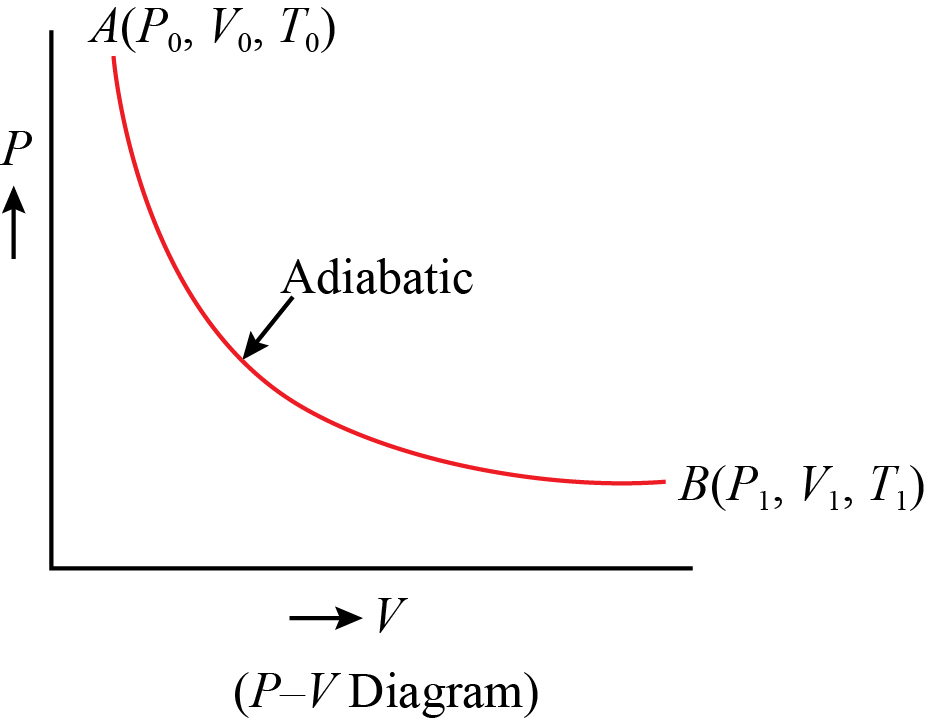
43 adiabatic process pv diagram
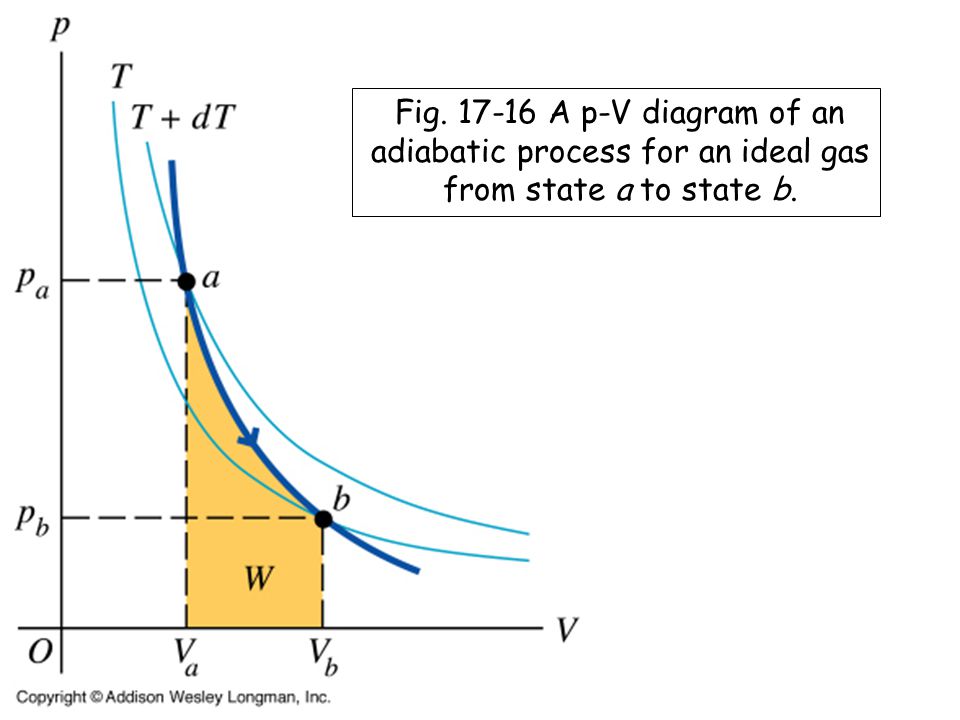
system, and the energy from the adiabatic combustion of a known mass of sample will heat the bomb calorimeter and the water a measurable amount. Through the use of a calibration sample of known combustion value (often benzoic acid[2], including here), the heat capacity of the calorimeter system can be determined, allowing for the calculation Solved Examples Question 1 A gas ($\gamma =1.4$) of 2m 3 Volume and at a pressure of $4 \times 10^5 N/m^2$ is compressed adiabatically to a volume .5 m 3.Find its new pressure. Calculate the work done in the process? Given $4^{1.4} =6.96$ Solution
Process functions: Work · Heat Specific heat capacity c= Compressibility β = − 1 V Thermal expansion α = 1 Property database Compressibility factor From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia The compressibility factor (Z), also known as the compression factor, is a useful …

Adiabatic process pv diagram
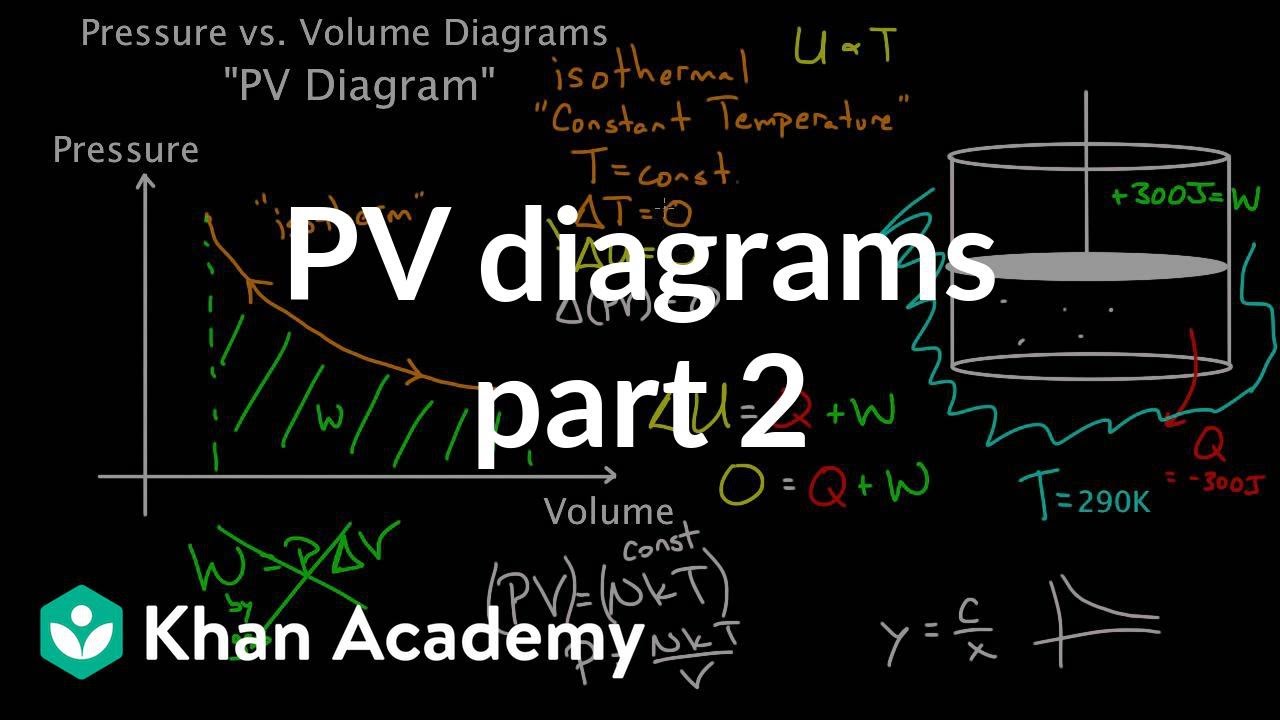
In thermodynamics, an isochoric process, also called a constant-volume process, an isovolumetric process, or an isometric process, is a thermodynamic process during which the volume of the closed system undergoing such a process remains constant. An isochoric process is exemplified by the heating or the cooling of the contents of a sealed, inelastic container: The thermodynamic process is … May 13, 2021 · During an adiabatic process no heat is transferred to the gas, but the temperature, pressure, and volume of the gas change as shown by the dashed line. As described on the work slide, the area under a process curve on a p-V diagram is equal to the work performed by a gas during the process. On the right of the figure we have plotted the ... Because the net variation in state properties during a thermodynamic cycle is zero, it forms a closed loop on a PV diagram.A PV diagram's Y axis shows pressure (P) and X axis shows volume (V).The area enclosed by the loop is the work (W) done by the process: = This work is equal to the balance of heat (Q) transferred into the system:
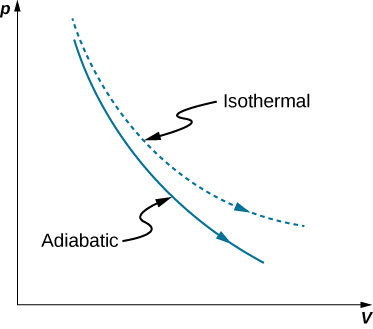
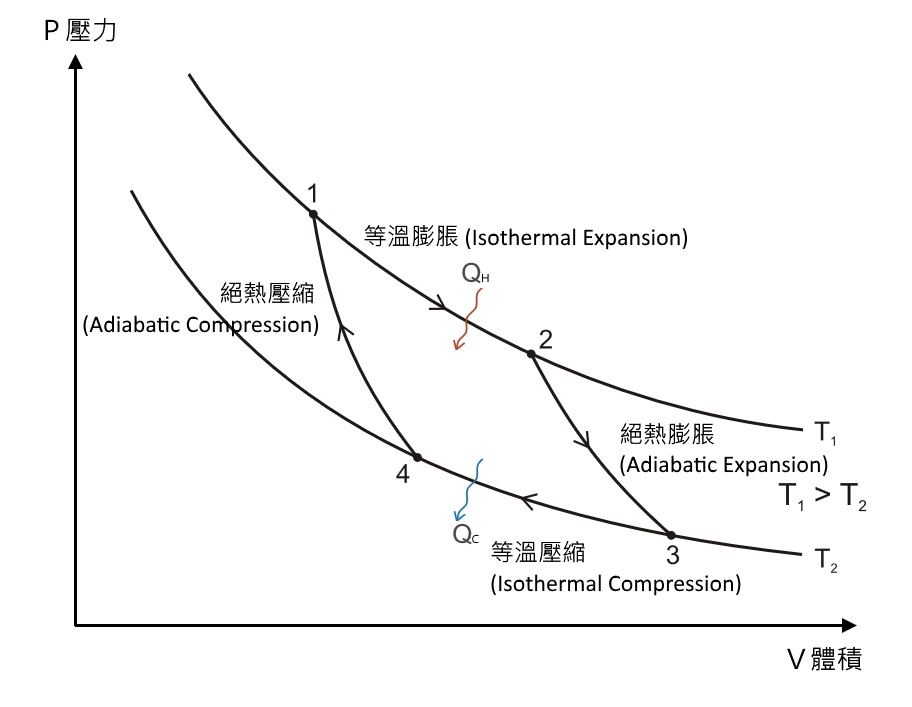
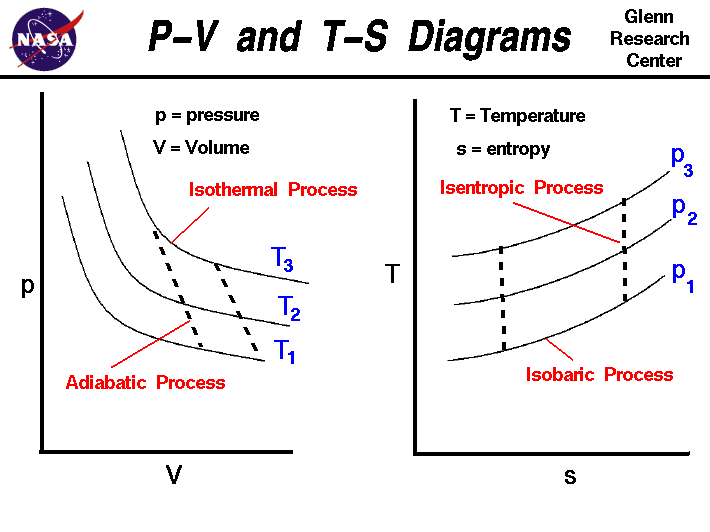
Adiabatic process pv diagram. Figure 6. (a) A PV diagram in which pressure varies as well as volume. The work done for each interval is its average pressure times the change in volume, or the area under the curve over that interval. Thus the total area under the curve equals the total work done. ... adiabatic process: a process in which no heat transfer takes place. The fundamental thermodynamic processes modelled on PV diagrams (isochoric, isobaric, and isothermal processes) all follow the ideal gas law except for adiabatic processes—which will be discussed in detail on its main page. The following are the examples of … Compared with the common internal combustion engine cycles, the cycle has no adiabatic process, so it is easier to realize in practical engineering. Since the cycle p v diagram is rectangular, it is called the RC. Ferreira [22] first applied the classical thermodynamic theory to study the performance of the RC and derived the work output and ... Adiabatic. Comparing isothermal and adiabatic processes. In this simulation, you can look at the difference between a constant temperature (isothermal) process and an adiabatic process. The paths look somewhat similar on the P-V diagram, but you should notice clear differences. Note that an isothermal process has no change in temperature, so the change in internal energy is zero, but in an adiabatic process the heat transferred is zero.
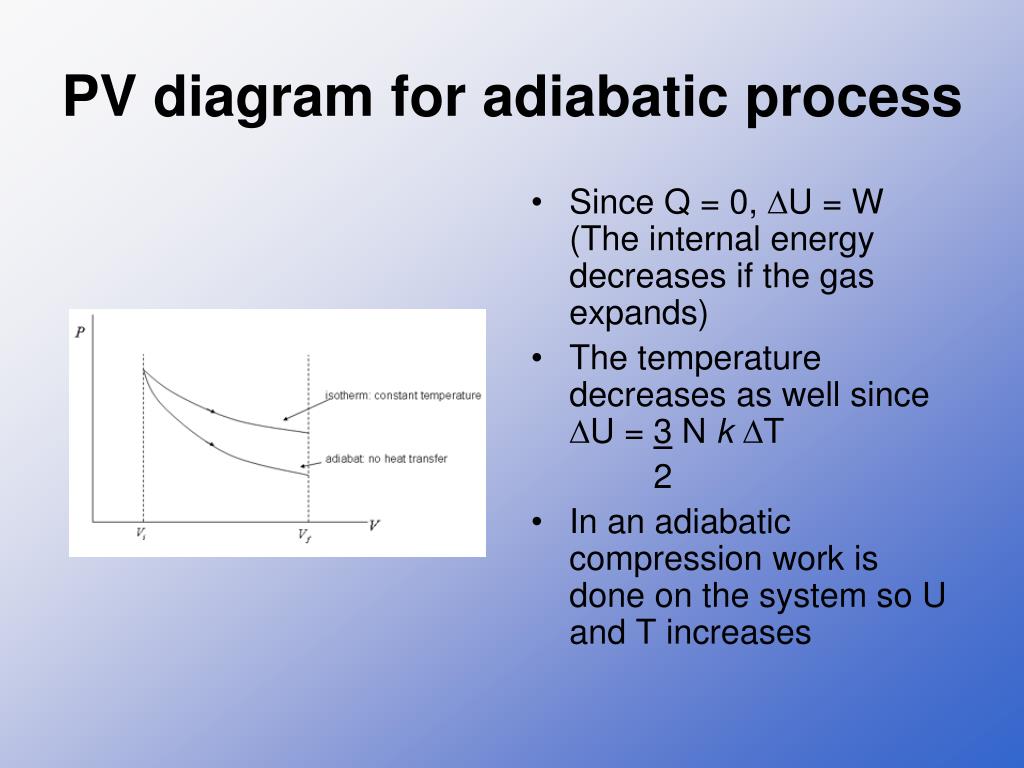
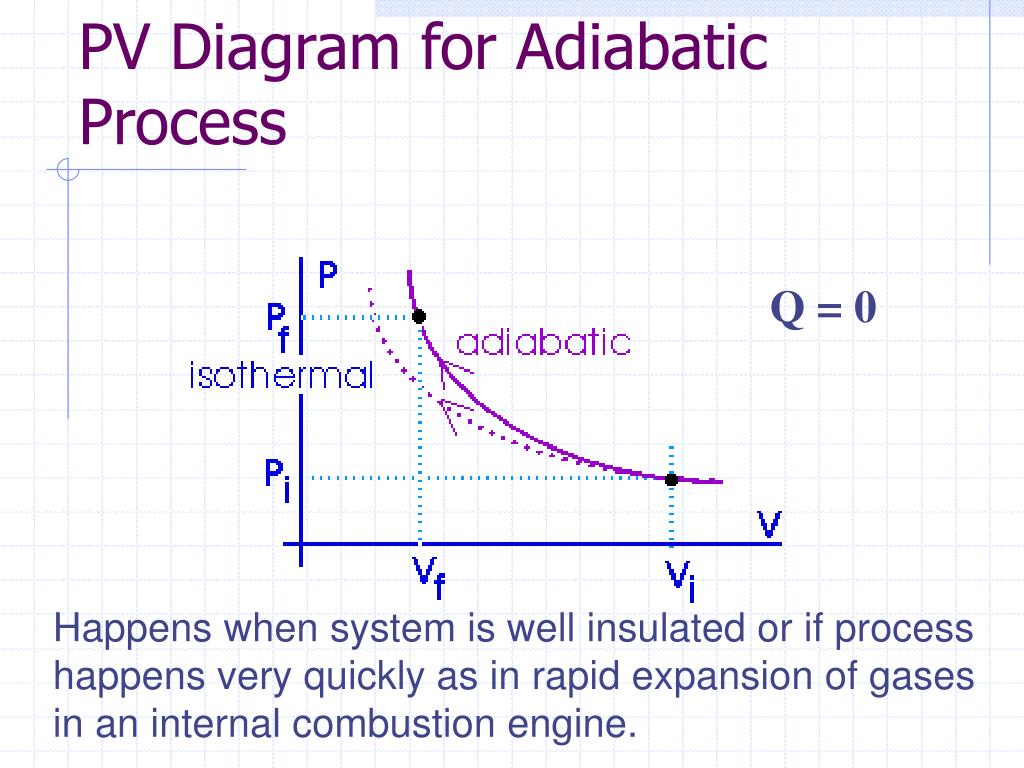
The PV diagram of an adiabatic expansion and adiabatic compression process are shown in Figure 8.30. The PV diagram for an adiabatic process is also called adiabat Note that the PV diagram for isothermal (Figure 8.25) and adiabatic (Figure 8.30) processes look similar. But actually the adiabatic curve is steeper than isothermal curve. Because the net variation in state properties during a thermodynamic cycle is zero, it forms a closed loop on a PV diagram.A PV diagram's Y axis shows pressure (P) and X axis shows volume (V).The area enclosed by the loop is the work (W) done by the process: = This work is equal to the balance of heat (Q) transferred into the system: May 13, 2021 · During an adiabatic process no heat is transferred to the gas, but the temperature, pressure, and volume of the gas change as shown by the dashed line. As described on the work slide, the area under a process curve on a p-V diagram is equal to the work performed by a gas during the process. On the right of the figure we have plotted the ... In thermodynamics, an isochoric process, also called a constant-volume process, an isovolumetric process, or an isometric process, is a thermodynamic process during which the volume of the closed system undergoing such a process remains constant. An isochoric process is exemplified by the heating or the cooling of the contents of a sealed, inelastic container: The thermodynamic process is …

Why Is The Curve Of An Isothermal Process Above The That Of A Adiabatic Process During Compression Chemistry Stack Exchange
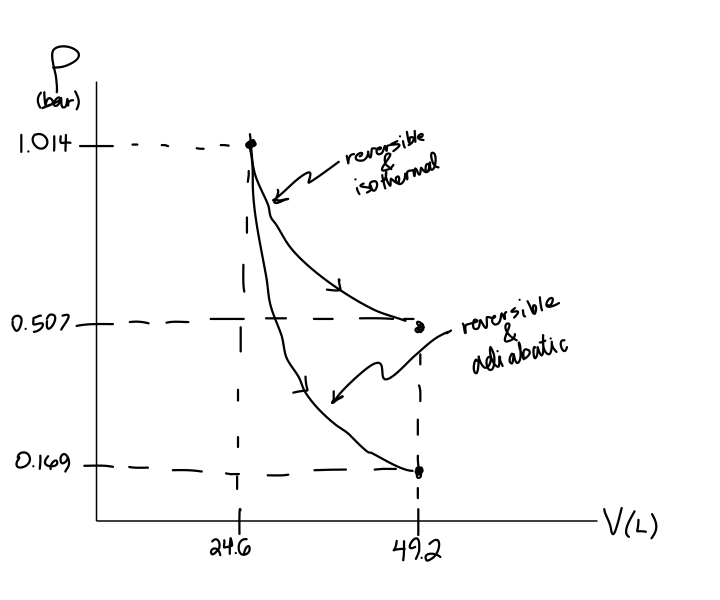
How Will You Prove That Work Done In Isothermal Process Is Always Greater Than Adiabatic Process Socratic
Draw The Pv Diagram For A Isothermal Process B Adiabatic Process C Isobaric Process D Isochoric Process Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
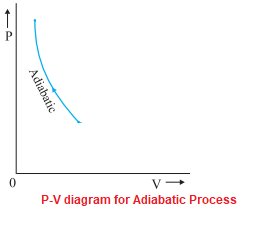
Thermodynamic Processes Quasi Static Processes Isothermal Process Adiabatic Process Isochoric Process Isobaric Process

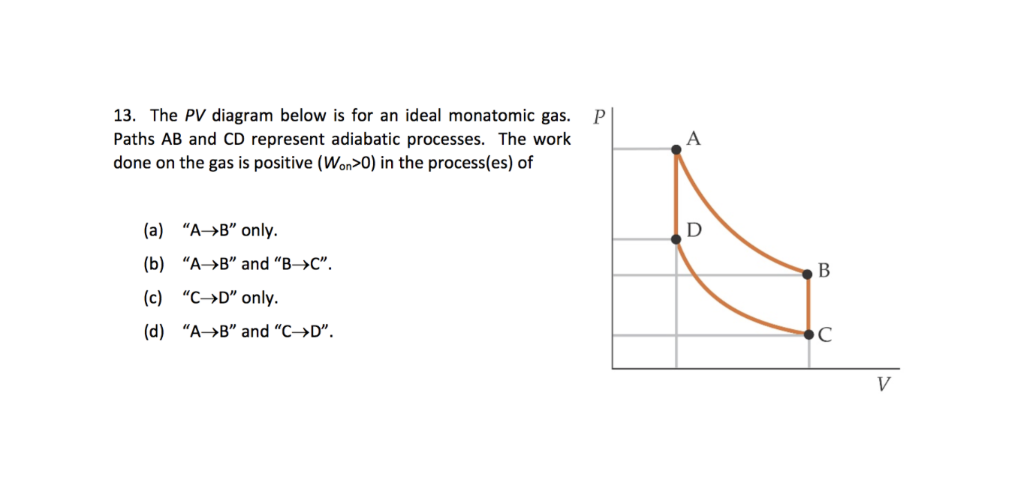
Jee Ma The Pt Diagram For An Ideal Gas Is Shown In The Figure Where Ac Is An Adiabatic Process Find The Corresponding Pv Diagram
Thermodynamic Processes Quasi Static Processes Isothermal Process Adiabatic Process Isochoric Process Isobaric Process


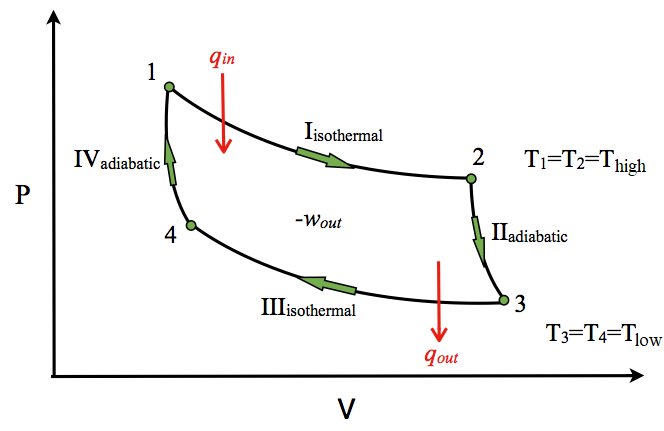

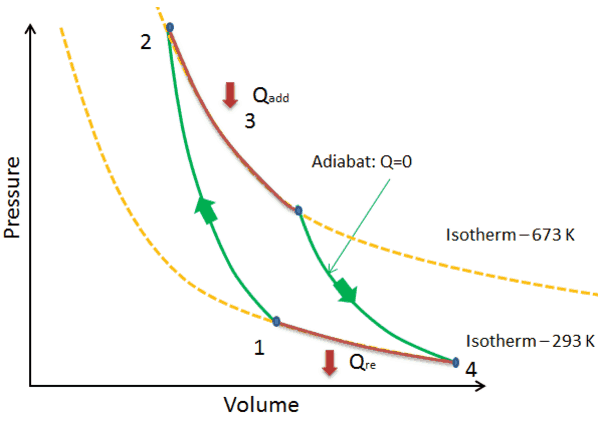


















0 Response to "43 adiabatic process pv diagram"
Post a Comment