45 orbital diagram for sodium
Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ 9. Draw orbit structure diagram of sodium chloride (NaCl) and calcium oxide (Cao).
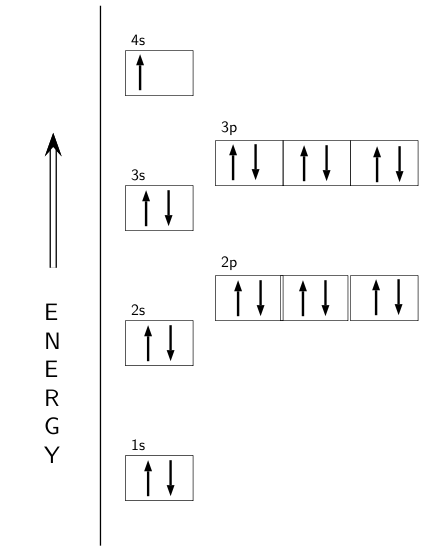
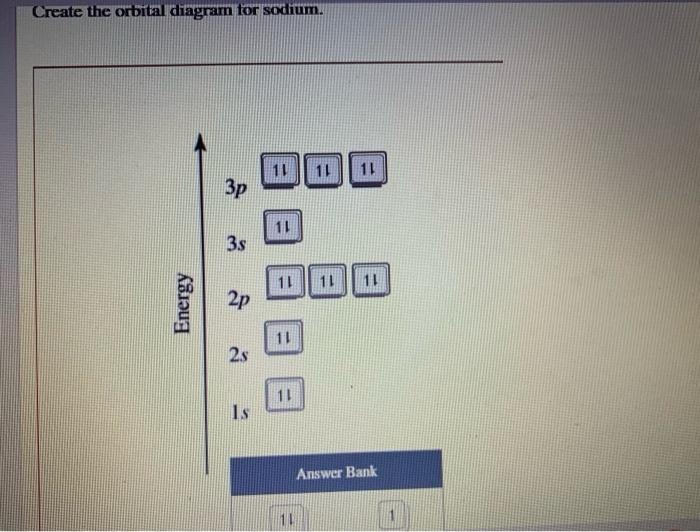
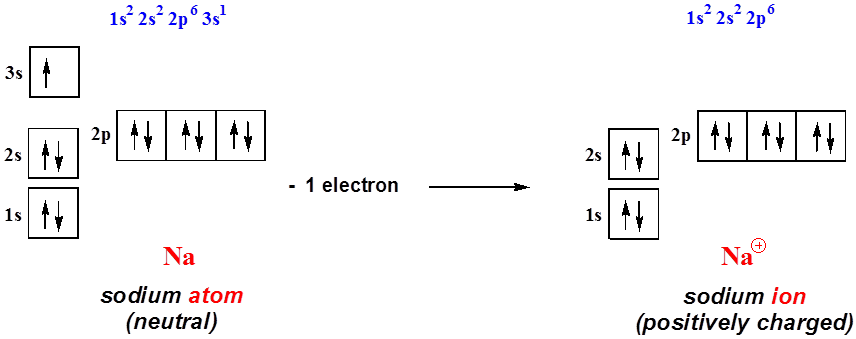
The electron configurations and orbital diagrams of these four elements are: The alkali metal sodium (atomic number 11) has one more electron than the neon atom. This electron must go into the lowest-energy subshell available, the 3s orbital, giving a 1s22s22p63s1 configuration.
Electron configuration of sodium atom through orbital diagram. Atomic energy levels are subdivided into sub-energy levels. These sub-energy levels are called orbital. The sub energy levels are expressed by ‘l’. The value of ‘l’ is from 0 to (n – 1). The sub-energy levels are known as s, p, d, f. Determining the value of ‘l’ for different energy levels is-If n = 1, (n – 1) = (1 ...

Orbital diagram for sodium
Sodium Spectrum The sodium spectrum is dominated by the bright doublet known as the Sodium D-lines at 588.9950 and 589.5924 nanometers. From the energy level diagram it can be seen that these lines are emitted in a transition from the 3p to the 3s levels. The line at 589.0 has twice the intensity of the line at 589.6 nm.
In atomic theory and quantum mechanics, an atomic orbital is a mathematical function describing the location and wave-like behavior of an electron in an atom. This function can be used to calculate the probability of finding any electron of an atom in any specific region around the atom's nucleus.The term atomic orbital may also refer to the physical region or space …
Draw orbit structure diagram of Sodium chloride (NaCl) Medium. View solution. >. Which of the following is the correct electron dot structure of N 2. .
Orbital diagram for sodium.
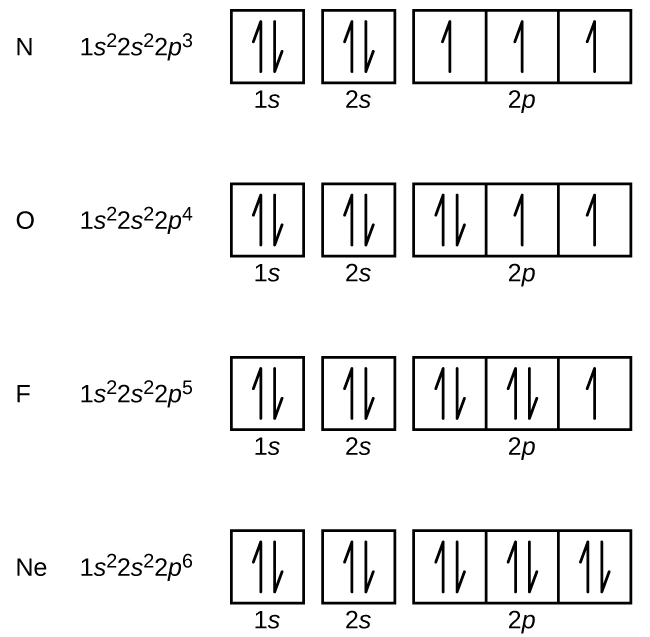
Electron configuration of oxygen atom through orbital diagram. Atomic energy levels are subdivided into sub-energy levels. These sub-energy levels are called orbital. The sub energy levels are expressed by ‘l’. The value of ‘l’ is from 0 to (n – 1). The sub-energy levels are known as s, p, d, f. Determining the value of ‘l’ for different energy levels is-If n = 1, (n – 1) = (1 ...
Which one of the following is the correct orbital diagram for nitrogen? ... If the electron configuration of a ground state sodium atom is 1s22s22p63s1, the electron configuration of the sodium cation (Na+) would be: A. 1s22s22p6 B. 1s22s22p63s2 C. 1s12s22p63s1 D. 1s22s22p63s1
Ionic bonding Sodium is an alkali metal, and chlorine is a halogen. This means that sodium contains one electron in its outer orbital and chlorine contains seven electrons in its outer orbital.
Sodium oxide – Na2O. Recognize the plane figures show several molecular shape of elementary school math worksheets cover the same. Some of the worksheets displayed are Orbital diagram and electron configuration work answers, Teacher workbooks, Answers to practice test questions 3 molecular orbital, Work 4 answers to critical thinking questions model, Inorganic chemistry …
August 13, 2020 - From the orbital diagram, we can write the electron configuration in an abbreviated form in which the occupied orbitals are identified by their principal quantum number n and their value of l (s, p, d, or f), with the number of electrons in the subshell indicated by a superscript.
Orbital Diagrams •Orbital diagram for sodium. •e-1config: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s 1s 2s 2p 3s . Orbital Diagrams •Orbital diagram for magnesium. •e-2config: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s 1s 2s 2p 3s . Orbital Diagrams
24 Jan 2021 — The sodium has 11 numbers of electrons. The orbital arrangement of atoms consists of first orbit 1s which can take only 2 electrons after this ...
Aug 3, 2020 - Na Sodium Element information, facts. Sodium properties, uses and trends | Periodic Table of the Elements - complete information about the sodium element - Facts, atomic mass, melting point, How to Locate on Periodic Table, History, Abundance, Physical Properties, Thermal Properties, ...
Write the orbital diagram for sulfur and determine its number of unpaired electrons. Electron configuration: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p4. Orbital diagram: 1s= 1 up 1 down. 2s= 1 up 1 down. 2p= 1 up 1 down 1 up 1 down 1 up 1 down. 3s= 1 up 1 down. 3p= 1 up 1 down 1 up 1 up. Two unpaired electrons. Write the electron configuration for Ge.
Orbital diagram of Nitrogen (N) 8. Orbital diagram of Oxygen (O) 9. Orbital diagram of Fluorine (F) 10. Orbital diagram of Neon (Ne) 11. Orbital diagram of Sodium (Na)
Sodium : atomic number (Z) = 11 (s block element) Aufbau Principle: 2 electrons occupy the completed first energy level (K shell), 8 electrons occupy the completed second energy level (L shell), and 1 electron occupies the third energy level (M shell) in an s orbital. electron configuration (shells): 2,8,1 . electron configuration (sub-shells): 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 1. condensed …
November 8, 2021 - In practice, chemists simplify ... from the preceding row because all the orbitals in a noble gas are filled. For example, [Ne] represents the 1s22s22p6 electron configuration of neon (Z = 10), so the electron configuration of sodium, with Z = 11, which is 1s22s22p63s1, is ...
For example, sodium (Na), which has a single electron in its outer 3s orbital, can lose that electron to attain the electron configuration of neon. Chlorine, with seven valence electrons, can gain one electron to attain the configuration of argon.
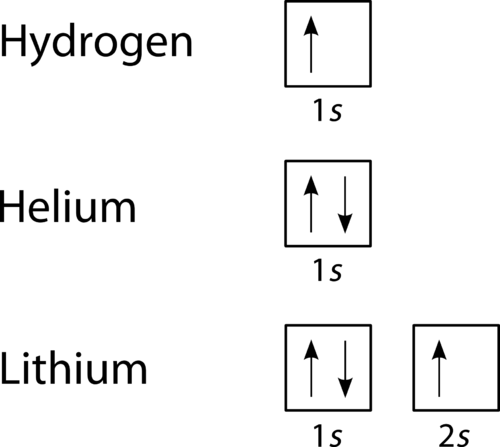
Hydrogen (H) Electron Configuration with Full Orbital Diagram. Hydrogen electron configuration is 1s 1. Hydrogen is a s-block element. This article gives an idea about the electron configuration of hydrogen, period and groups, valency and valence electrons of hydrogen, bond formation, compound formation, application of different principles.
The electron configurations and orbital diagrams of these four elements are: The alkali metal sodium (atomic number 11 11) has one more electron than the neon atom. This electron must go into the lowest-energy subshell available, the 3s 3 s orbital, giving a 1s22s22p63s1 1 s 2 2 s 2 2 p 6 3 s 1 configuration.
Sodium (Na) has an atomic mass of 11. Find out about its chemical and physical properties, states, energy, electrons, oxidation and more.
November 7, 2021 - The purpose of introducing quantum numbers has been to show that similarities in the electron arrangement or electron configuration lead to the similarities and differences in the properties of …
The electronic configuration of Sodium (atomic number is 11) is- 1s^2 2s^2 2p^6 3s^1 Note:- For writing the electronic configuration of elements, the Aufbau Principle is used. In Aufbau Principle, the electrons are filled according to the increasing energy level of orbitals. According to the Aufbau Principle, first the atomic number of element is determined (like here oxygen has atomic number ...
Electron orbital diagrams and written configurations tell you which orbitals are filled and which are partially filled for any atom. The number of valence electrons impacts on their chemical properties, and the specific ordering and properties of the orbitals are important in physics, so many students have to get to grips with the basics.
The groundstate for Sodium (11-Na) is: 1S2 , 2S2, 2P6, 3S1 If you count the ^powers you notice it'll sum to 11, when Sodium is excited the outermost electron (3S1) will be excited from the 3S ...
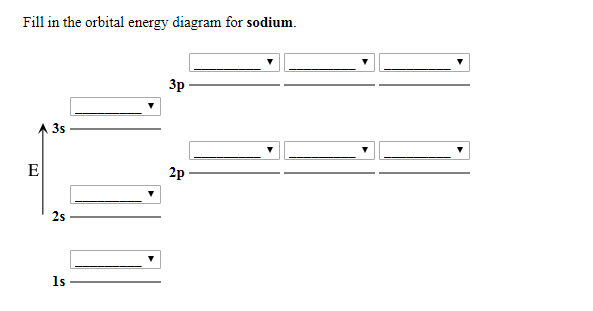
Chemistry questions and answers. 1 attempts left Check my work Select the single best answer. Choose the correct orbital diagram for the ground-state electron arrangement for sodium. Be sure to follow the three orbital filling rules: the aufbau principle, the Pauli exclusion principle, and Hund's rule. 1s 2s 2p 3s 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 1s 2s 2p 3s 1s ...
The electron configuration of a neutral sodium atom is 1s^2 2s^2 2p^6 3s^1. In this configuration we note that there is only one electron in the 3rd energy level. Atoms prefer to gain the stability of octet, by having eight electrons in the outer shell, the electrons of the s and p orbitals. These are referred to as the valence orbitals and the valence electrons.
For example, the abbreviated electron configuration for sodium is written as [Ne]3s1, where [Ne] represents the core electrons in the 1s, 2s, and 2p subshells. Which element will not have an abbreviated electron configuration beginning with a noble gas configuration? In your response, use the elemental symbol. The orbital diagram provided ...
This video shows how to draw the orbital diagram of Sodium (Na). It also shows how to write the electron configuration of Sodium (Na) and the shorthand nobl...
This WebElements periodic table page contains properties of free atoms for the element sodium
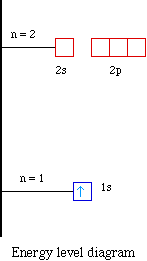
The orbital diagram, the electron configuration and the energy diagram. All three ways are useful. The next atom is helium with 2 electrons. So the second electron could go into the 1s orbital with the opposite spin of the first electron or it could go into the next orbital in the n = 2 level.
In this video, we determine how to draw the orbital diagram of sodium.
In writing the electron configuration for sodium the first two electrons will go in the 1s orbital. Since 1s can only hold two electrons the next 2 electrons for sodium go in the 2s orbital. The nex six electrons will go in the 2p orbital. The p orbital can hold up to six electrons.
Electronic configuration of the Sodium atom. Valence electrons. Orbital diagram
For orbital diagrams, this means two arrows go in each box (representing two electrons in each orbital) and the arrows must point in opposite directions (representing paired spins). The electron configuration and orbital diagram of helium are: The n = 1 …
August 14, 2020 - Remember electrons are negatively charged, so ions with a positive charge have lost an electron. For main group elements, the last orbital gains or loses the electron. For transition metals, the last s orbital loses an electron before the d orbitals. Na: 1s22s22p63s1. Sodium cation loses one ...
For example, take the electron configuration for carbon: 2 electrons will pair up in the 1s orbital, 2 electrons pair up in the 2s orbital, and the remaining 2 electrons will be placed into the 2p orbitals. The correct orbital diagram, obeying Hund’s Rule, will note the two 2p electrons to ...
In the case of the sodium doublet, the difference in energy for the 3p 3/2 and 3p 1/2 comes from a change of 1 unit in the spin orientation with the orbital part presumed to be the same. The change in energy is of the form . ΔE = μ B gB = 0.0021 eV. where μ B is the Bohr magneton and g is the electron spin g-factor with value very close to 2. This gives an estimate of the internal …
The orbital diagram is one way of writing the atom's electronic configuration. Answer and Explanation: 1 Become a Study.com member to unlock this answer! Create your account View this answer The...
August 5, 2021 - In practice, chemists simplify ... the preceding row because all the orbitals in a noble gas are filled. For example, [Ne] represents the 1s2 2s2 2p6 electron configuration of neon (Z = 10), so the electron configuration of sodium, with Z = 11, which is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1, ...
The orbital angular momentum for an atomic electron can be visualized in terms of a vector model where the angular momentum vector is seen as precessing about a direction in space. While the angular momentum vector has the magnitude shown, only a maximum of l units can be measured along a given direction, where l is the orbital quantum number.. Since there is a …
An orbital diagram is similar What is the orbital diagram for. For example, write the electron configuration of scandium, Sc: 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 1. So for scandium the 1 st and 2 nd electron must be in 1s orbital, the 3 rd and 4 th in the 2s, the 5 th through 10 th in the 2p orbitals, etc. 6/14/ Ch 8 4/18 Correct Part B Complete ...
Sodium Atomic Emission Spectrum The sodium spectrum is dominated by the bright doublet known as the Sodium D-lines at 588.9950 and 589.5924 nanometers. From the energy level diagram it can be seen that these lines are emitted in a transition from the 3p to the 3s levels. The line at 589.0 has twice the intensity of the line at 589.6 nm. Taking the range from 400 …
In this article, we will study the Cyanide (CN-) lewis structure, molecular orbital diagram(MO), its bond order, formal charges, and hybridization. Cyanide can be a colorless gas in the form of hydrogen cyanide, sodium cyanide, potassium cyanide, etc. It is released as a decay product of many plants and it is one of the most poisonous chemicals in chemistry. Some bacteria, fungi, …
Draw Orbit Structure Diagram of Sodium Chloride (Nacl) CISCE ICSE Class 9. Question Papers 10. Textbook Solutions 19257. Important Solutions 6. Question Bank Solutions 14520. Concept Notes & Videos 431. Syllabus. Advertisement Remove all ads. Draw Orbit Structure Diagram of Sodium Chloride (Nacl) - Chemistry ...
I wanted to ask a question about metallic bond - band electron theory. Consider the diagram of Sodium below: Circled are orbitals both containing $2$ electrons each which combine using LCAO to give a set of bonding and antibonding electrons.. However, the $4$ electrons involved in this bonding appear to only give $3$ electrons in the bonding and antibonding MO's produced.
Chem4Kids.com: Sodium: Orbital and Bonding Info. Check out the blackboard. That box on the left has all of the information you need to know about one element. It tells you the mass of one atom, how many pieces are inside, and where it should be placed on the periodic table . In the next section we're going to cover electron orbitals or electron ...
February 28, 2021 - Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\): A Bhor's model can be used to diagram the location of electrons in each energy shell for an atom. Notice that protons go in the nucleus of the atom and electrons are drawn on orbits surrounding the nucleus. Image from Wikimedia commons. ... Draw the Bohr's model for sodium ...


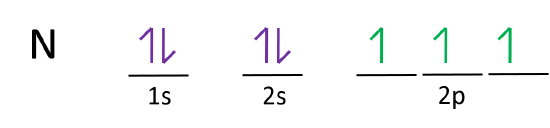






























0 Response to "45 orbital diagram for sodium"
Post a Comment