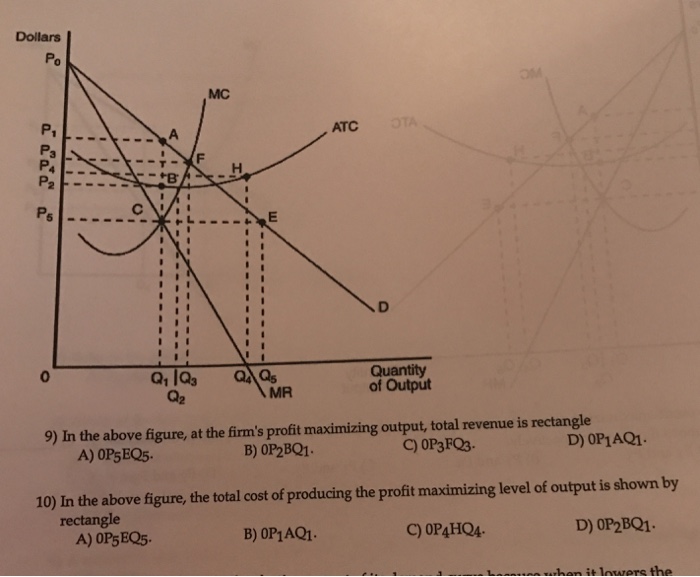
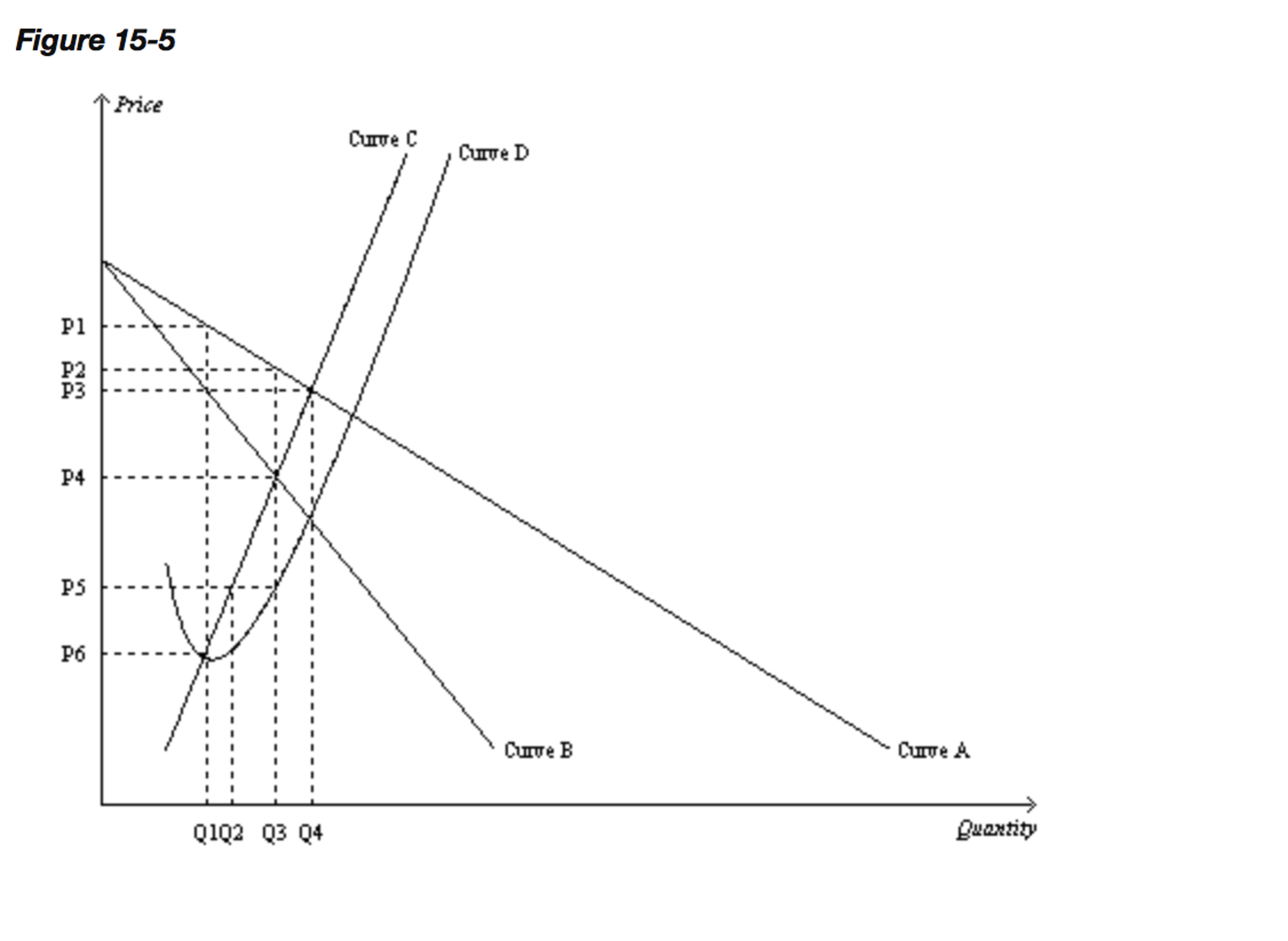
45 refer to the diagram. at the profit-maximizing level of output, total revenue will be
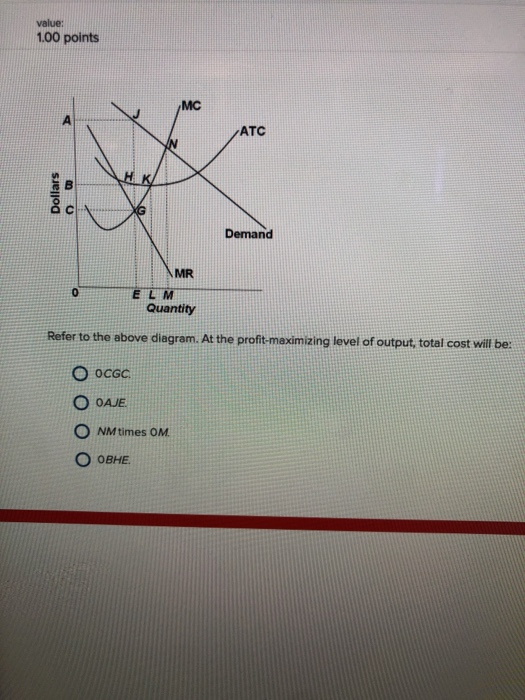
Refer to the diagram. To maximize profits or minimize losses, this firm should produce E units and charge price A. Refer to the diagram. At the profit-maximizing level of output, total revenue will be 0 AJE. Refer to the diagram. At the profit-maximizing level of output, total cost will be 0 BHE. Refer to the diagram. What is the monopolistic competitor's profit maximizing price? 20) A) P 1 B) P 2 C) P 3 D) P 4 21) Refer to Figure 13 -11. The firm represented in the diagram 21) A) makes zero economic profit. B) should exit the industry. C) should expand its output to take advantage of economies of scale. D) makes zero accounting profit. 22) Refer to Figure ...
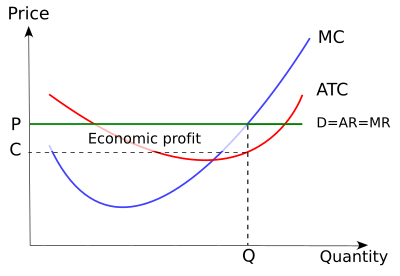
At its profit-maximizing output, this firm's price will exceed its marginal cost by ____ and its average total cost by $30; $20.50 Refer to the above data for a nondiscriminating monopolist.
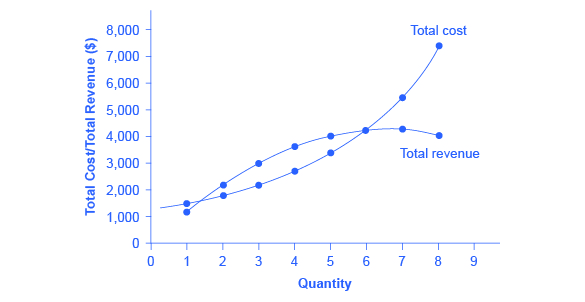
Refer to the diagram. at the profit-maximizing level of output, total revenue will be
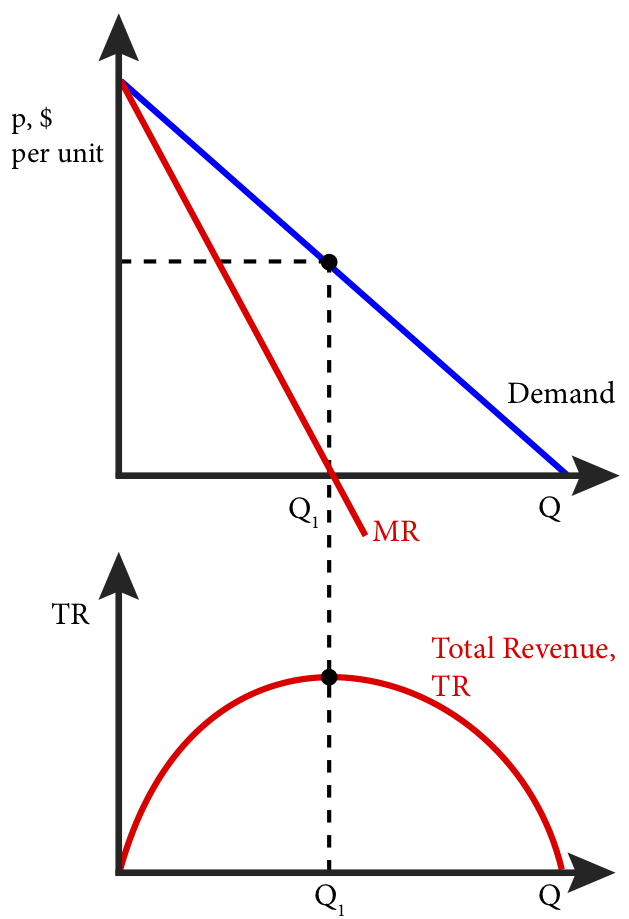
Refer to the diagram. At the profit-maximizing level of output, total revenue will be. 0AJE. Which of the following is correct. a purely competitive firm is a price taker, while a monopolist is a price maker. which of the following best approximates a pure monopoly. the only bank in a small town. excess capacity refers to the . amount by which actual production falls short of the minimum ATC ... At the profit-maximizing level of output, total revenue will be: A) NM times 0M. B) 0AJE. C) 0EGC. D) 0EHB. B) Refer to the above ... 3. Refer to the above diagram. To maximize profit or minimize losses this firm will produce: 1. K units at price C. 2. D units at price J. 3. E units at price A. 4. E units at price B. 4. Refer to the above diagram. At the profit-maximizing output, total revenue will be: 1. 0AHE. 2. 0BGE. 3. 0CFE. 4. ABGE. 5. Refer to the above diagram.
Refer to the diagram. at the profit-maximizing level of output, total revenue will be. economic profits will be zero. ... Refer to the diagram for a purely competitive producer. ... At the profit-maximizing output, total revenue will be:. The profit-maximizing price and output are 15 and 5, respectively. Optimal Price and Output in Monopolistically Competitive Markets In this market structure, the short-run profit-maximizing choice occurs at the point where marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost (MR=MC). 37. Refer to the above diagram. If this somehow was a costless product (that is, the total cost of any level of output was zero), the firm would maximize profits by: Refer to the above diagram. To maximize ... At the profit-maximizing output, total revenue will be: ... In the above diagram by producing output level Q:
2. Assume the price of a product sold by a purely competitive firm is $5. Given the data in the accompanying table, at what output is total profit highest in the short run? Refer to the above diagram. To maximize profits or minimize losses this firm should ... At the profit-maximizing level of output, total revenue will be:. Profits will be highest at the quantity of output where total revenue is most above total cost. Of the choices in Table 2, the highest profits happen at an output of 4. The profit-maximizing level of output is not the same as the revenue-maximizing level of output, which should make sense, because profits take costs into account and revenues do ... Figure 12 - 4 shows the cost and demand curves for a profit - maximizing firm in a perfectly competitive market. 16) Refer to Figure 12 -4. If the market price is $30, the firm's profit - maximizing output level is 16) A) 0. B) 130. C) 180. D) 240. 17) Refer to Figure 12 -4. If the market price is $30 and if the firm is producing output, what ...
At the profit maximizing level of output total revenue will be. Refer to the diagram for a purely competitive producer. 9 2 How A Profit Maximizing Monopoly Chooses Output And B an economic profit of acgj. Refer to the diagram at the profit maximizing level of output total revenue will be. A nm times 0m. 37. Marginal revenue is the addition to total revenue resulting from the sale of one more unit of output. True False 38. Refer to the above diagram. This firm will maximize profits by producing output D. True False 39. Refer to the above diagram. At the profit-maximizing output total revenue will be 0GLD. True False 40. Refer to the above diagram. Refer to the above diagram. To maximize ... At the profit-maximizing output, total revenue will be: ... In the above diagram by producing output level Q: Rating: 5 · 2 reviews At the profit-maximizing output level, the slopes of the revenue and totalthe slopes of the revenue and total cost curves are equal, i.e. MR(y*) = MC(y*) Marginal Revenue: ExampleMarginal Revenue: Example p = a – by (inverse demand curve)by (inverse demand curve) TR = py (total revenue)TR = py (total revenue) TR = ay - by2 Therefore, MR(y) = a - 2by < a - by = p for y > 0. Marginal Revenue ...
Refer to the diagram. At the profit-maximizing level of output, total revenue will be: 0AJE. Image: Refer to ...
Refer To The Diagram At The Profit Maximizing Level Of Output Total Revenue Will Be Drivenheisenberg
a. maximize its total revenue. ... At the profit-maximizing level of output, a. marginal revenue equals average total cost. ... Refer to Figure 15-7. A profit-maximizing monopolist would earn total revenues of: a. $81. b. $144. c. $225. d. $240. d. Refer to Figure 15-7. A profit-maximizing monopolist would incur total costs of:
Solved In The Figure Below What Is The Maximum Profit And The Profit Maximizing Level Of Output Of The Firm When The Market Price Is 8 50 A Q 60 Course Hero
Suppose that TC = 20 + 10Q + Q2 for a firm in a competitive market and that output, Q, sells for a price, P, of $90. How much output will the firm produce to maximize profit? 21. Suppose that the short-run production function is Q = 10L. If the wage rate is $4 per unit of labor, then average variable cost equals.
Chapter 9: Profit Maximization Profit Maximization The basic assumption here is that firms are profit maximizing. Profit is defined as: Profit = Revenue - Costs Π(q) = R(q) - C(q) To maximize profits, take the derivative of the profit function with respect to q and set this equal to zero.
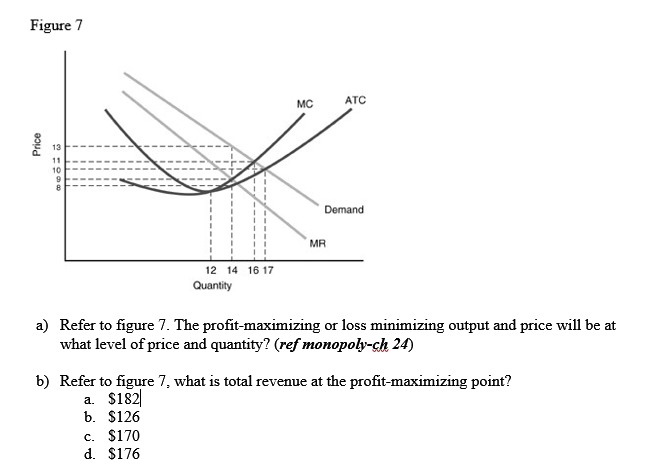
10) Refer to Figure 13 -8. What is the firm's profit - maximizing price? 10) A) $12 B) $13 C) $14 D) $16 11) Refer to Figure 13 -8. At the profit - maximizing output level the firm will 11) A) earn a profit of $60. B) break even. C) earn a profit of $88. D) earn a profit of $176. 12) Refer to Figure 13 -8. Based on the diagram, one can conclude ...
Profit maximizing output chapter 10. Refer to the diagram at the profit maximizing output total variable cost is equal to. A 0 ahe. At the profit maximizing output total fixed cost is equal to. Refer to the above data. Refer to the above diagram. Prof keep econ pr test chap 21 ed 17 page 2 of 9. At output level q total variable cost is.
Refer To The Diagram At The Profit Maximizing Level Of Output Total Revenue Will Be Wiring Site Resource
Refer to the above diagram. If this somehow was a costless product (that is, the total cost of any level of output was zero), the firm would maximize profits by: producing Q 2 units and charging a price of P 2.
To find the profit-maximizing price, substitute this quantity into the demand equation: P = 27 −(1.5)(5.67)= $18.5. Total revenue is price times quantity: TR =(18.5)(5.67) =$104 .83. The profit of the firm is total revenue minus total cost, and total cost is equal to average cost times the level of output produced.
The change in total cost from producing the eightieth unit of output is seventh unit of output is and the change in total revenue from; Question: Refer to the figure. At the profit-maximizing level of output in this diagram, the firm's average cost is Price $20 18 -МС 16 14 MR 12 AC 10 8 6 4 2 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 200 Quantity ...
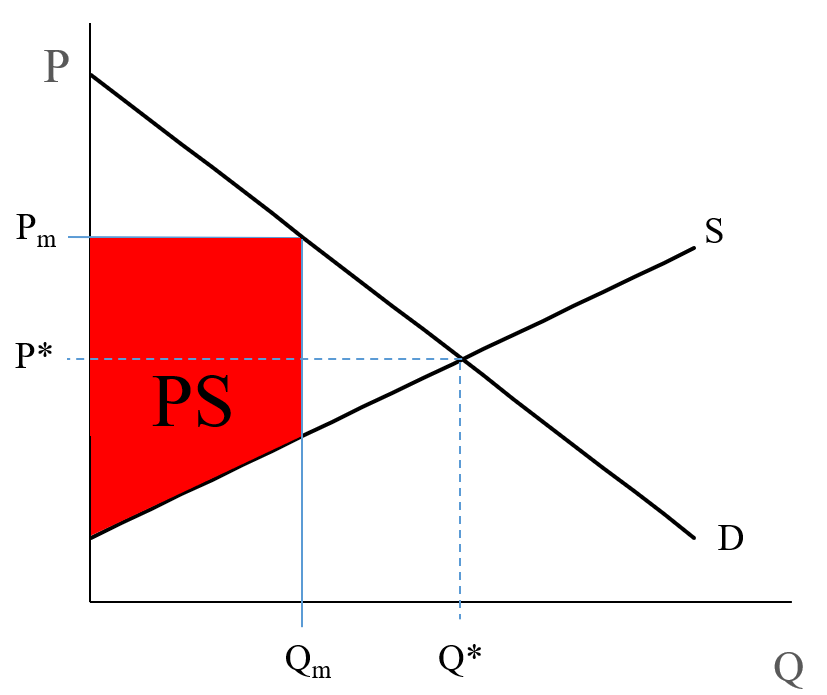
Since price or average revenue equals total revenue divided by a level of output, price charged by the firm at output level OQ is given TR/OQ or QJ/OQ. The simple profit-maximizing model of the firm provides very useful guidelines for the decision making by the firm with regard to efficient resource management.
Refer to the above diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. ... At the profit-maximizing output the firm's total revenue is:
In economics, profit maximization is the process by which a firm determines the price and output level that returns the greatest profit. There are several approaches to profit maximization. 1. Total Cost-Total Revenue Method. To obtain the profit maximizing output quantity, we start by recognizing that profit is equal to total revenue (TR ...
This is the 2nd of 6 videos going through an exam-type question on using quadratic and linear functions to solve business math/economics problems.
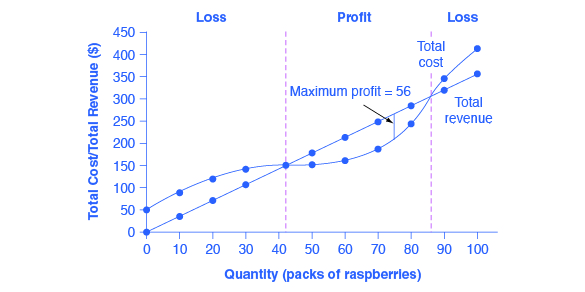
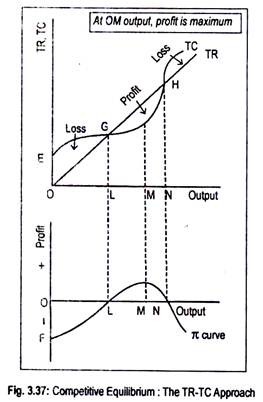
Figure 1 shows total revenue, total cost and profit using the data from Table 1. The vertical gap between total revenue and total cost is profit, for example, at Q = 60, TR = 240 and TC = 165. The difference is 75, which is the height of the profit curve at that output level. The firm doesn't make a profit at every level of output.
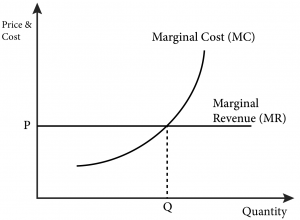
Step 1: The Monopolist Determines Its Profit-Maximizing Level of Output. The firm can use the points on the demand curve D to calculate total revenue, and then, based on total revenue, calculate its marginal revenue curve. The profit-maximizing quantity will occur where MR = MC—or at the last possible point before marginal costs start ...
Refer To The Diagram At The Profit Maximizing Level Of Output Total Revenue Will Be Wiring Site Resource
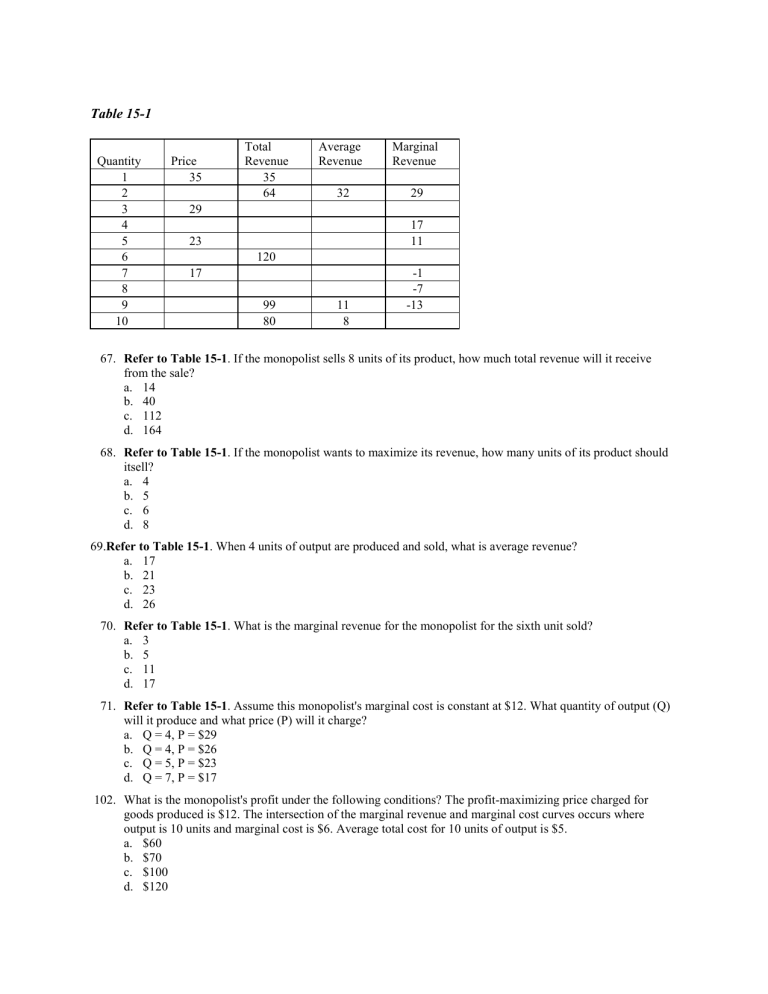
In Figure 2, the profit maximising level of output is OQ and the profit maximisation price is OP (=QA). If more than OQ output is produced, MC will be higher than MR, and the level of profit will fall. If cost and demand conditions remain the same, the firm has no incentive to change its price and output. The firm is said to be in equilibrium.
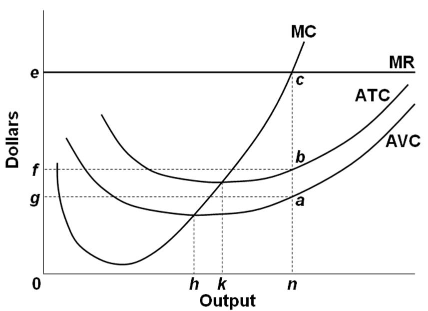
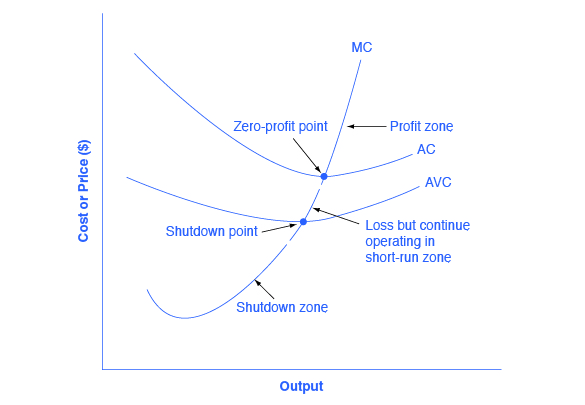
Refer to the above diagram. The profit-maximizing level of output for this firm: A. is at point a. B. is at point b. C. is at point c. D. cannot be determined from the information given. C. CH8 #29 In the above figure, curves 1, 2, 3, and 4 represent the: A. ATC, MC, AFC, and AVC curves respectively. B. MC, AFC, AVC, and ATC curves respectively. C. MC, ATC, AVC, and AFC curves respectively. D ...
Total revenue is maximized. C) Marginal revenue is zero. D) ... In Figure 8.1, diagram "a" presents the cost curves that are relevant to a firm's production decision, and diagram "b" shows the market demand and supply curves for the market. ... In Figure 9.2, the profit-maximizing level of output is: A) 12 units. B) 20 units. C) 22 units. D)
what is the firm's profit-maximizing level of output? 6 (where MR=MC) b. Calculate the firm's total revenue. $20 X 6 = $120 c. Calculate the firm's total cost. $29.50 X 6 = $177 d. Calculate the firm's profit or loss. $120 - $177 = -$57 (or a loss of $57) e. If AVC were $22 at the profit-maximizing level of output, would the
56. Refer to the above diagram. At the profit-maximizing level of output, the firm will realize: A. an economic profit of ABHJ. B. an economic profit of ACGJ. C. a loss of GH per unit. D. a loss of JH per unit.
Refer to the above diagram. To maximize profits or minimize losses this firm should produce: E units and charge price A. Refer to the above diagram. At the profit-maximizing level of output, total revenue will be: 0,A,J,E. Refer to the above diagram. At the profit-maximizing level of output, total cost will be: 0,B,H,E. Refer to the above diagram. At the profit-maximizing level of output, the ...
If a purely competitive firm is producing at some level less than the profit maximizing output, then: marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost. Refer to the above diagram for a purely competitive producer.
Refer to the above data for a nondiscriminating monopolist. This Firm will maximize its ... At the profit-maximizing level of output, total revenue will be:
Profit = Total Revenue (TR) – Total Costs (TC). Therefore, profit maximisation occurs at the biggest gap between total revenue and total costs. A firm can maximise profits if it produces at an output where marginal revenue (MR) = marginal cost (MC) Diagram of Profit Maximisation. To understand this principle look at the above diagram. If the firm produces less than Output of 5, MR is greater ...
3. Refer to the above diagram. To maximize profit or minimize losses this firm will produce: 1. K units at price C. 2. D units at price J. 3. E units at price A. 4. E units at price B. 4. Refer to the above diagram. At the profit-maximizing output, total revenue will be: 1. 0AHE. 2. 0BGE. 3. 0CFE. 4. ABGE. 5. Refer to the above diagram.
At the profit-maximizing level of output, total revenue will be: A) NM times 0M. B) 0AJE. C) 0EGC. D) 0EHB. B) Refer to the above ...
Refer to the diagram. At the profit-maximizing level of output, total revenue will be. 0AJE. Which of the following is correct. a purely competitive firm is a price taker, while a monopolist is a price maker. which of the following best approximates a pure monopoly. the only bank in a small town. excess capacity refers to the . amount by which actual production falls short of the minimum ATC ...

Refer To The Graph Above At The Profit Maximizing Level Of Short Run Output This Monopolistically Competitive Firm Will Be Making A Profit Of A 275 B 350 C 500 D 525 Study Com
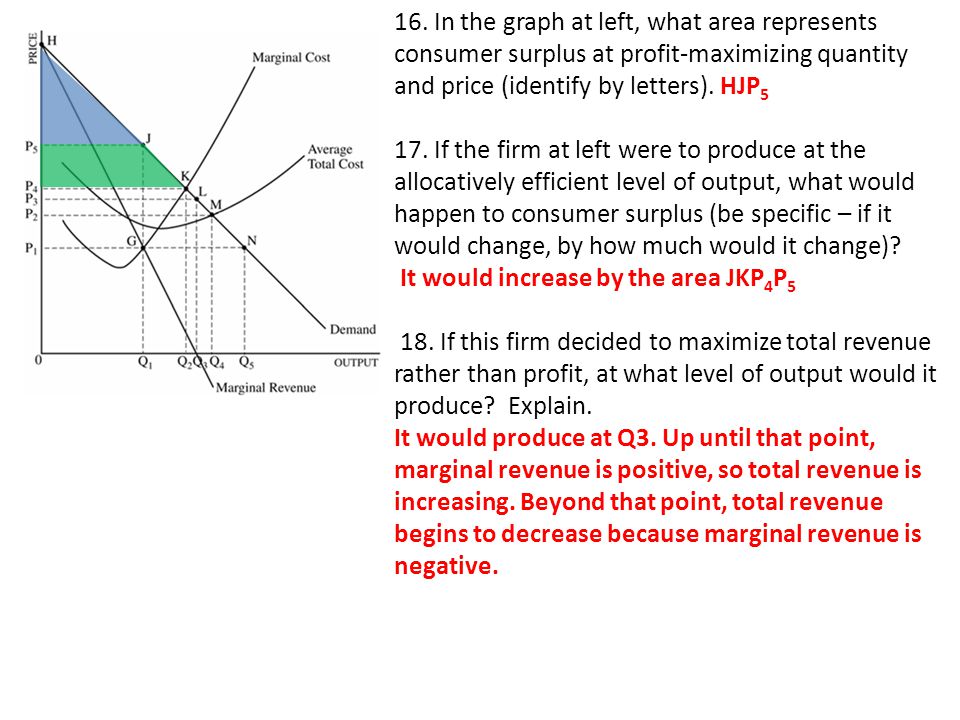
1 If The Monopolist Depicted In The Graph Produces At The Profit Maximizing Output What Will Be The Firm S Economic Profit Explain 2 Lightly Shade Ppt Video Online Download
Solved Draw The Demand Marginal Revenue Average Total Cost And Marginal Cost Curves For A Monopolist
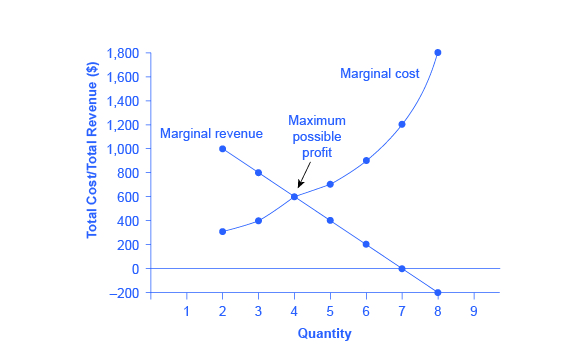










0 Response to "45 refer to the diagram. at the profit-maximizing level of output, total revenue will be"
Post a Comment