40 free body diagram roller coaster
The two diagrams below depict the free-body diagram for a 1000-kg roller coaster on the first drop of two different roller coaster rides. Use the above principles of vector resolution to determine the net force and acceleration of the roller coaster cars. Assume a negligible effect of friction and air resistance. Use Newton's second law to determine the normal force acting upon Anna's 1000 kg roller coaster car. Steps 1 and 2 involve the construction of a free body diagram and the identification of known and unknown quantities. This is shown in below. Given Info: m = 1000 kg Given Info: m = 1000 kg a top = 15.0 m/s 2, down a bottom = 20.0 m/s 2, up Find:
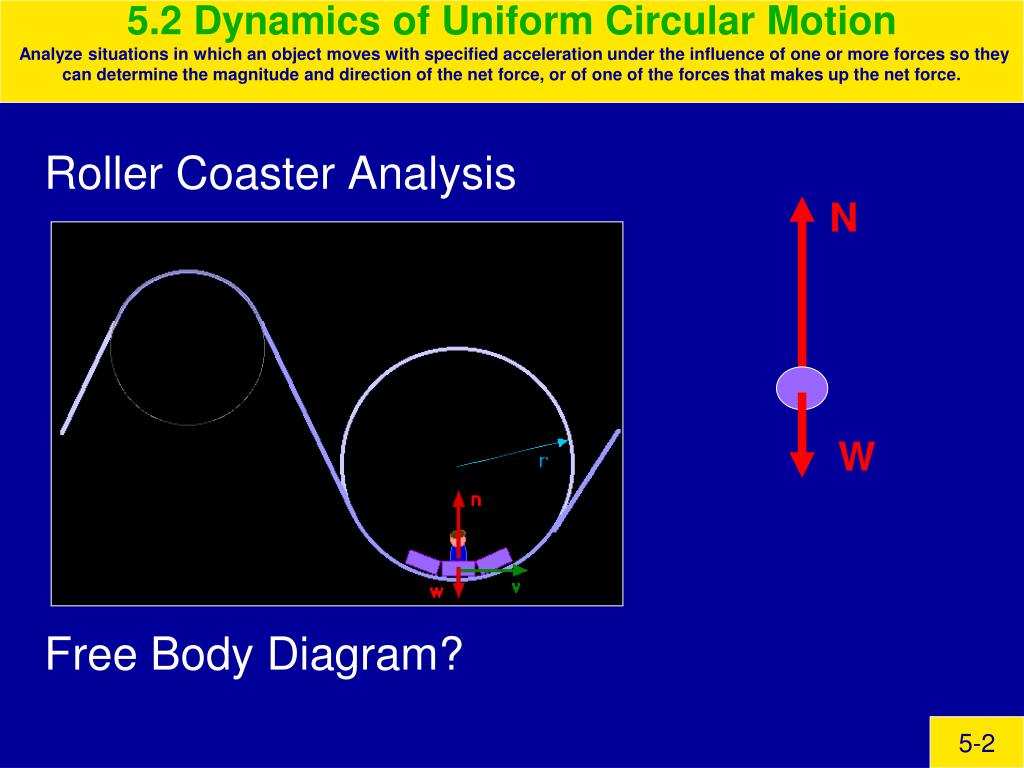
Let's start with the roller coaster / water bucket example. As usual, begin with a free-body diagram. Follow this up with an appropriate choice of coordinate system. At rest, the free-body diagram is simple, with an upward normal force and a downward force of gravity. These are the only two forces in the system even when circular motion is ...
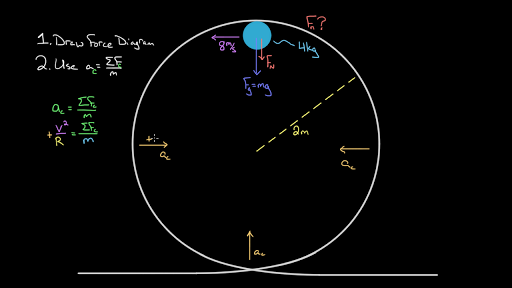
Free body diagram roller coaster
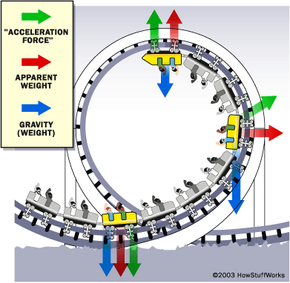
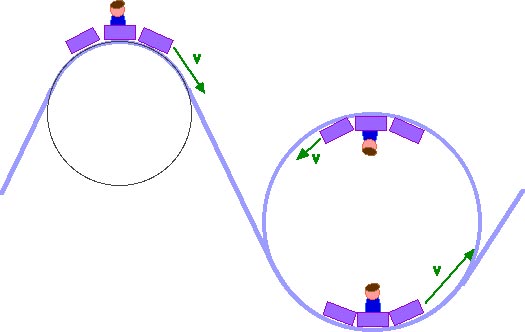
If the speed of a roller coaster car is 15 m/s at the top of a 20 m loop, and 25 m/s at the bottom. What is the cars average angular acceleration if it takes 1.6 seconds to go from the top to the bottom? t f 0 w w R V w 2.5 10 25 wf 1.5 10 15 w 0 = 0.64 rad/s2 1.6 2.5 1.5 A stunt plane does a series of vertical loop-the-loops. Al what point in the circle does the pilot feel the heaviest? Explain. Include a free-body diagram with your explanation. 19. A roller-coaster car goes around the inside of a loop-the-loop. One of the following statements is true at the highest point in the loop, and one is true at the ... Free-body diagram for the water. Sketch a free-body diagram for just the water, if the speed is less than the critical speed. a = g "down" is down. mg m. b. g. N=0. If same . v. o, same path! Roller coaster. On a roller coaster, when the coaster is traveling fast at the bottom of a circular loop, you feel much heavier than usual. Why? Draw ...
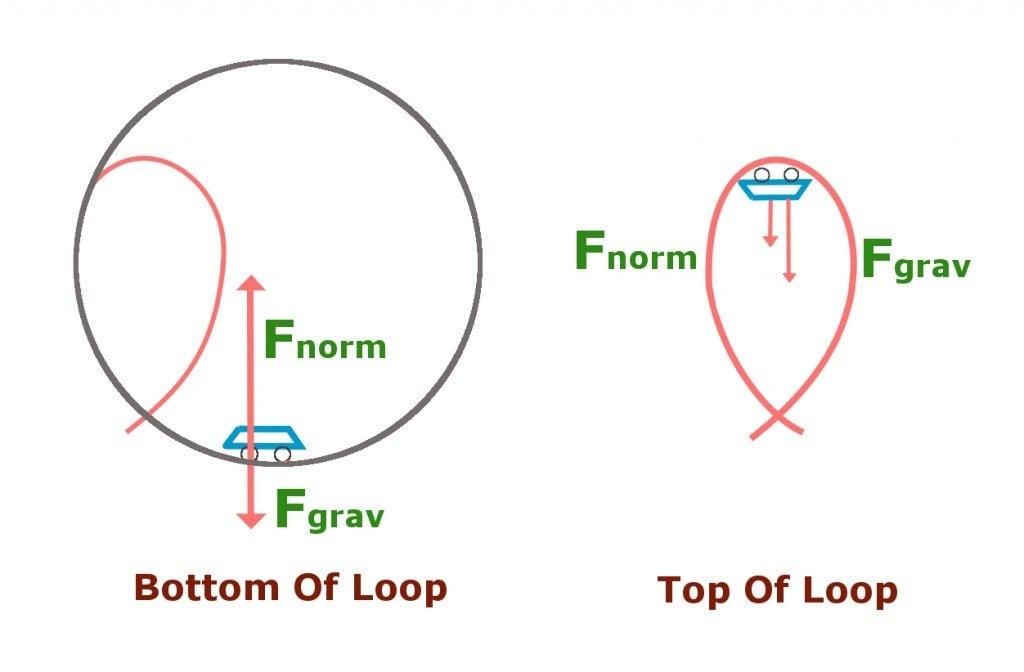
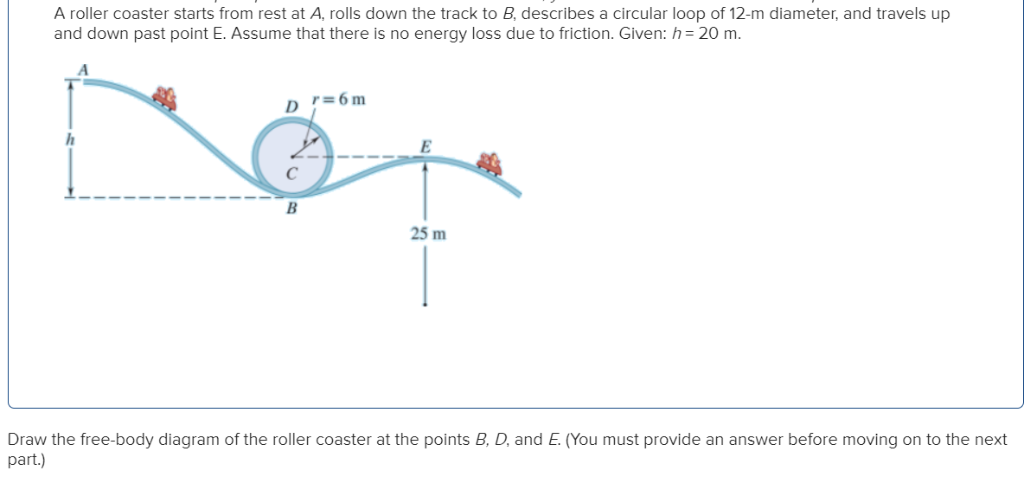
Free body diagram roller coaster. Physics Q&A Library Draw a free body diagram of the roller coaster car with all appropriate forces in three locations. At the bottom of the loop Halfway up the loop (or ¼ of the way around the entire thing) At the top of the loop Based only on your diagrams, where will the rider experience the greatest force? Q. In which free-body diagram are the forces correct on a roller coaster car when it is upside down at the top of the . loop-de loop? answer choices . alternatives . answer explanation . Tags: Topics: Question 9 . SURVEY . Ungraded . 30 seconds ... Draw the free body diagram of the roller coaster car. Chapter 14, Problem 72P is solved. View this answer View this answer View this answer done loading The free body diagram above depicts the roller coaster at the bottom of the loop, where Normal Force is pointed upwards and Force of Gravity is pointed downwards. This gives us a net force equation of Fnet = Fn - Fg. The free body diagram above depicts the roller coaster at the left of the loop, where Normal Force is pointed rightwards and ...
This physics video tutorial explains how to calculate the normal force at the bottom and at the top of the hill given the speed and radius of the circular hi... Free-body diagrams are widely used in physics to show the relative magnitude and direction of all forces acting upon objects in given situations. For this problem, a body's weight and surface friction are the forces acting on a spherical body rolling on an incline. ... roller coaster: An amusement park ride that consists on an elevated ... A roller coaster car of mass 330 kg (including passengers) travels around a horizontal curve of radius 37 m. Its speed is 14 m/s. What is the magnitude and direction of the total force exerted on the car by the track? The free-body diagram for this situation is very similar to that of the last problem. In this case we will consider the only two ... Which free-body diagram describes the car at this instant? A. A roller coaster car does a loop-the-loop. Which of the free-body diagrams shows the forces on the car at the top of the loop? Rolling friction can be neglected. E. A coin sits on a turntable as the table steadily rotates counterclockwise. What force or forces act in the plane of the ...
The two diagrams below depict the free-body diagram for a 1000-kg roller coaster on the first drop of two different roller coaster rides. Use the above principles of vector resolution to determine the net force and acceleration of the roller coaster cars. Assume a negligible effect of friction and air resistance. The free-body diagram of a block being pushed up a rough ramp is best represented by a. A d. D b. B e. E c. C ... Imagine you are a passenger upside-down at the top of a vertical looping roller coaster. The centripetal force acting on you at this position a. is perhaps the least of anywhere in the loop The two diagrams below depict the free-body diagram for a 1000-kg roller coaster on the first drop of two different roller coaster rides. Use the above principles of vector resolution to determine the net force and acceleration of the roller coaster cars. Assume a negligible effect of friction and air resistance. The motion of objects along curved sections of roller coaster tracks (loops, turns, bumps and hills, etc.) can be analyzed using a free-body diagram, ...
This video describes different forces that are encountered during a roller coaster ride. Potential and kinetic energy are mentioned here. This is a good place to mention frames of reference, which will be looked at with greater detail later in the course. ... Free body diagrams are simple representation of a given situation. At this level ...
Inclined Plane Practice The two diagrams below depict the free-body diagram for a 1000-kg roller coaster on the first drop of two different roller coaster rides. Use the principles of vector resolution to determine the net force and acceleration of the roller coaster cars. Assume a negligible affect of friction and air resistance. The F grav can be calculated from the mass of the object.
Roller coaster loops assume a tear-dropped shape that is geometrically referred to as As depicted in the free body diagram, the magnitude of Fnorm is always. Energy conservation and forces on a train in a vertical roller coaster loop.. Figure 3 shows free-body diagrams for a rider in the front, middle and back of.
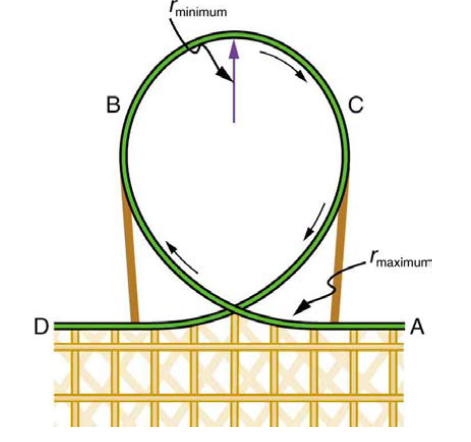
Modern Roller Coasters Have Vertical Loops Like The One Shown In Figure 6 38 The Radius Of Curvature Is Smaller At The Top Than On The Sides So That The Downward Centripetal Acceleration
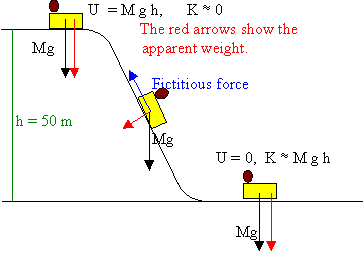
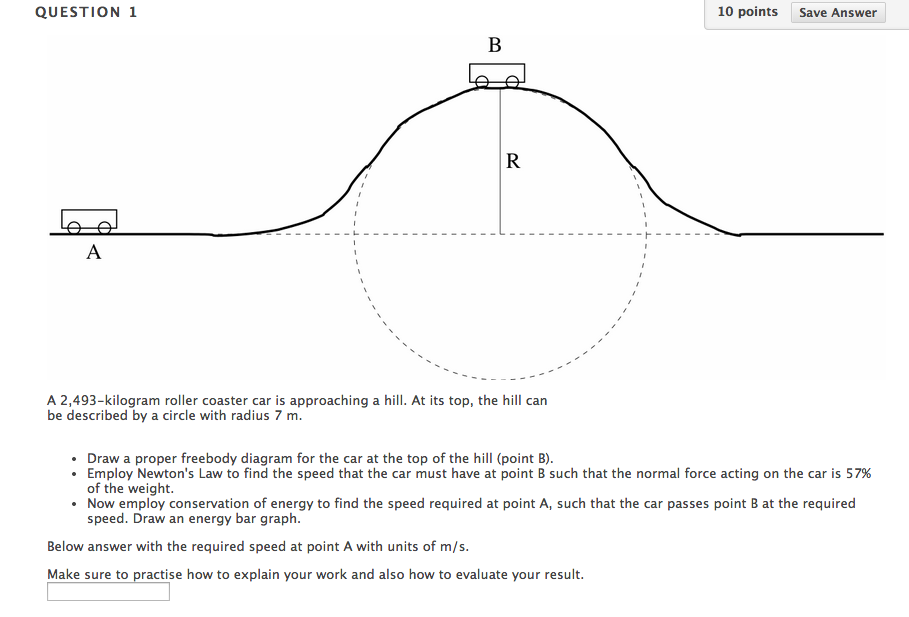
We might ask how fast the coaster can go until the rider just (barely) looses contact with the seat. That means the normal force between seat and rider is zero. That occurs for. n = mg - m v 2 / r = 0. m v 2 / r = mg. v 2 / r = g. v 2 = g r. We have described this with a diagram showing a guest on the top of a hill of a roller coaster.
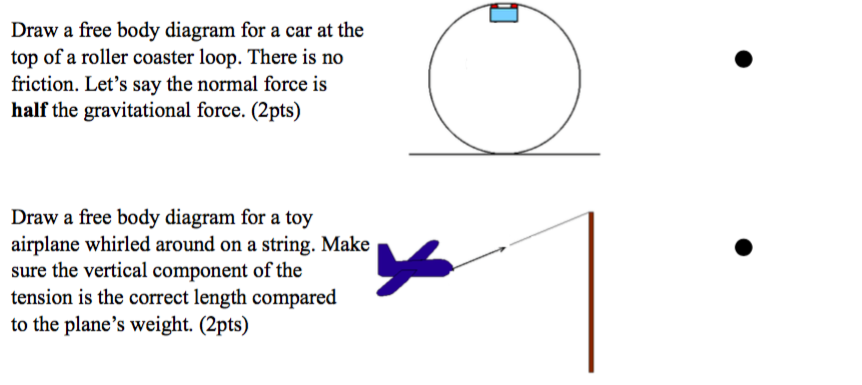
Free Body Diagrams on a Loop‐the‐Loop Roller Coaster Draw the free body diagrams for a coaster at the boom and top of a loop and write the equaons for the net force. mg F net F N F net =ma = ma c The net force in the loop must be centripetal force F net = F N

How To Determine The Minimum Height Of A Roller Coaster Provided An Acceleration As A Threshold Parameter Mathematics Stack Exchange
EXAMPLE 5.8B - Apparent weight on a roller coaster You are riding on a roller coaster that is going around a vertical circular loop. What is the expression for the normal force on you at the bottom of the circle? SOLUTION Once again, we apply the general method, starting with a diagram and a free-body diagram in Figure 5.21.

Consider A Roller Coaster As It Travels Near The Bottom Of Its Track As Sketched In The Figure Below At This Point The Normal Force On The Roller Coaster Is Three Times
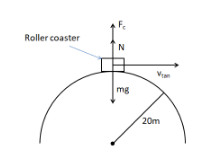
The figure shows the roller-coaster free-body diagram at the top of the loop. ! The track can only push on the wheels of the car, it cannot pull, therefore presses downward. ! The car is still moving in a circle, so the net force is also downward: ! The normal force at the at the top can exceed mg if v top is large enough. Slide875$
a) See free-body diagram in attachment. b) Net force in the y-direction: [/tex] c) The velocity at which the roller coaster will fall is [/tex] d) The speed of the roller coaster must be 17.1 m/s. e) The roller coaster should start from a height of 90 m. f) The roller coaster should start from a height of 100 m. Explanation: a)
One of the main analytical tools that we will learn to use is the Free Body Diagram. Using this vector analysis technique will enable students to resolve the various forces that are acting on the roller coaster at any given point in time and determine the level of excitement.
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators ...

The Diagram Shows A Roller Coaster In Which The Car Going Over It Has A Mass Of 125 0 Kilograms A How Much Work Must Be Done To Get The Car To The
7,171. 509. souljaxd said: i researched about free body diagrams and roller coasters. all i have now for the straight away is , f-gravity, f-normal, f - applied, and f- friction. Other than when the coaster ( and passengers) are being pulled up the incline by a chain mechanism or other means, there is no applied force; otherwise you have ...
The motion of objects along curved sections of roller coaster tracks (loops, turns, bumps and hills, etc.) can be analyzed using a free-body diagram, Newton's second law, and circular motion equations. The Physics Classroom demonstrates how using numerous examples.
Homework Statement There is a roller coaster cart with passengers sitting on the top of a 23 degree incline. The ride is about to start. The combined mass of the cart and passengers is 363kg. a) What would the free body diagram look like? b) How do you solve for normal force? c) How do...
Free-body diagram for the water. Sketch a free-body diagram for just the water, if the speed is less than the critical speed. a = g "down" is down. mg m. b. g. N=0. If same . v. o, same path! Roller coaster. On a roller coaster, when the coaster is traveling fast at the bottom of a circular loop, you feel much heavier than usual. Why? Draw ...
A stunt plane does a series of vertical loop-the-loops. Al what point in the circle does the pilot feel the heaviest? Explain. Include a free-body diagram with your explanation. 19. A roller-coaster car goes around the inside of a loop-the-loop. One of the following statements is true at the highest point in the loop, and one is true at the ...
If the speed of a roller coaster car is 15 m/s at the top of a 20 m loop, and 25 m/s at the bottom. What is the cars average angular acceleration if it takes 1.6 seconds to go from the top to the bottom? t f 0 w w R V w 2.5 10 25 wf 1.5 10 15 w 0 = 0.64 rad/s2 1.6 2.5 1.5

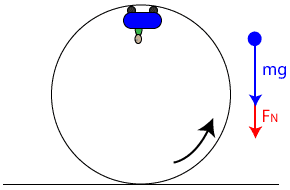

















0 Response to "40 free body diagram roller coaster"
Post a Comment