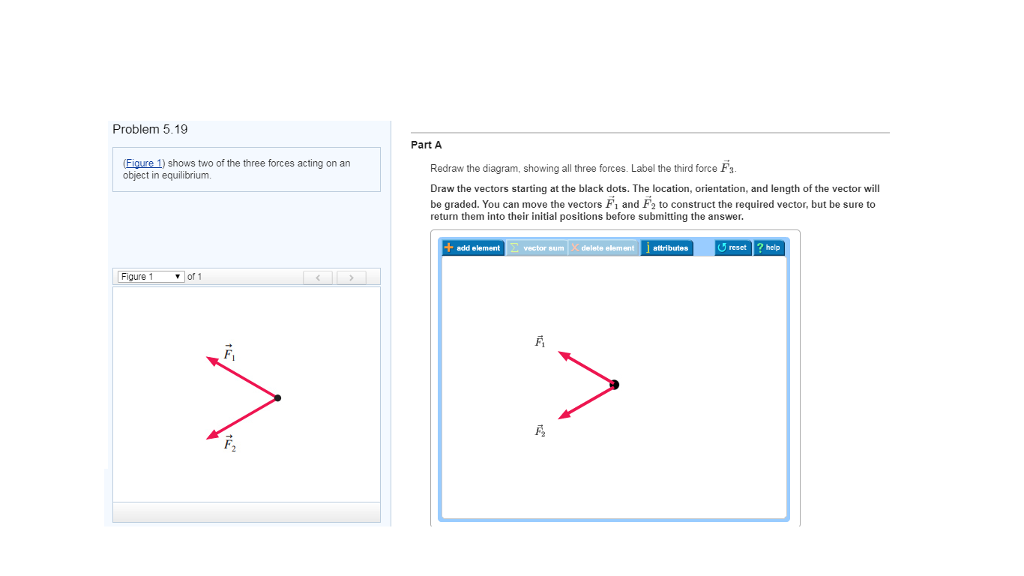
40 redraw the diagram, showing all three forces. label the third force f⃗ 3.
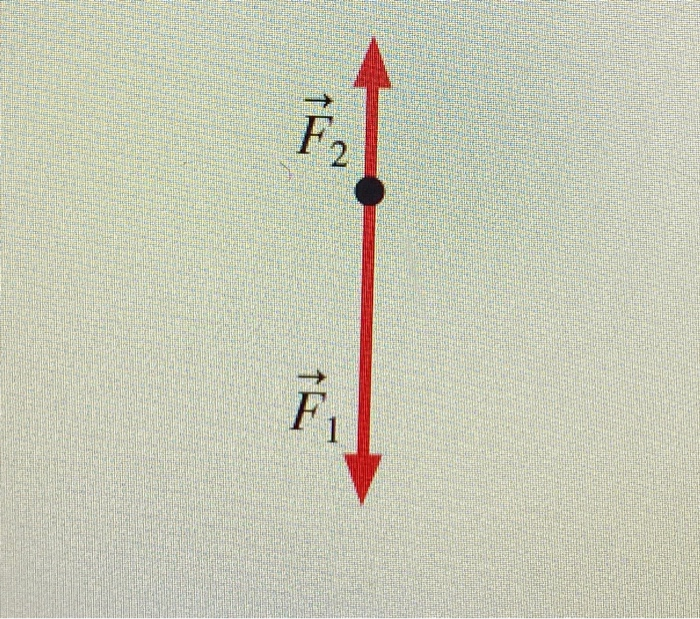
The figure shows two forces acting on an object at rest. Redraw the diagram, then add a third force that will cause the object to remain at rest. Resultant Force Vector Diagrams Of Forces Graphical. ... Redraw The Diagram Showing All Three Forces Label The. Click Images to Large View Redraw The Diagram Showing All Three Forces Label The.
Add a third force that will cause the object to remain at rest. label the new force. Label the new force f 3. Label the new force f 3. Add a third force that will cause the object to remain at rest. The figure shows two forces acting on an object at rest. Part a redraw the diagram showing all three forces.
Redraw the diagram, showing all three forces. label the third force f⃗ 3.
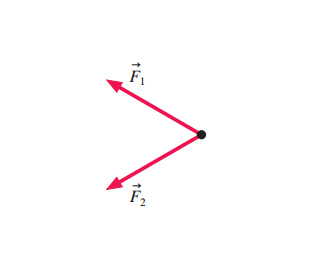
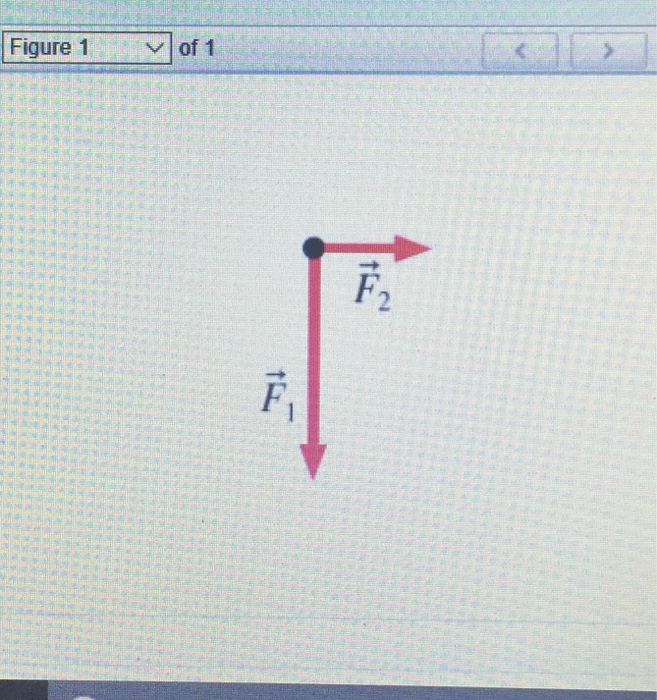
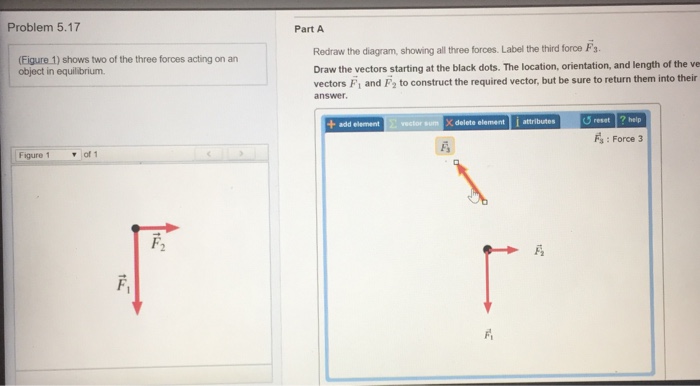
Question: (Figure 1) shows two of the three forces acting on an object in equilibrium. You may want to review (Page 121) - Part A Redraw the diagram, showing all three forces. Label the third force 13 Draw the force vector starting at the black dot. The location, orientation, and length of the vector will be graded. The figure (Figure 1) below shows two of the three forces acting on an object in equilibrium. Redraw the diagram, showing all three forces. Label the third force F 3. Draw the force vector with its tail at the dot. The orientation of your vectors will be graded. Redraw the diagram, showing all three forces. label the third force f⃗ 3.. Label the third force f3. Figure below shows two of the three forces acting on an object in equilibrium. The location and orientation of the vector will be graded. Redraw the diagram showing all three forces. Part a redraw the diagram showing all three forces.
Redraw the diagram, showing all three forces. label the third force f⃗ 3.. Redraw the diagram, showing all three forces. Label the third force F? 3. Draw the force vector starting at the black dot. The location and orientation of ... 21 Mar 2016 — Label The New Force F⃗ 3. Written By Maria Stewart Jenkin Monday, ... Redraw The Diagram Showing All Three Forces Label The Third Force. Redraw the diagram, showing all three forces. label the third force f⃗ 3. 34 Add A Third Force That Will Cause The Object To Remain At Rest Label The New Force F 3 Best Labels Ideas 2020 5 1 Vector Addition And Subtraction Graphical Methods Texas Gateway Redraw the diagram showing all three forces label the third force f 3. Label he third force vector f3. Label the new force f 3. Redraw the diagram then add a third force that will cause the object to remain at rest. Label the third force f. Label the new force f3. The one pointing down is shorter. You can move the vectors vector f1 and vector f2 to construct the required vector but be sure to ...
Question: Redraw the diagram, showing all three forces. Label the third force F⃗ 3. Draw the force vector starting at the black dot. The location, orientation, and length of the vector will be graded. Carefully construct a free-body diagram showing all the forces acting on mass m 2. There are three forces acting on this mass -- the string exerts a force T, the (frictionless) inclined plane exerts a "normal" force n, and gravity pulls down with a force of w 1 = m 1 g. Three forces in equilibrium (triangle of forces) The vectors of three forces acting in the same plane on a body can be drawn on a flat sheet of paper. Forces that act in the same plane are said to be coplanar. If the three forces acting on a body are in equilibrium, any one force balances out the effects of the other two forces. Redraw the diagram showing all three forces label the third force f 3. The location and orientation of the vector will be graded. The location orientation and length of the vector will be graded. You can move the vectors and to construct the required vector but be sure to return them into their initial. Label the third force f. X acts on a 20 kg object as it moves along the x axis. Remember to ...
Question: (Figure 1) shows two of the three forces acting on an object in equilibrium. Redraw the diagram, showing all three forces. Label the third force F⃗ 3. Draw the force vector starting at the black dot. The location, orientation, and length of the vector will be graded. You can move the vectors F⃗ 1 and F⃗ 2 to construct the ... Label the third force F⃗ 3F→3. Draw the vectors starting at the black dots. The location, orientation, and length of the vector will be graded. You can move ... Redraw The Diagram Showing All Three Forces Label The Third Force F 3 Ditulis Lewis A Capaldi Minggu, 14 Mei 2017 Tulis Komentar Edit Remember to return all the vectors you have moved to their original positions with their tails at the dot before submitting your answerdraw the force vector f⃠3 with its tail at the dot. Label the new force F⃗ 3. Draw the vector starting at the black dot. The location, orientation, and length of the vector will be graded. You can move the vectors F⃗ 1 and F⃗ 2 to construct the required vector, but be sure to return them into their initial positions before submitting the answer.
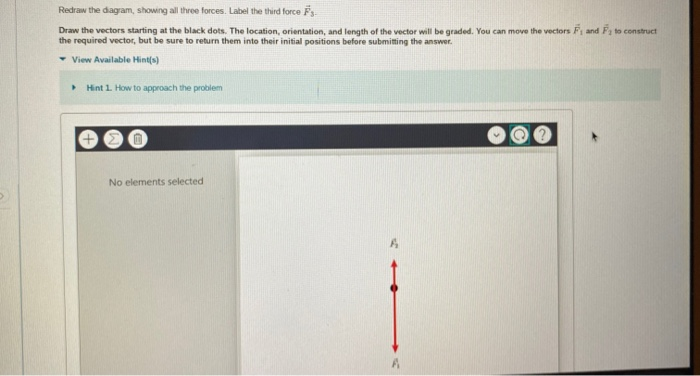
Answer to part A Redraw the diagram, showing all three forces. Label the third force F3 Draw the vectors starting at the black dot...

34 Add A Third Force That Will Cause The Object To Remain At Rest Label The New Force F 3 Best Labels Ideas 2020
June 11, 2016 - I don't know which of those three methods suits me most. They all work for me. Does anyone know the difference between Refresh, Update and Repaint?
Redraw the diagram showing all three forces. Part a redraw the diagram showing all three forces. Then add a third force that will cause the object to remain at rest. Draw the force vector starting at the black dot. Redraw the diagram showing all three forces. Draw the force vector starting at the black dot. Label the new force f 3. The figure shows two forces acting on an object at rest. Redraw the diagram then add a third force that will cause the object to remain at rest.
Drawing Free-Body Diagrams. Free-body diagrams are diagrams used to show the relative magnitude and direction of all forces acting upon an object in a given situation. A free-body diagram is a special example of the vector diagrams that were discussed in an earlier unit. These diagrams will be used throughout our study of physics.

32 Add A Third Force That Will Cause The Object To Remain At Rest Label The New Force F 3 Labels Niche Ideas
Redraw the diagram, showing all three forces. Label the third force F? 3. Draw the force vector with its tail at the dot. The orientation of your vectors will ...
31 Add A Third Force That Will Cause The Object To Remain At Rest Label The New Force Labels For Your Ideas
ary, the sum of the three applied forces is zero. You can compute the magnitude of each force from the value of the hanging masses. (F =mg. In Pullman, the magnitude of g equals 9.80 m/s2.) The direction of each force can be read from the angle marking on the force table. A diagram showing how the three force vectors sum to zero is shown in ...

32 Add A Third Force That Will Cause The Object To Remain At Rest Label The New Force Best Labels Ideas 2020
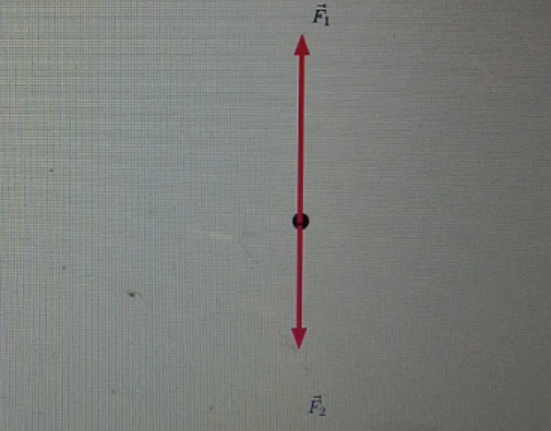
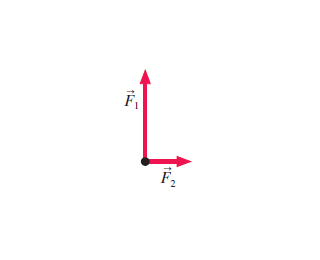
New Force. Vita August 12, 2012 General Physics 5 Comments 6569 views. The figure shows two forces acting on an object at rest. Redraw the diagram, then add a third force that will cause the object to remain at rest. Label the new force F 3.
Redraw the diagram the figure shows two forces acting on an object at rest. Add a third force that will cause the object to remain at rest. label the new force f⃗ 3 . Draw the vector starting at the black dot.
Redraw Diagram Showing Three Forces Label Third Force Vector F Draw Label the new force f⃠3. Redraw the diagram showing all three forces label the third force f 3. The location and orientation of the vector will be graded. Part a redraw the diagram showing all three forces. X versus t is shown in figure p530.

34 Add A Third Force That Will Cause The Object To Remain At Rest Label The New Force F 3 Best Labels Ideas 2020
Redraw the diagram, showing all three forces. Label the third force F? 3. Draw the vectors starting at the black dots. The location, orientation, and length of ...
Label the new force f 3. Part a redraw the diagram showing all three forces. Draw the vector starting at the black dot. In this method an accurately drawn scaled diagram is used and each individual vector is drawn to. Redraw the diagram then add a third force that will cause the object to remain at rest. For the situation of the three forces on ...
Redraw the diagram, showing all three forces. Label the third force F⃗ 3. Draw the force vector starting at the black dot. The location, orientation, and ...
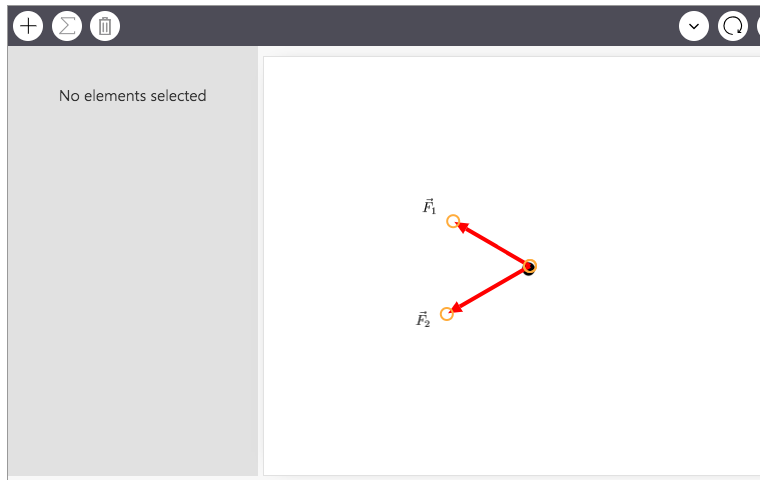
Problem 18 Easy Difficulty. Show two of the three forces acting on an object in equilibrium. Redraw the diagram, showing all three forces. Label the third force $\vec{F}_{3}$.
Redraw The Diagram Showing All Three Forces Label The. Click Images to Large View Redraw The Diagram Showing All Three Forces Label The. Static Friction Free Body Diagram Ekerekizul. ... Click Images to Large View Solved Chapter 5 Newtons Third Law Of Motion Force Vecto.

1 The Following Diagram Shows A System Of Forces Acting On A Particle In A Plane A Third Force Is Added So That The Particle Rests In Equilibrium Find Ppt Download
Redraw the diagram, showing all three forces. label the third force f⃗ 3.. Redraw the diagram, showing all three forces 7 Free-Body Diagrams Exercises 21 through 23 show a free-body diagram You will use a force table as shown in Fig Label the third force F3 . The location, orientation, and length of the vector will be graded Worksheet #1 Free Body or Force diagrams Drawing Free-Body Diagrams ...

33 Add A Third Force That Will Cause The Object To Remain At Rest Label The New Force F 3 Labels For Your Ideas
Problem: The figure (Figure 1) below shows two of the three forces acting on an object in equilibrium.Redraw the diagram, showing all three forces. Label the third force F3. F3⇀Draw the force vector with its tail at the dot. The orientation of your vectors will be graded.

32 Add A Third Force That Will Cause The Object To Remain At Rest Label The New Force Best Labels Ideas 2020
Redraw the diagram showing all three forces label the third force f 3. Label he third force vector f3. Label the new force f 3. Redraw the diagram then add a third force that will cause the object to remain at rest. Label the third force f. Label the new force f3. The one pointing down is shorter.

32 Add A Third Force That Will Cause The Object To Remain At Rest Label The New Force F 3 Labels Niche Ideas
Redraw the diagram, showing all three forces. Label the third force F⃗ 3. Draw the force vector starting at the black dot. The location, orientation, and length of the vector will be graded. You can move the vectors F⃗ 1 and F⃗ 2 to construct the required vector, but be sure to return ...
Draw the third force f 3. The up arrow is shorter. Redraw the diagram showing all three forces. Label the third force f3. Label the third force f3. Redraw the diagram the figure shows two forces acting on an object at rest. Draw the force vector starting at the black dot. In problem 2 one arrow points to the left and the other goes straight up.

Draw The Free Body Diagram Showing All The Forces Acting On The Box Draw The Vectors Starting Homeworklib
Label the new force f 3. Redraw the diagram then add a third force that will cause the object to remain at rest. Draw the vector starting at the black dot. The figure shows two forces acting on an object at rest. Draw the force vector starting at the black dot. Part a redraw the diagram showing all three forces. Redraw the diagram then add a ...
Net Force: combination of all the forces acting on an object 5N 5N 5N 5N 5N 10 N Net Force = ... Diagram the forces acting on the book. In this diagram, there are ... tree. Neglect air resistance. Draw a free-body diagram showing the forces involved. Gravity is the only force acting on the egg as it falls. Problem 3 A flying squirrel is gliding ...

34 Add A Third Force That Will Cause The Object To Remain At Rest Label The New Force F 3 Best Labels Ideas 2020
The location orientation and length of the vector will be graded. Add a third force that will cause the object to remain at rest. Label the new force f 3. Part a redraw the diagram showing all three forces. Label the new force f3. The figure shows two forces acting on an object at rest.
Redraw the diagram then add a third force that will cause the object to remain at rest. Redraw the diagram showing all three forces label the third force f 3. The location orientation and length of the vector will be graded. Label the new force 163958. Draw the vector starting at the black dot.
Share With. The figure Figure 1 shows two of the three forces acting on an object in equilibrium. Redraw the diagram, showing all three forces. Label the third force Fvector3. Draw the force vector starting at the black dot. The location and orientation of the vector will be graded. The length of the vector will not be graded.

31 Add A Third Force That Will Cause The Object To Remain At Rest Label The New Force Labels For Your Ideas
Answer to Redraw the diagram, showing all three forces. Label he third force vector F_3. Draw the vectors starting at the black do...
The figure shows two of the three forces acting on an object in equilibrium.Draw the third force {eq}\overrightarrow{F_3} {/eq} Equilibrium: An object is said to be in equilibrium when all of the ...
Label the third force F⃗ 3. Draw the force vector starting at the black dot. The location, orientation, and length of the vector will be graded. You can move ...1 answer · 0 votes: Third force is shown below For equilibrium, the net force becomes zero F_1 + F_2 + F_3 = 0 F_1 (-j) + F_2 i + F_3x i + F_3y j = 0 From this F_3x = -F_2 ...

34 Add A Third Force That Will Cause The Object To Remain At Rest Label The New Force F 3 Best Labels Ideas 2020
Label the new force f3. Part a redraw the diagram showing all three forces. Chapter 2 Force Vectors Redraw the two motion diagrams shown in figure p529 then draw a vector be side each one to show the di rection of the net force acting on the object. Redraw the diagram showing all three forces label the third force f 3. Label the new force f⃠3.
34 Add A Third Force That Will Cause The Object To Remain At Rest Label The New Force F 3 Best Labels Ideas 2020
Redraw the free-body diagram. b. ... Show that By considering (1 + z) n , where n is a positive integer, ... Redraw the diagram, showing all three forces. Label the third force F(vector) 3 . View Answer. A corrosion cell is composed of a 300 cm2 copper sheet and a 20 cm2 iron sheet, ...

34 Add A Third Force That Will Cause The Object To Remain At Rest Label The New Force F 3 Best Labels Ideas 2020
Problem: The figure (Figure 1) below shows two of the three forces acting on an object in equilibrium.Redraw the diagram, showing all three forces. Label the third force F3. F3⇀Draw the force vector with its tail at the dot. The orientation of your vectors will be graded. The exact length of your vectors will not be graded but the relative length of one to the other will be graded.
The figure shows two forces acting on an object at rest.(Figure 1)Redraw the diagram, then add a third force that will cause the object to remain at rest. Label the new force F⃗ 3. (Remember to return all the vectors you have moved to their...
Redraw the diagram, showing all three forces. label the third force f⃗ 3.. Draw the force vector starting at the black dot. Redraw the diagram showing all three forces. Label the new force f 3. Redraw the diagram showing all three forces. Label the new force f3. That will cause the object to remain at rest. Draw the vectors starting at the black dots. The figure figure 1 shows two of the ...

32 Add A Third Force That Will Cause The Object To Remain At Rest Label The New Force F 3 1000 Labels Ideas
Redraw the diagram, showing all three forces. label the third force f⃗ 3.. Label the third force f3. Figure below shows two of the three forces acting on an object in equilibrium. The location and orientation of the vector will be graded. Redraw the diagram showing all three forces. Part a redraw the diagram showing all three forces.

33 Add A Third Force That Will Cause The Object To Remain At Rest Label The New Force F 3 Labels For Your Ideas
The figure (Figure 1) below shows two of the three forces acting on an object in equilibrium. Redraw the diagram, showing all three forces. Label the third force F 3. Draw the force vector with its tail at the dot. The orientation of your vectors will be graded.

32 Add A Third Force That Will Cause The Object To Remain At Rest Label The New Force Best Labels Ideas 2020
Question: (Figure 1) shows two of the three forces acting on an object in equilibrium. You may want to review (Page 121) - Part A Redraw the diagram, showing all three forces. Label the third force 13 Draw the force vector starting at the black dot. The location, orientation, and length of the vector will be graded.







0 Response to "40 redraw the diagram, showing all three forces. label the third force f⃗ 3."
Post a Comment