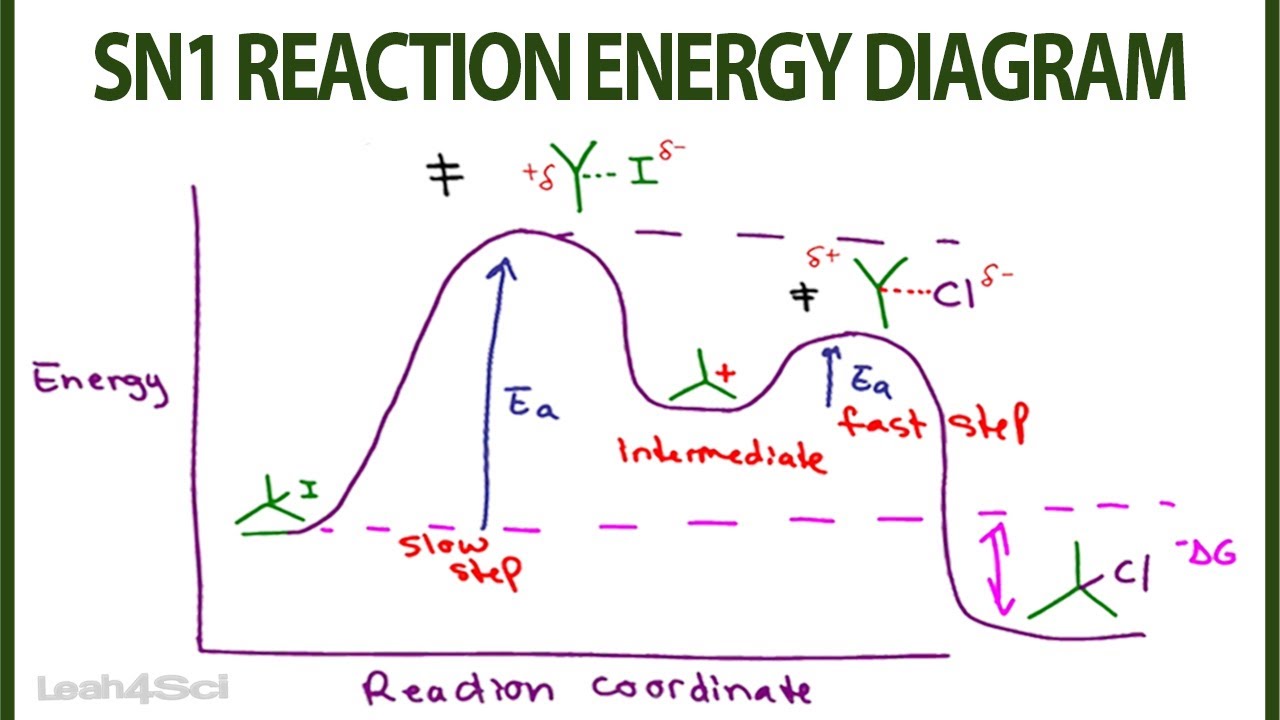
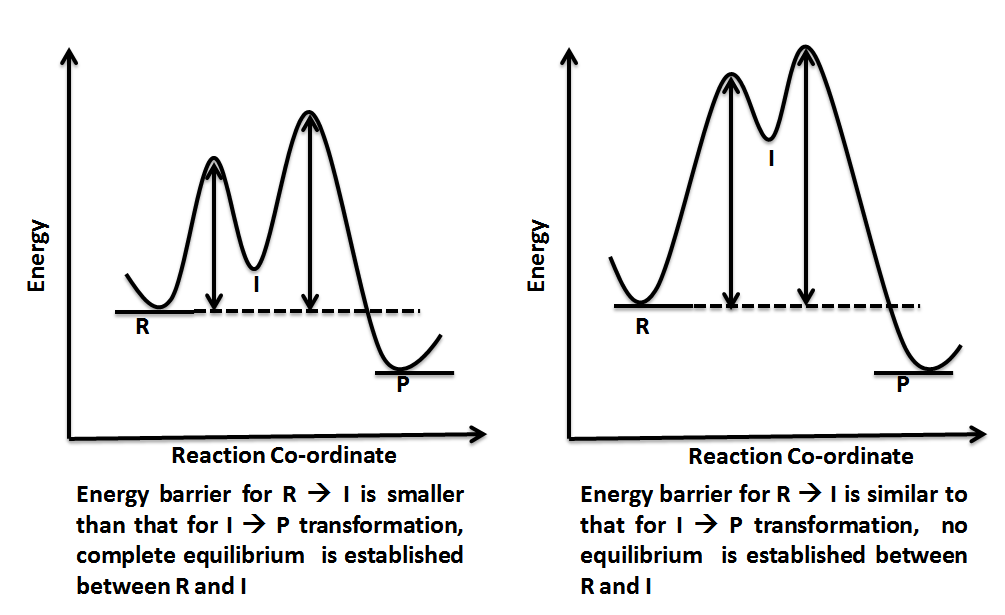
reaction coordinate Br Figure 9.11 Reaction free-energy diagram for the S N1-E1 solvolysis reaction of (CH 3) 3CBr with ethanol.The rate-limiting step,ionization of the alkyl halide (red curve),has the transition state of highest standard free energy.The
Explains the energy versus reaction coordinate diagram. Relates the activation energies for the forward and reverse reactions of an exothermic reaction to th...
The potential energy diagram represents a reaction. Reaction Coordinate Which arrow represents the activation energy of the forward reaction? On the set of axes below, sketch the potential energy diagram for an endothermic chemical reaction that shows the activation energy and the potential energy of the reactants and the potential energy of ...
One such reaction is catalytic hydrogenation, the process by which hydrogen is added across an alkene C=C bond to afford the saturated alkane product. A comparison of the reaction coordinate diagrams (also known as energy diagrams) for catalyzed and uncatalyzed alkene hydrogenation is shown in Figure 1. Figure 1.
Labelthe following reaction coordinate diagram by matching betweenletters and numbers: Answer +20. Watch. 1. answer. 0. watching. 31. views. For unlimited access to Homework Help, a Homework+ subscription is required. Jean Keeling Lv2. 10 Aug 2019. Unlock all answers. Get 1 free homework help answer. Unlock ...
Reaction coordinate diagrams. The intrinsic reaction coordinate (IRC), derived from the potential energy surface, is a parametric curve that connects two energy minima in the direction that traverses the minimum energy barrier (or shallowest ascent) passing through one or more saddle point(s). However, in reality if reacting species attains enough energy it may deviate from the IRC to some extent.
Solved Draw A Reaction Coordinate Diagram That Is Consistent With The Shown Chemical Equations And Observations Clearly Label Reactants Products Course Hero
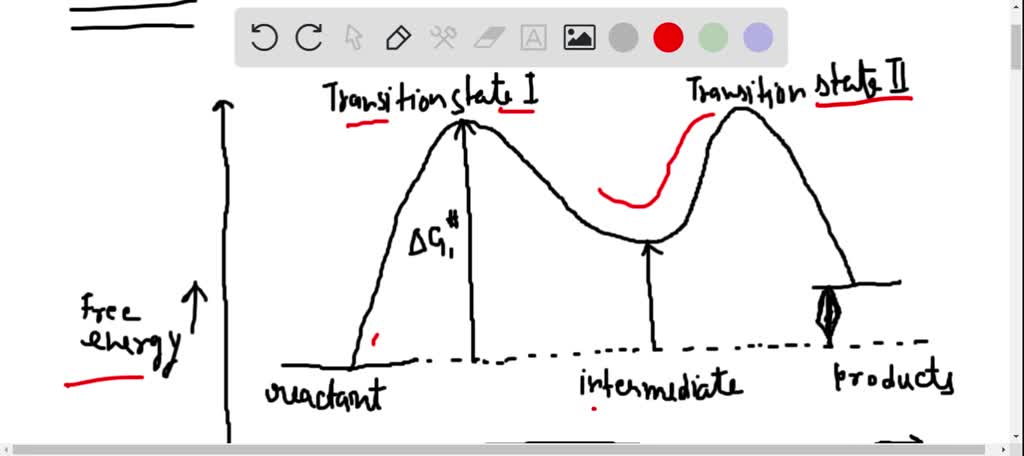
Solved Draw A Reaction Coordinate Diagram For A Two Step Reaction In Which The First Step Is Endergonic The Second Step Is Exergonic And The Overall Reaction Is Endergonic Label The Reactants Products Intermediates

May The Reaction Coordinate In A Chemical Reaction Coordinate Diagram Be Represented By A Time Axis Physics Stack Exchange

Draw A Labelled Reaction Coordinate Diagram For The Both Sn Reactions Label The Activation Energy Free Homeworklib

Draw A Labeled Reaction Energy Diagram For A Two Step Reaction With An Early First Transition State And A Late Second Transition State State Whether The Transition States Resemble The Starting Material Intermediate Or









0 Response to "40 labeled reaction coordinate diagram"
Post a Comment